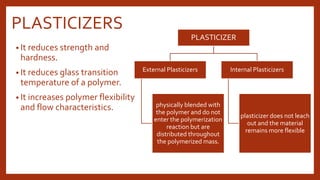
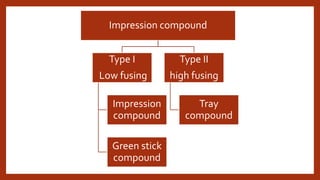
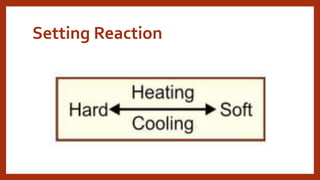
The document provides an overview of various impression materials used in dentistry, categorized primarily into rigid and elastic types, detailing their properties, setting mechanisms, and clinical applications. It covers materials like impression compounds, zinc oxide eugenol pastes, and their compositional aspects, including plasticizers and fillers. Additionally, it discusses advantages and disadvantages along with techniques for manipulation and use in obtaining dental impressions.