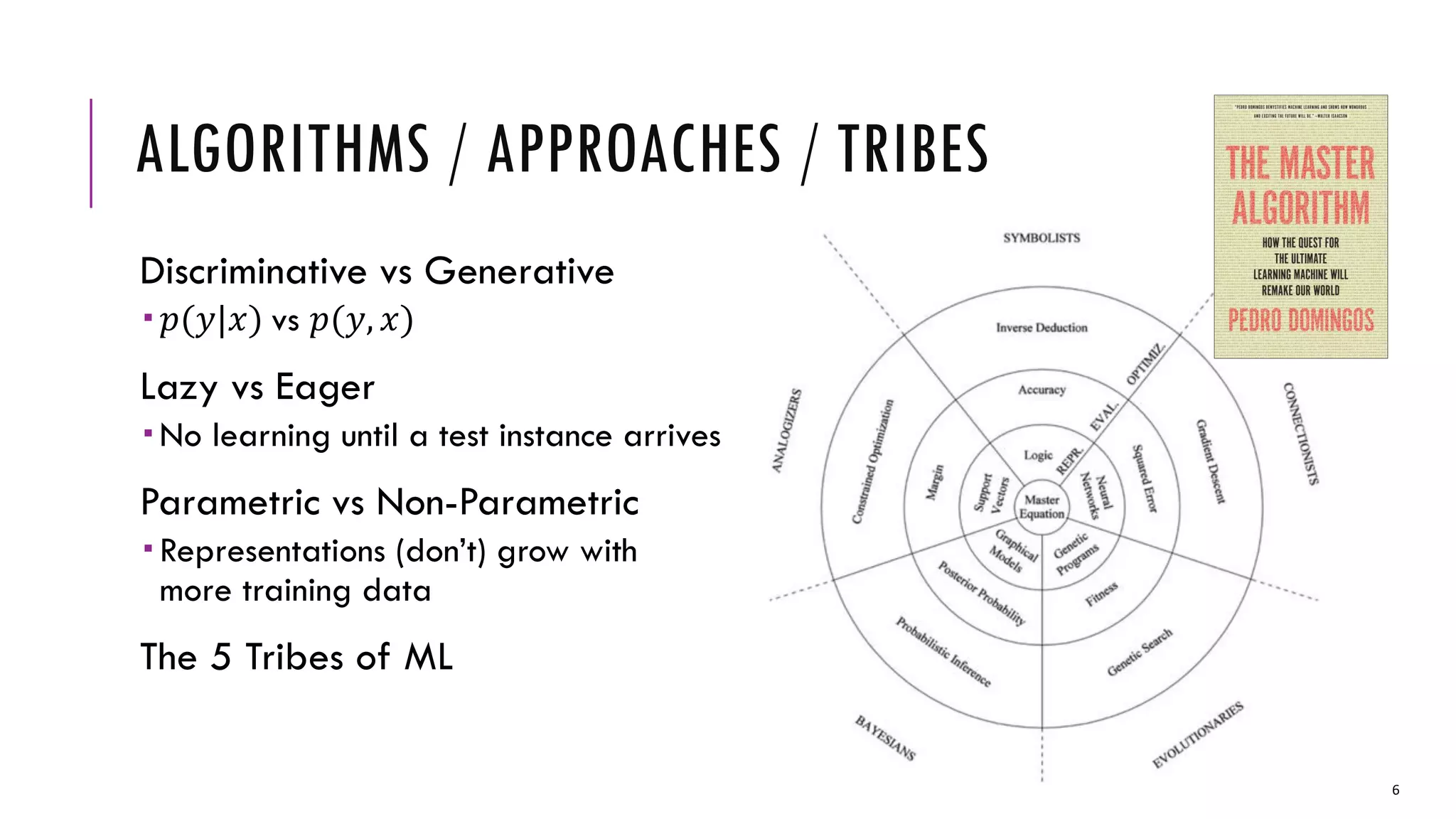
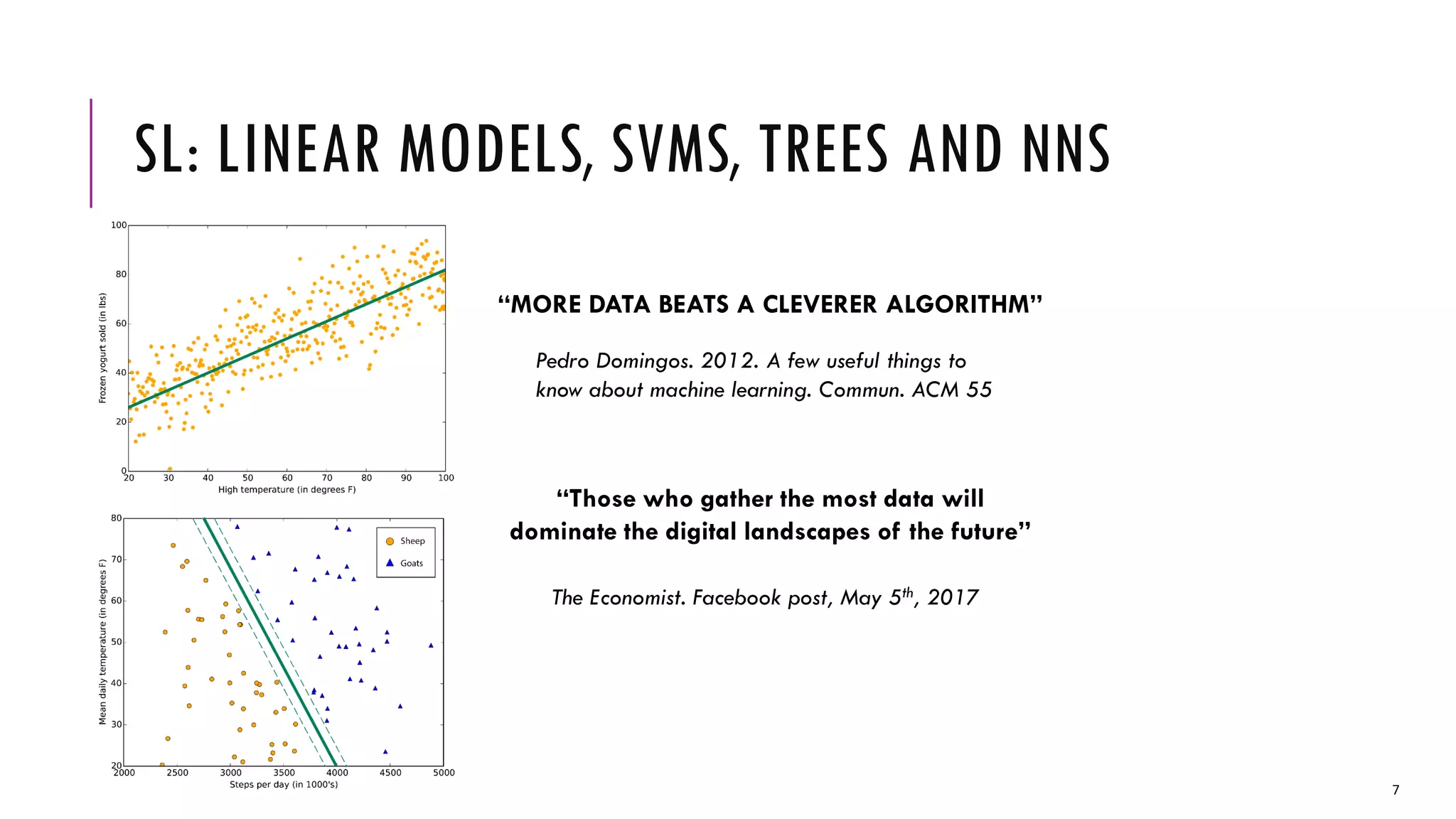
The document provides an overview of machine learning, including its definitions, types (supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning), and key tasks such as anomaly detection and recommender systems. It discusses the significance of data, algorithm diversity, and feature engineering in the field, alongside industrial applications in areas like natural gas load forecasting and academic publication analysis. The increasing computational power and data volume are noted as influencing factors driving advancements in machine learning applications.