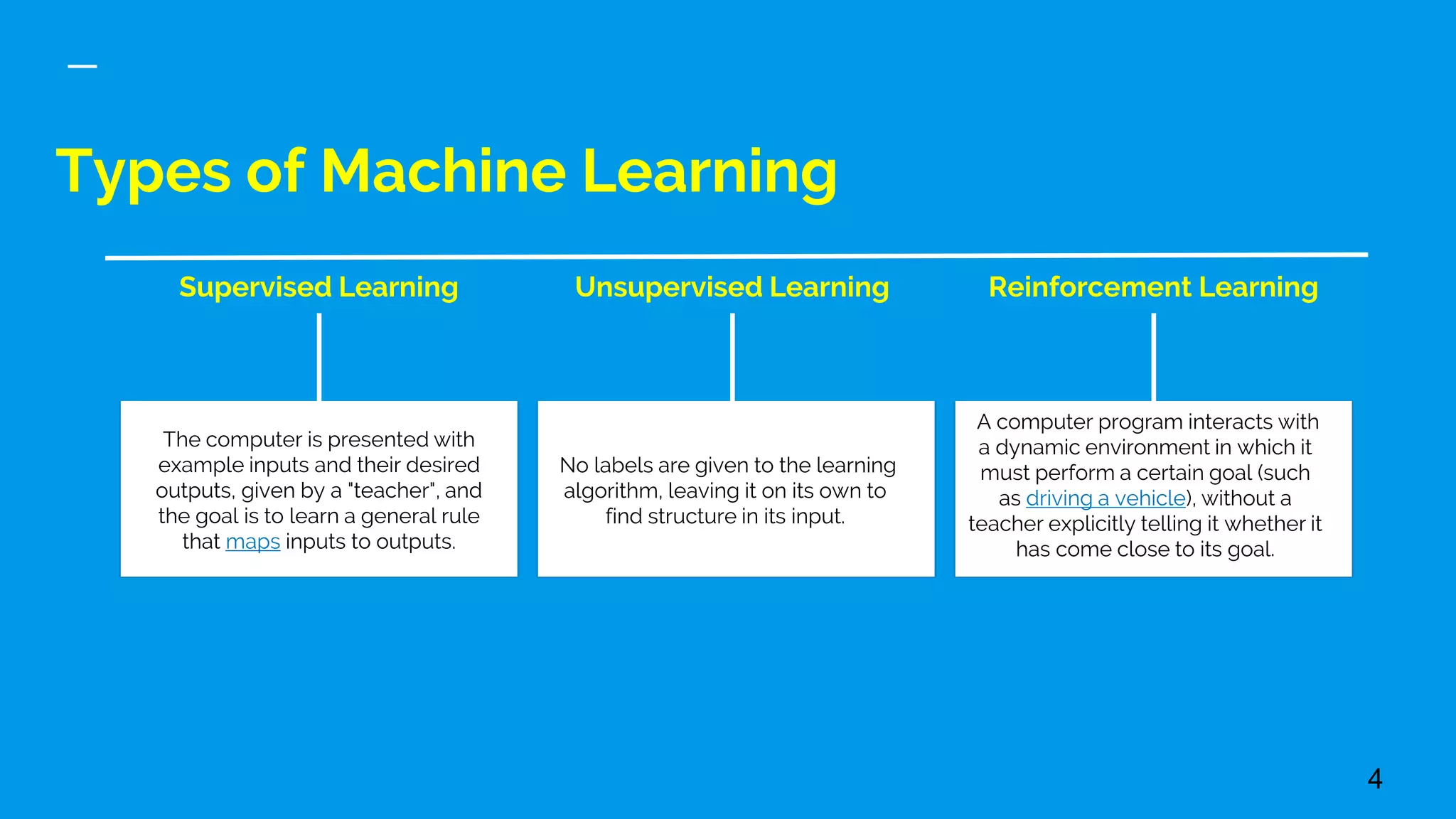
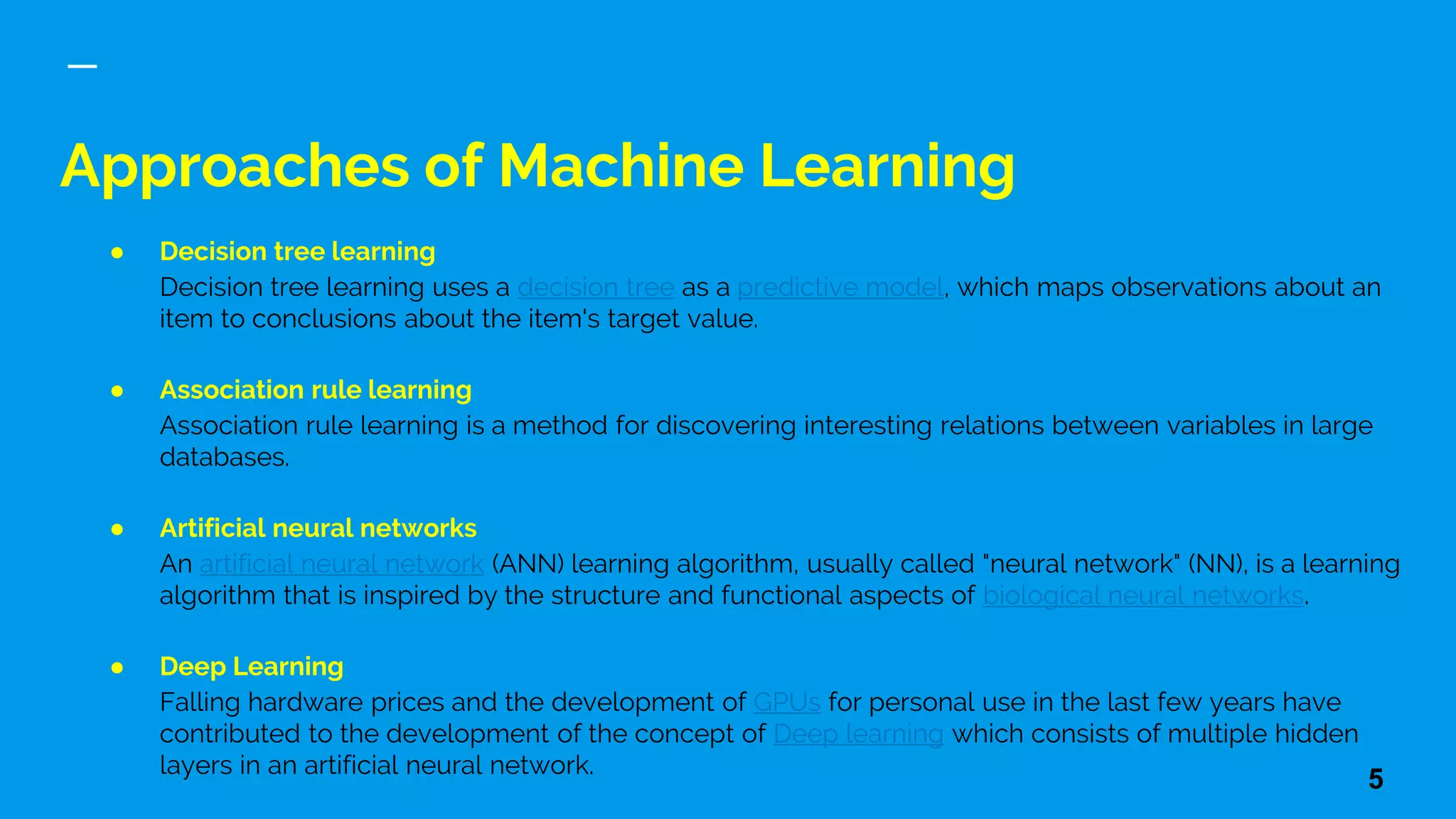
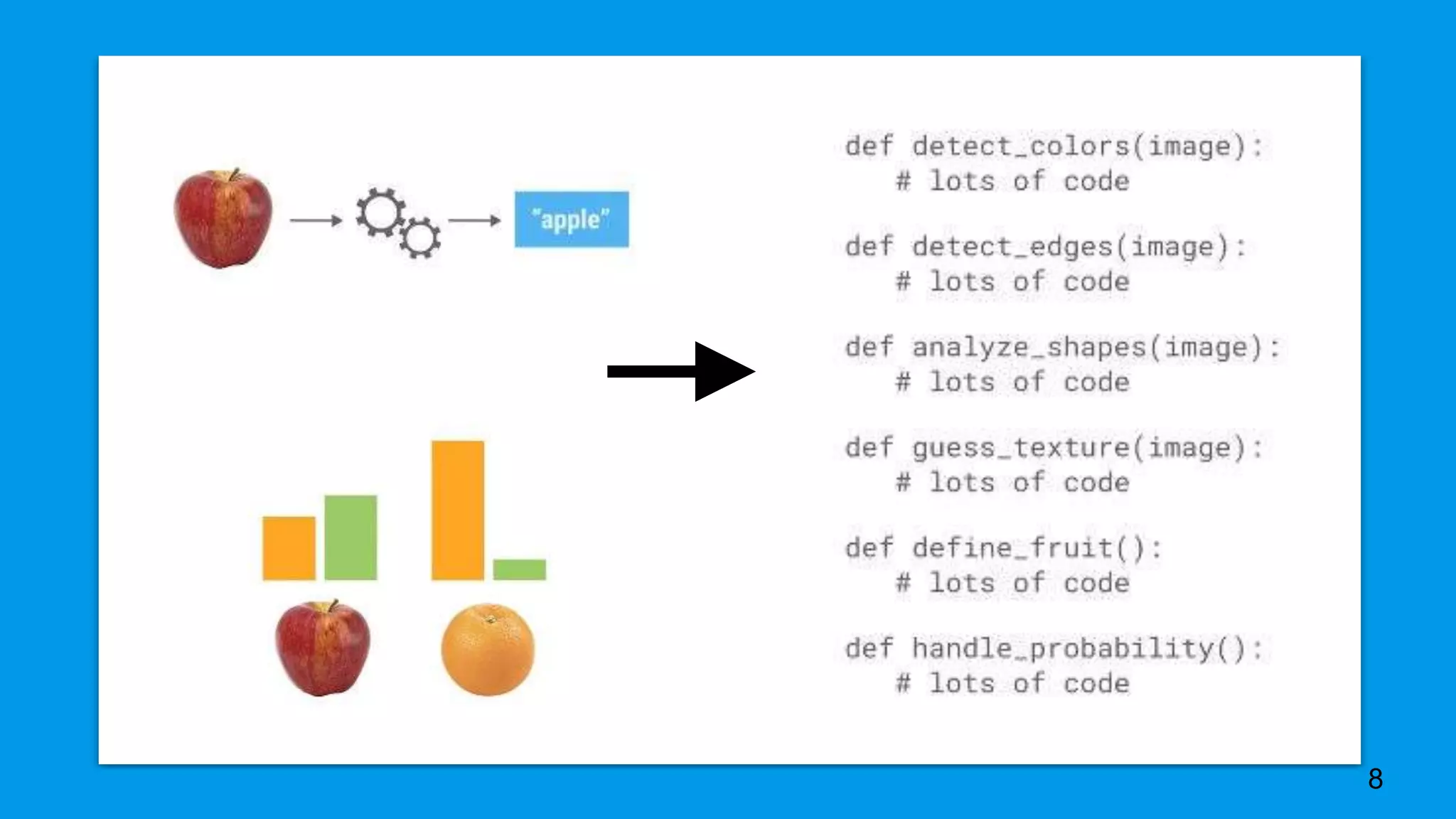
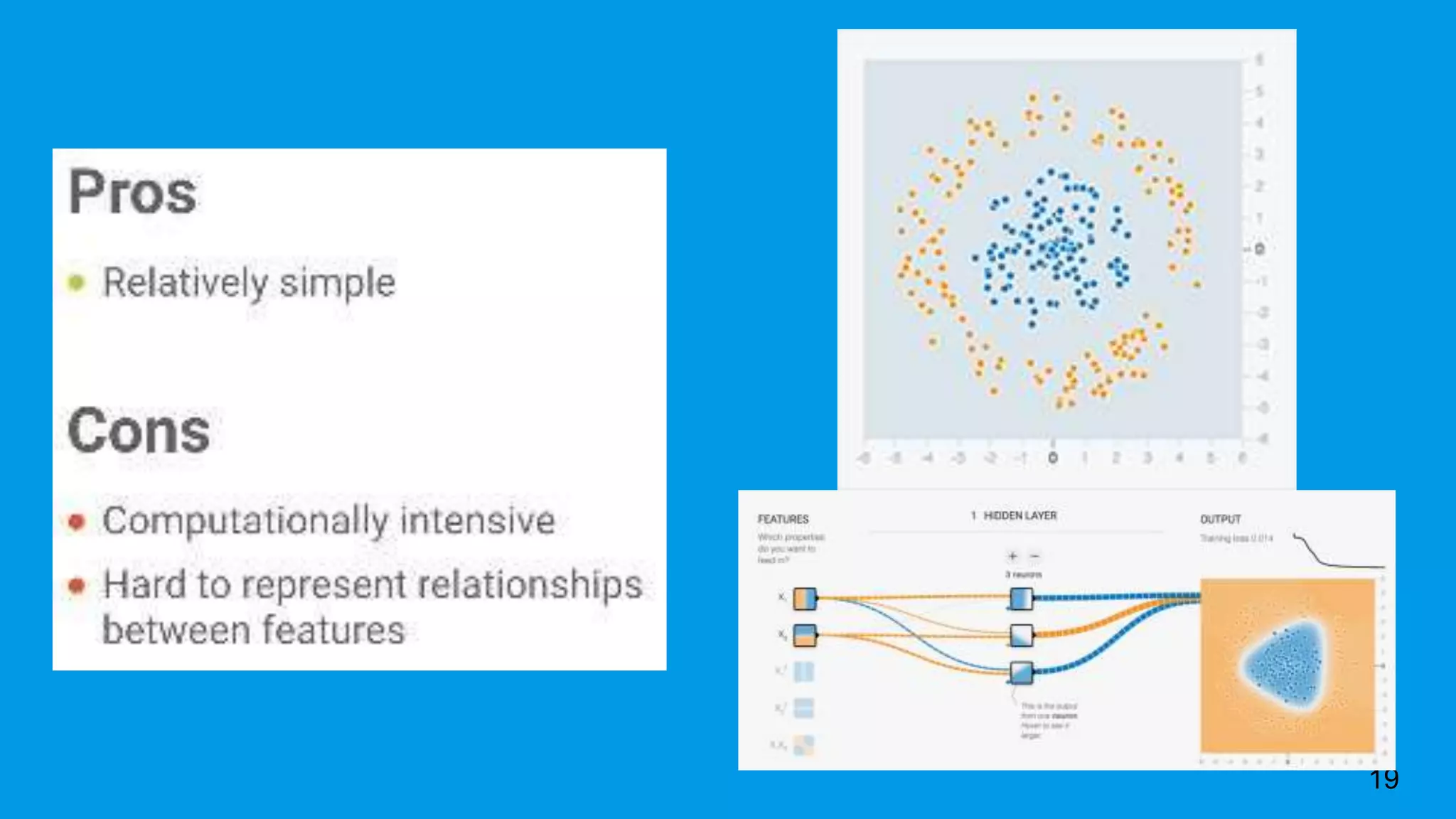
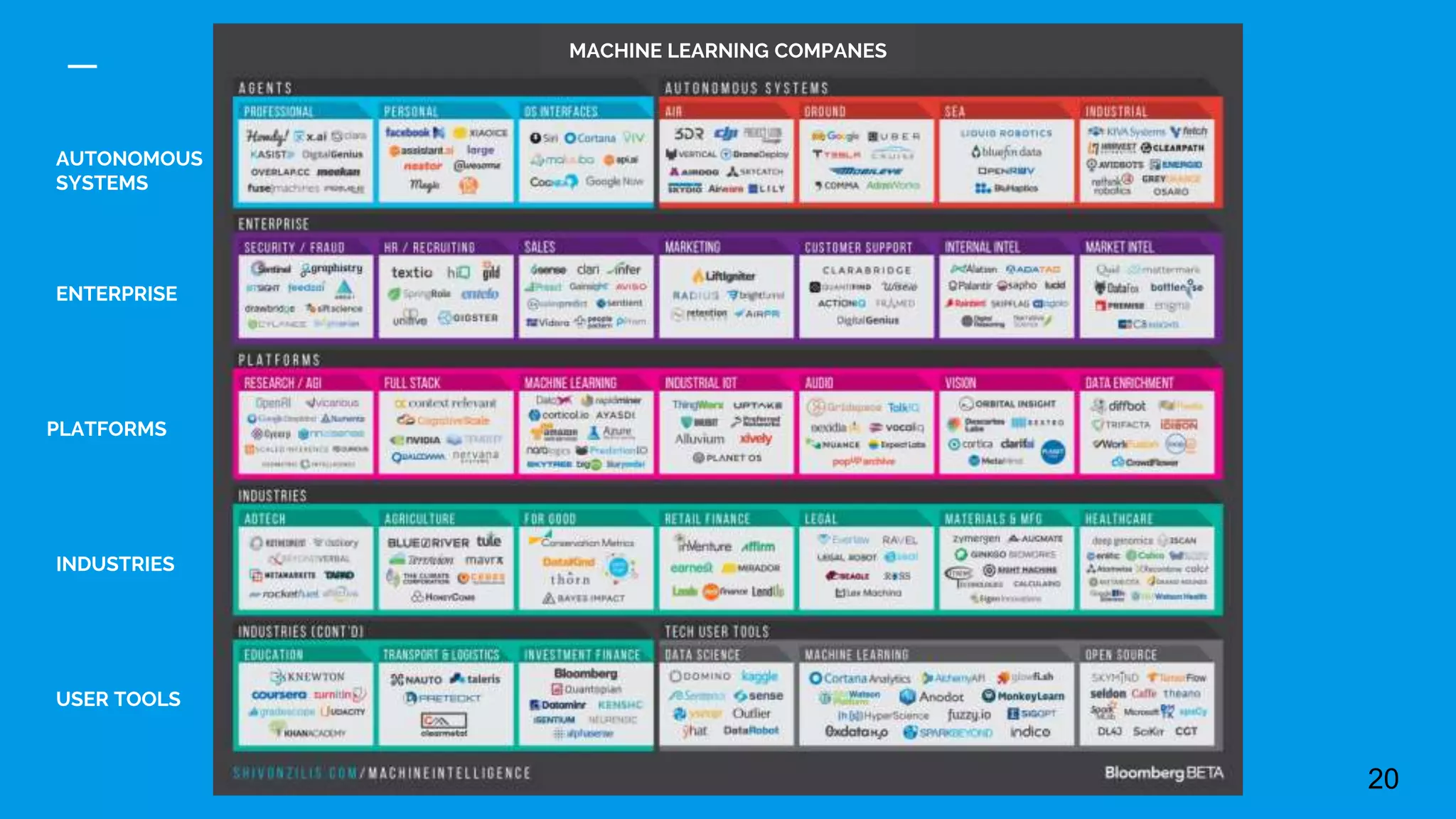
This document provides an overview of machine learning, discussing its definition, importance, and various types including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. It also covers different machine learning approaches like decision trees, genetic algorithms, and neural networks, and highlights challenges in training deep learning models. The document concludes by addressing the computational requirements and data needs for effective machine learning implementations.








![References
23
1. Kaz Sato (Google Inc.), "Understanding neural networks with
TensorFlow Playground", in Google Cloud Platform, 2016. [Online].
Available: https://goo.gl/HRZaX5. Accessed: Aug. 31, 2016.
2. A.Geitgey, "Machine learning is fun!," in Medium, Medium, 2014.
[Online]. Available: http://goo.gl/z8cF7N. Accessed: Aug. 31, 2016.
3. "Machine learning," in Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 2016.
[Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Machine_learning.
Accessed: Aug. 31, 2016.
4. Udacity, "Intro to machine learning," in YouTube, YouTube, 2015.
[Online]. Available: http://goo.gl/8TvyJx. Accessed: Aug. 31, 2016.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machinelearningseminar1-170520031755/75/Machine-learning-23-2048.jpg)
