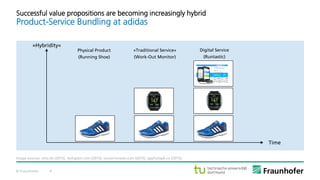
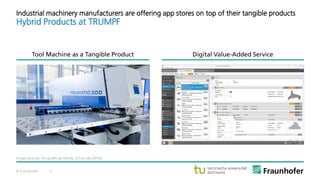
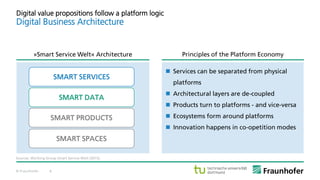
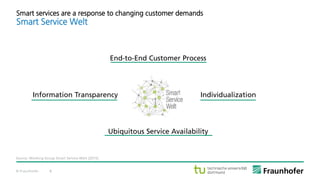
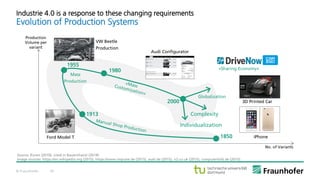
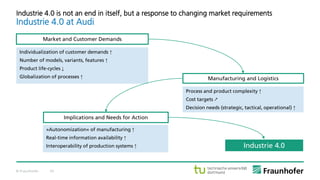
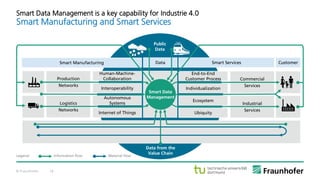
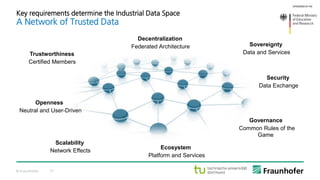
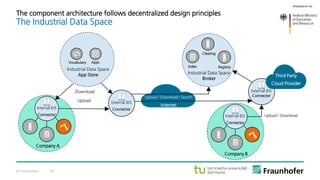
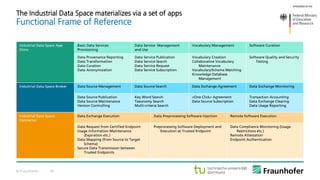
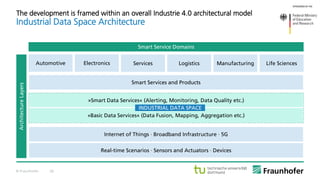
The document discusses the concept of the Industrial Data Space, highlighting its role in enabling smart manufacturing and Industrie 4.0 through digital services and hybrid business models. It illustrates how companies like Adidas and agricultural machinery manufacturers are integrating digital value propositions into their operations, emphasizing the importance of smart data management and collaborative data ecosystems. Key architectural elements and use cases are presented, showcasing the need for trusted data exchange and interoperability among various stakeholders in the industry.