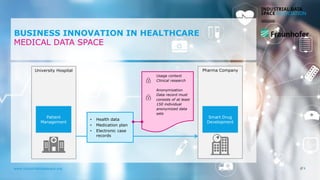
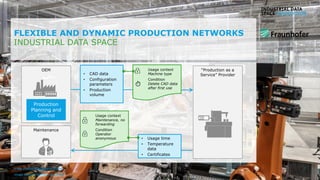
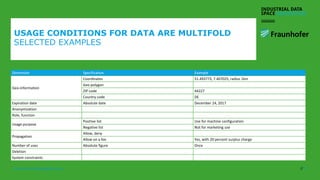
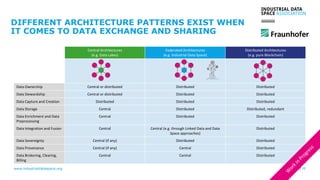
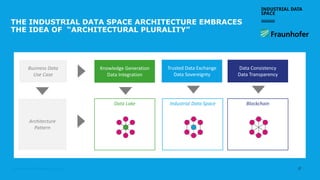
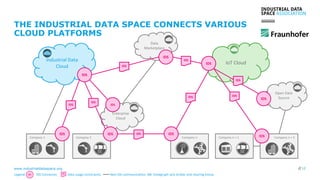
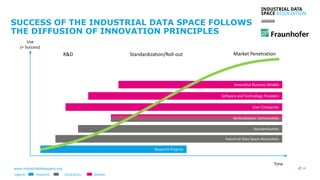
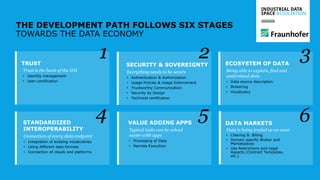
The document discusses the Industrial Data Space and its significance in facilitating data sharing across various sectors such as mobility, healthcare, and manufacturing to foster business model innovation. It addresses concerns around data security, ownership, and interoperability while outlining architectural patterns for data exchange. Emphasizing the importance of trust among ecosystem partners, the document advocates for a structured approach to enable a thriving data economy.