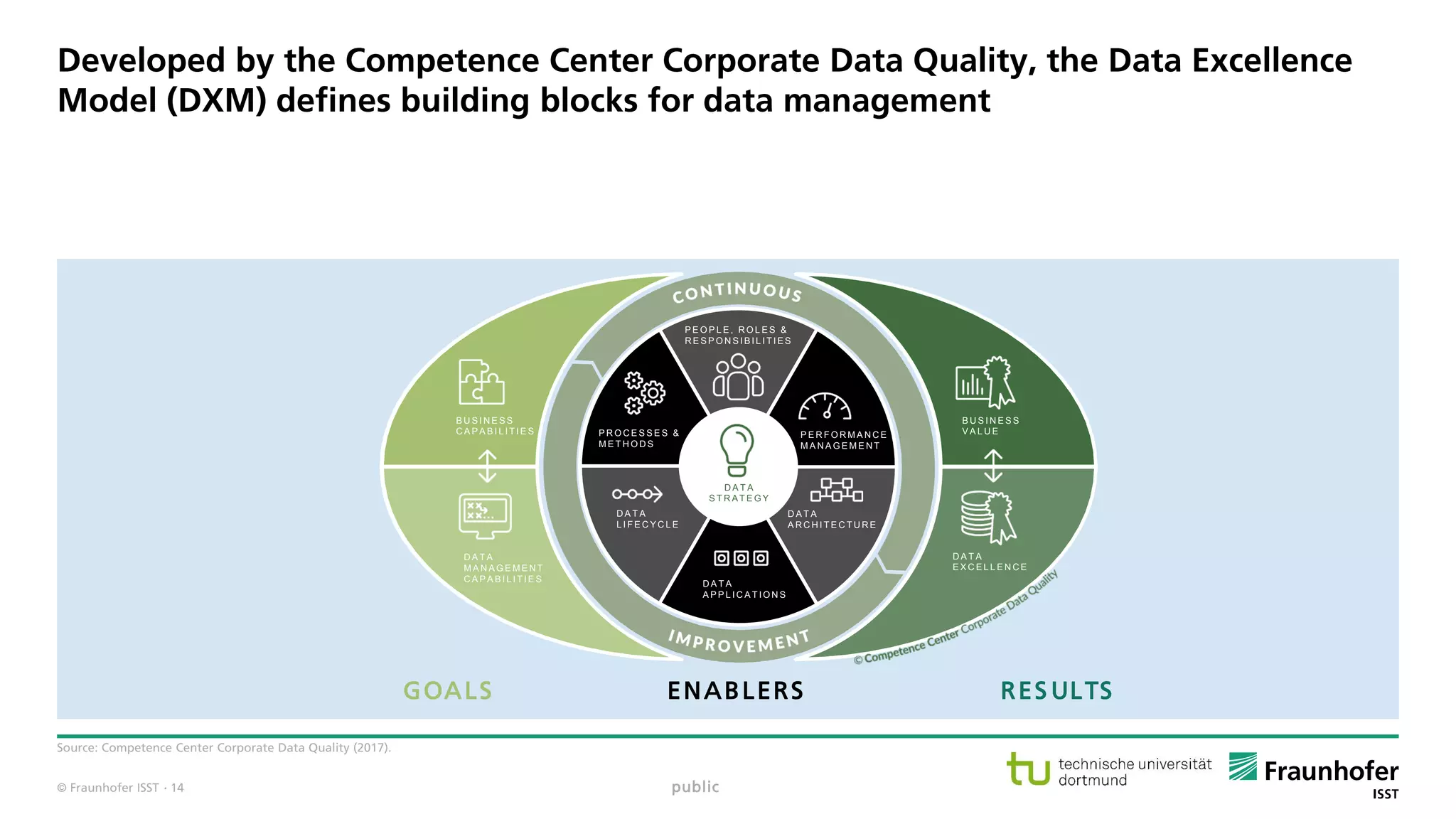
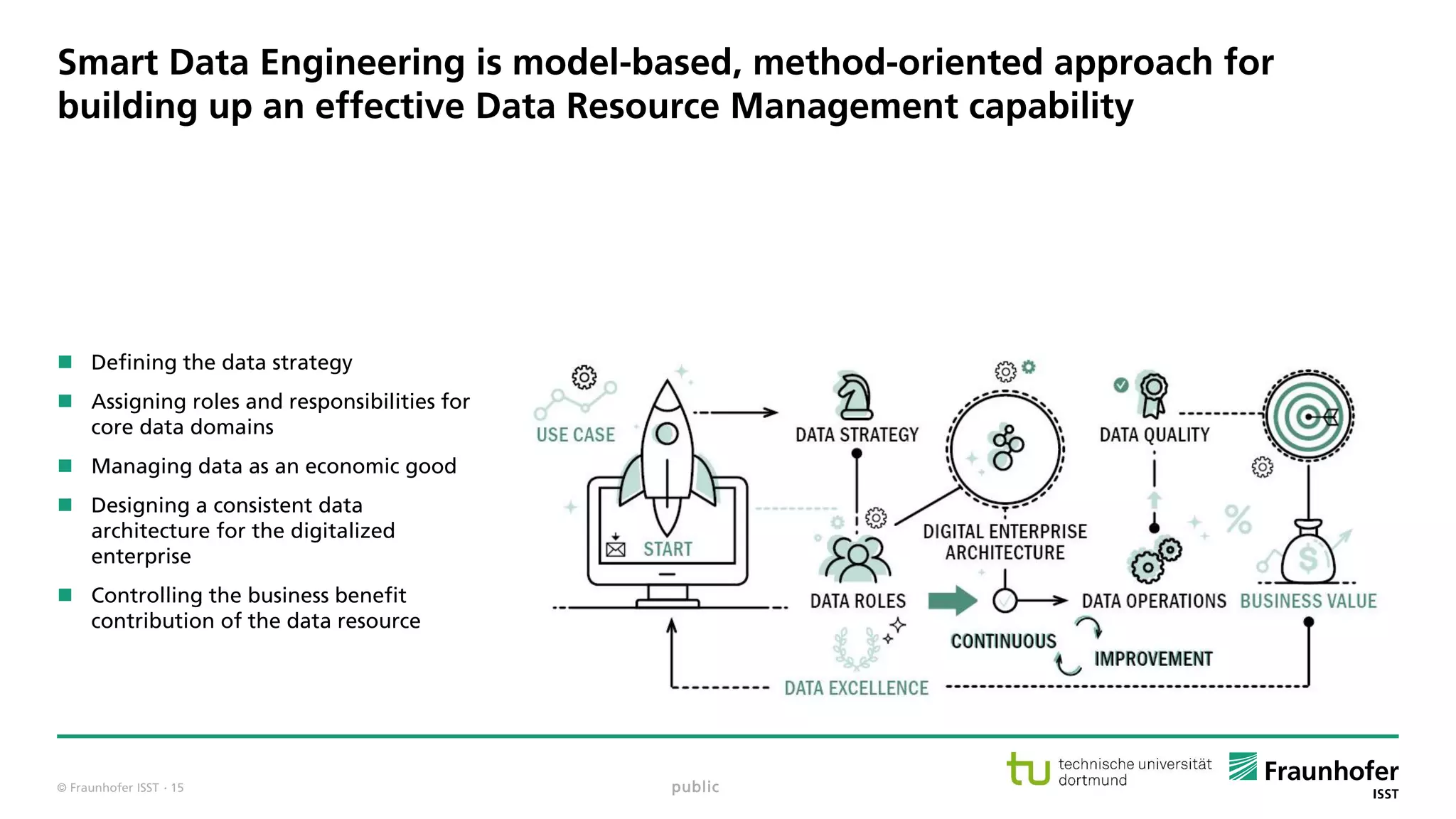
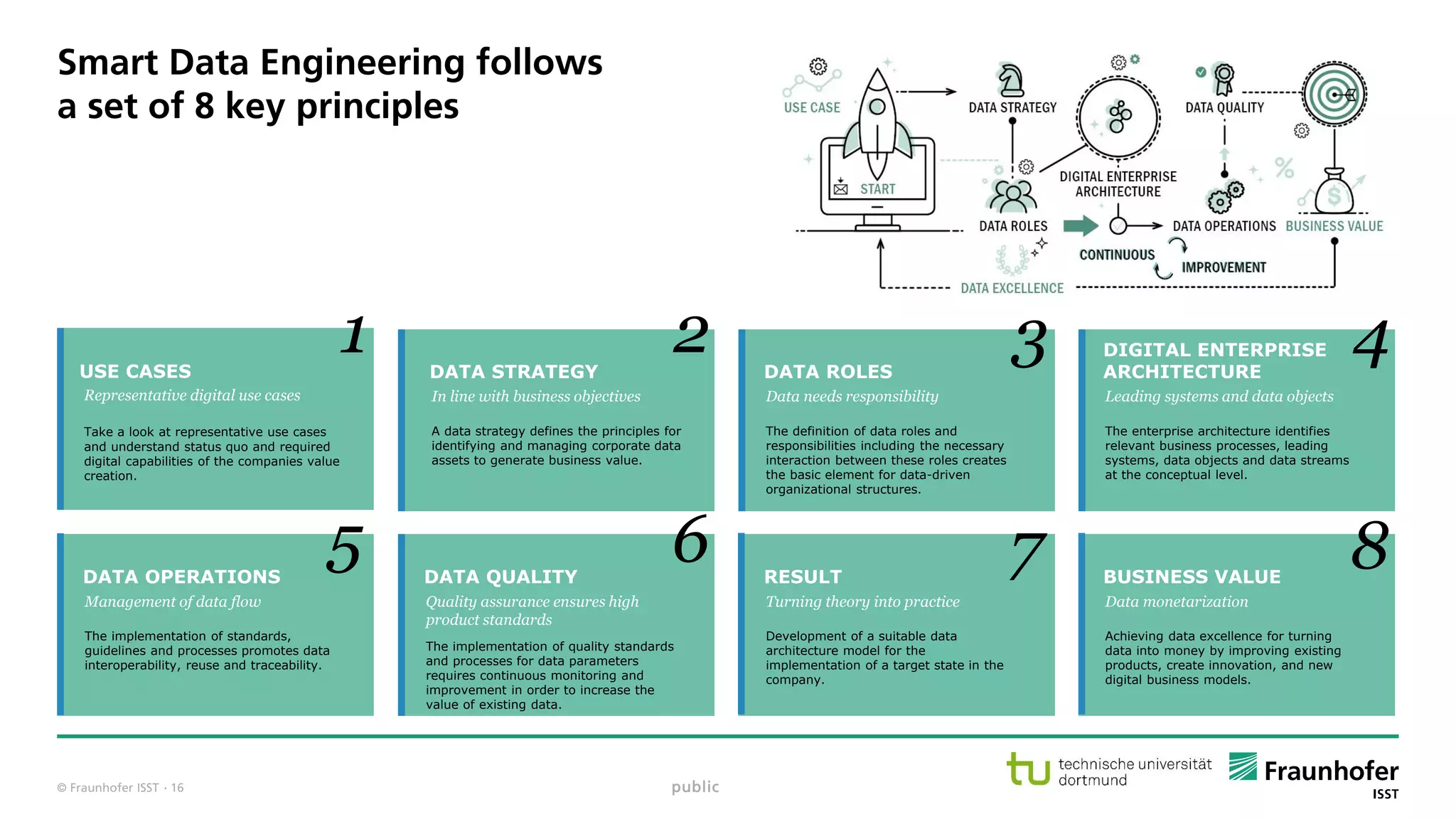
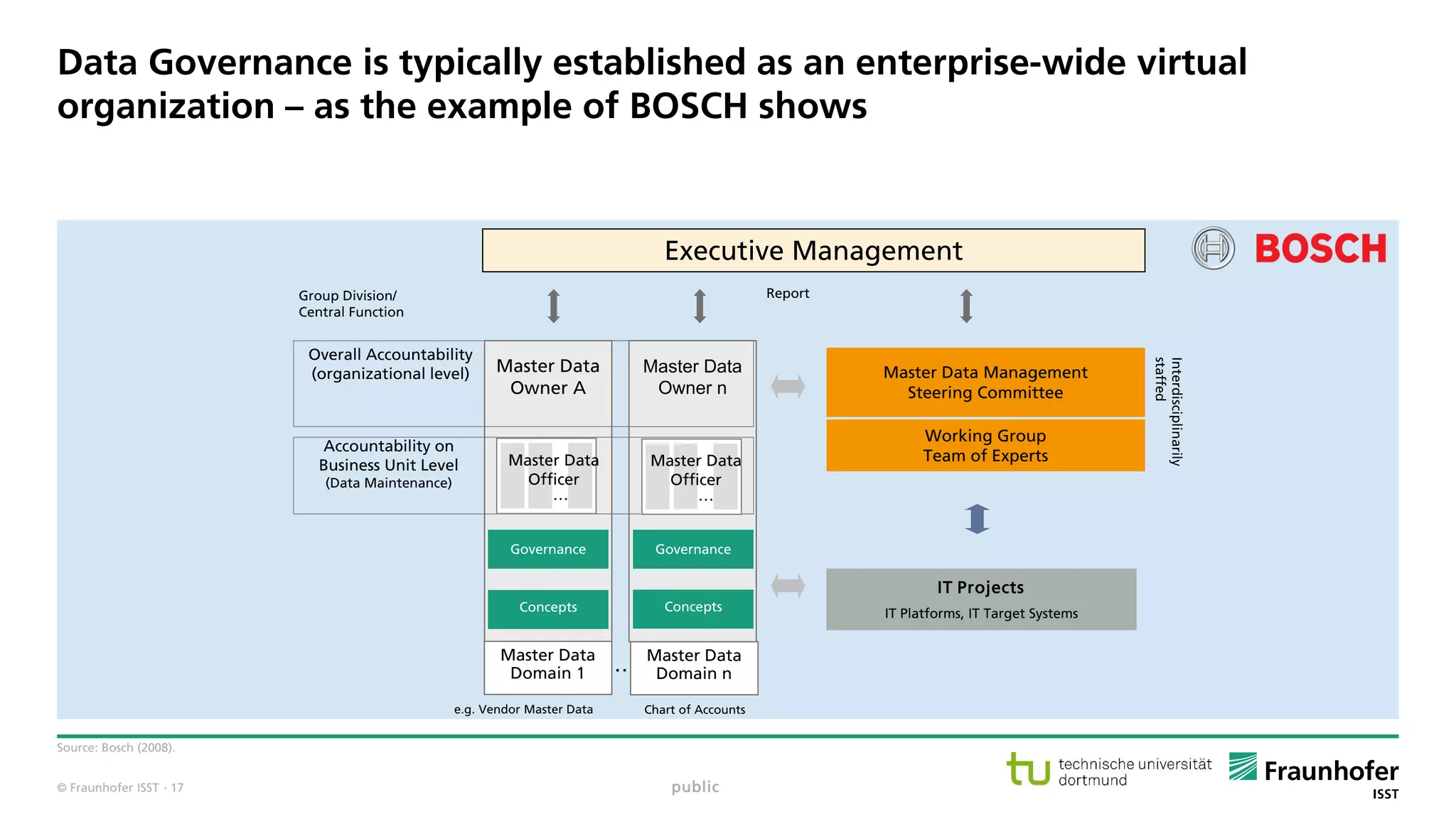
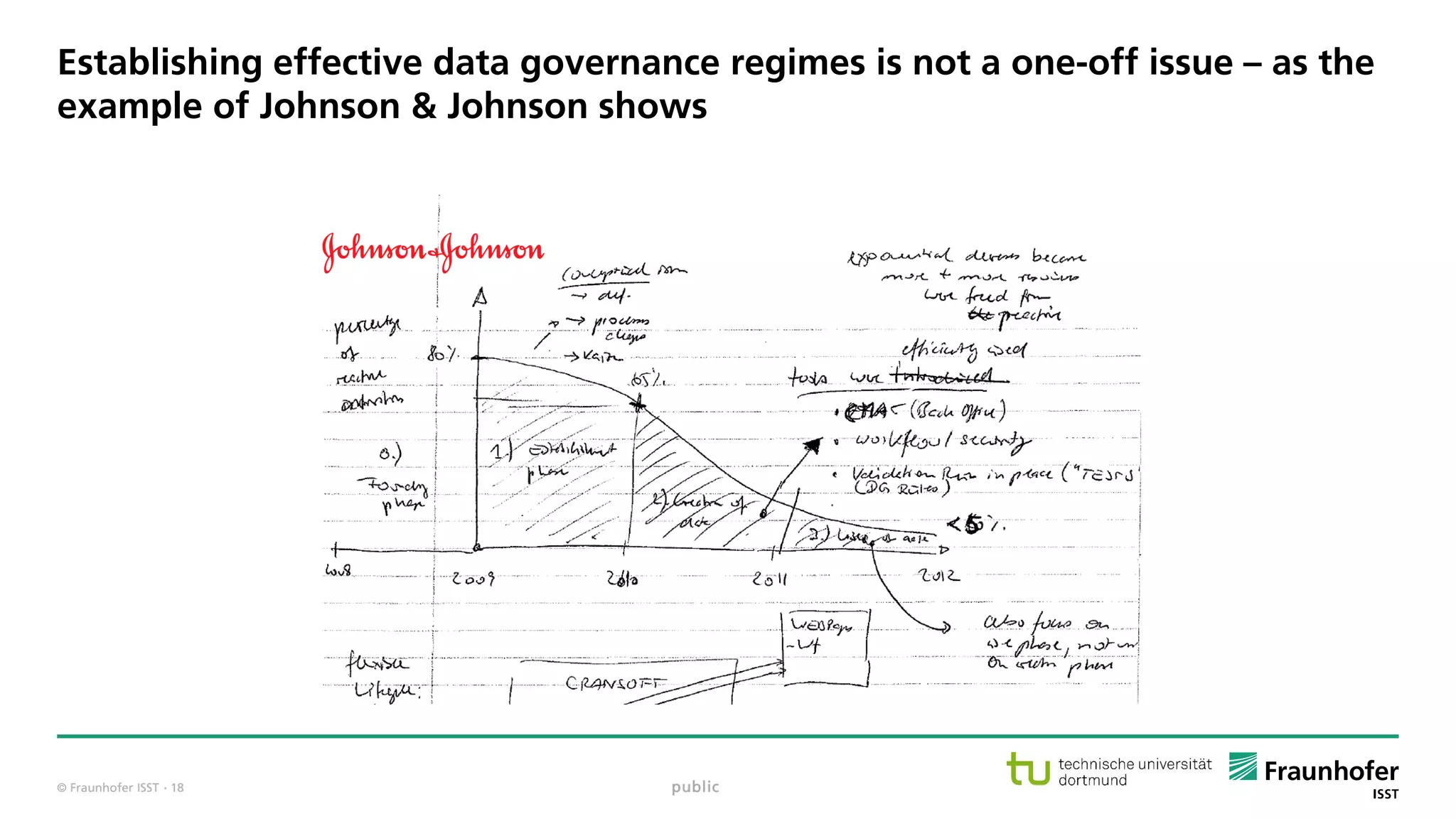
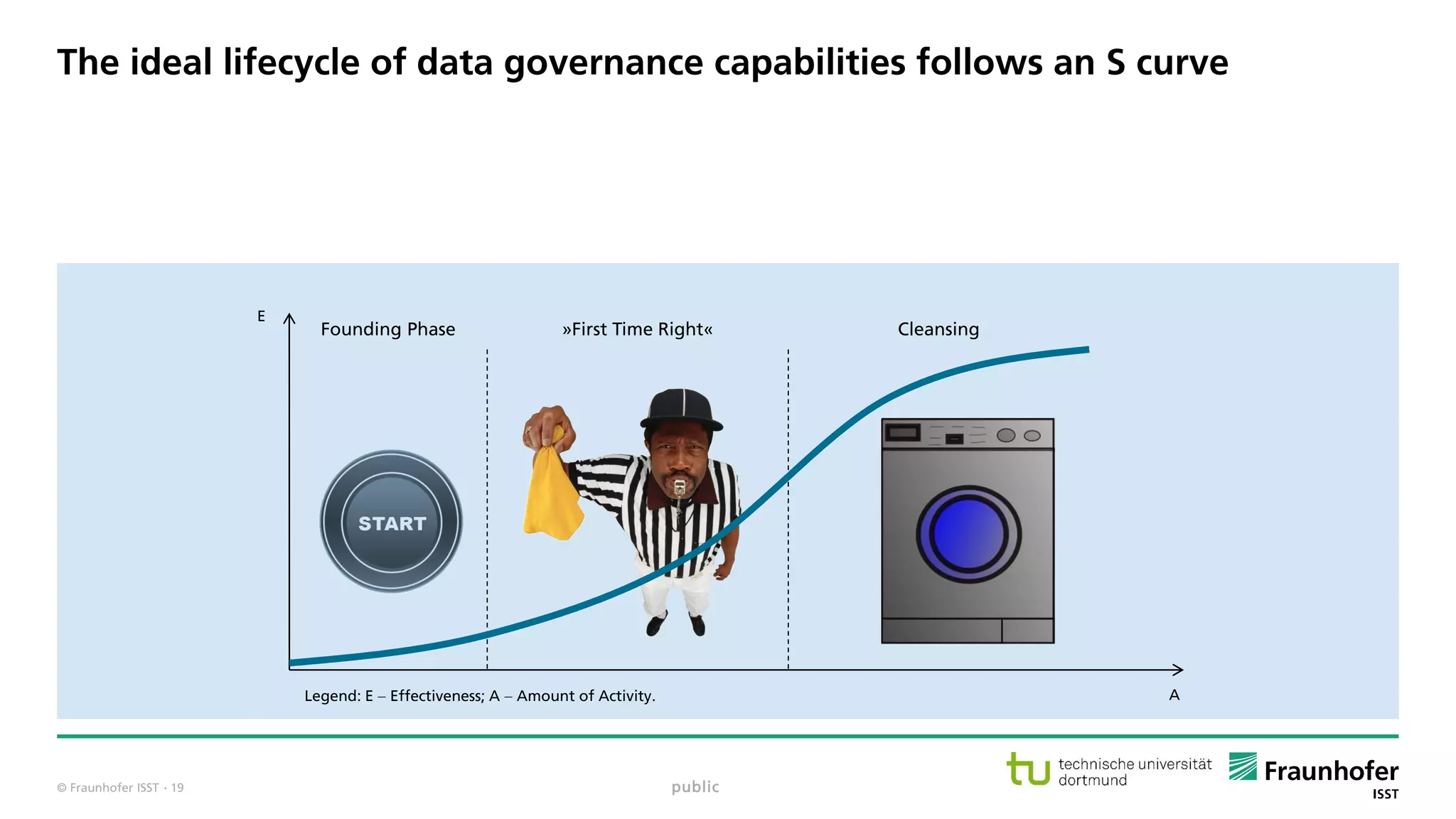
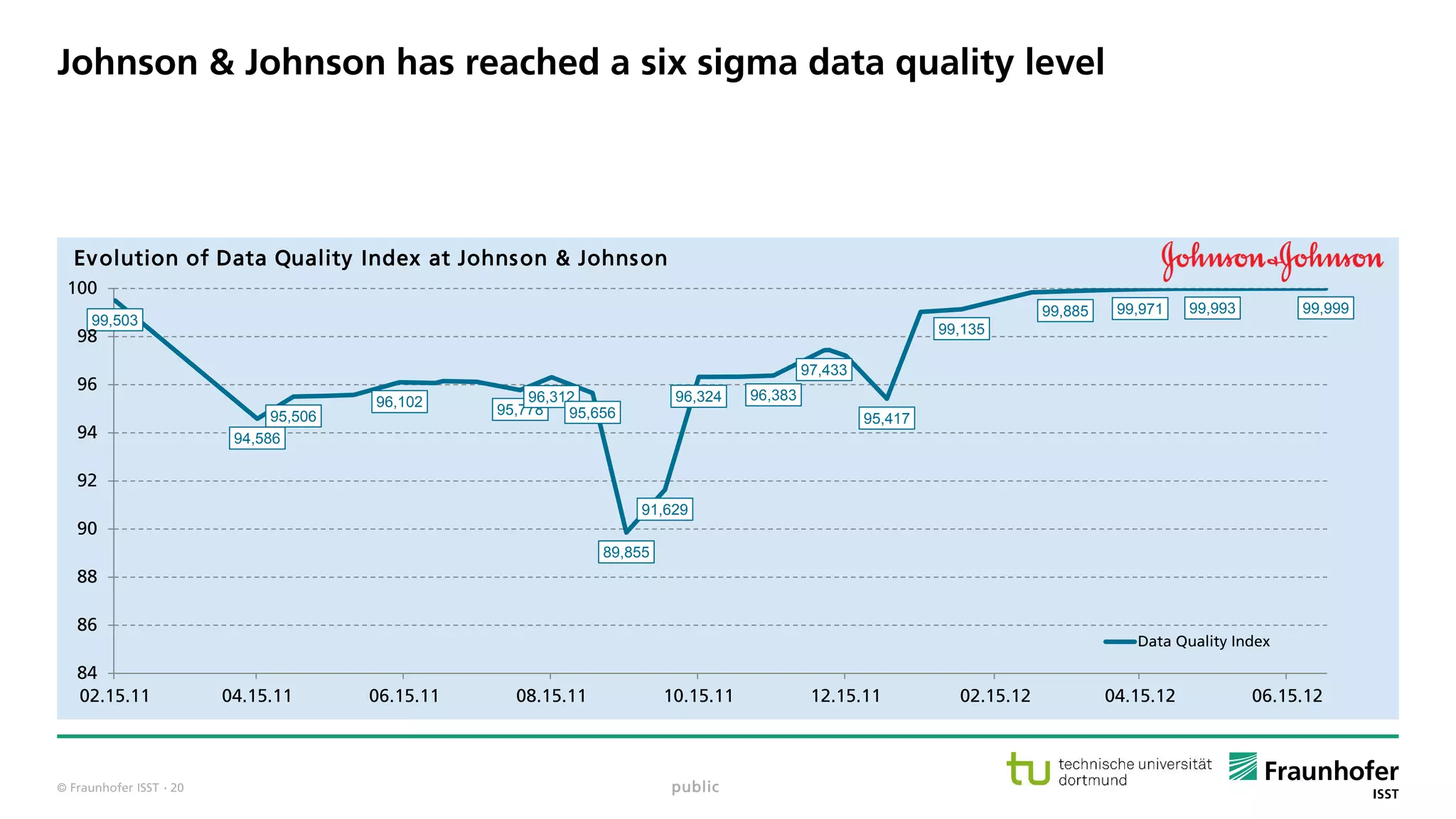
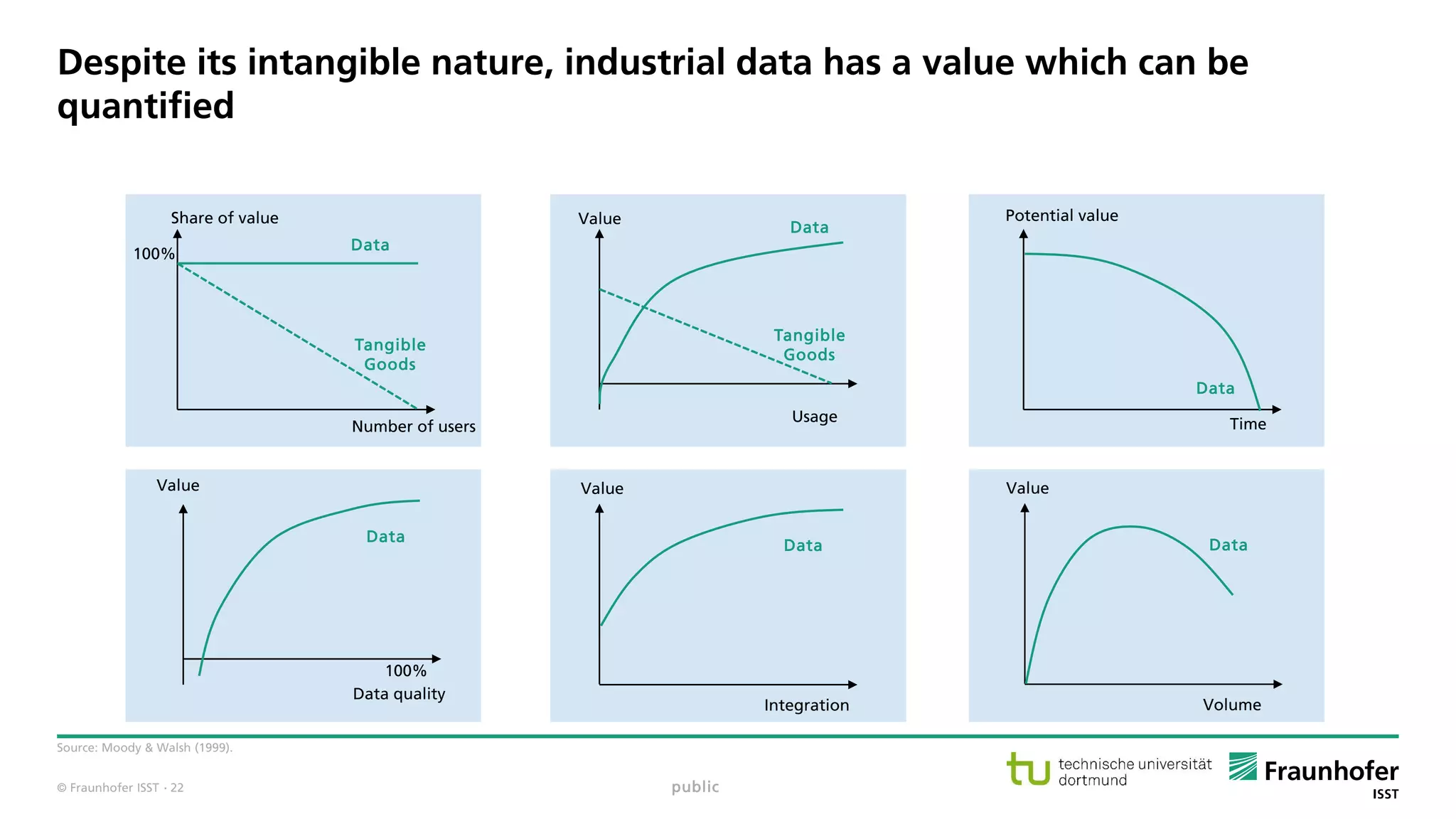
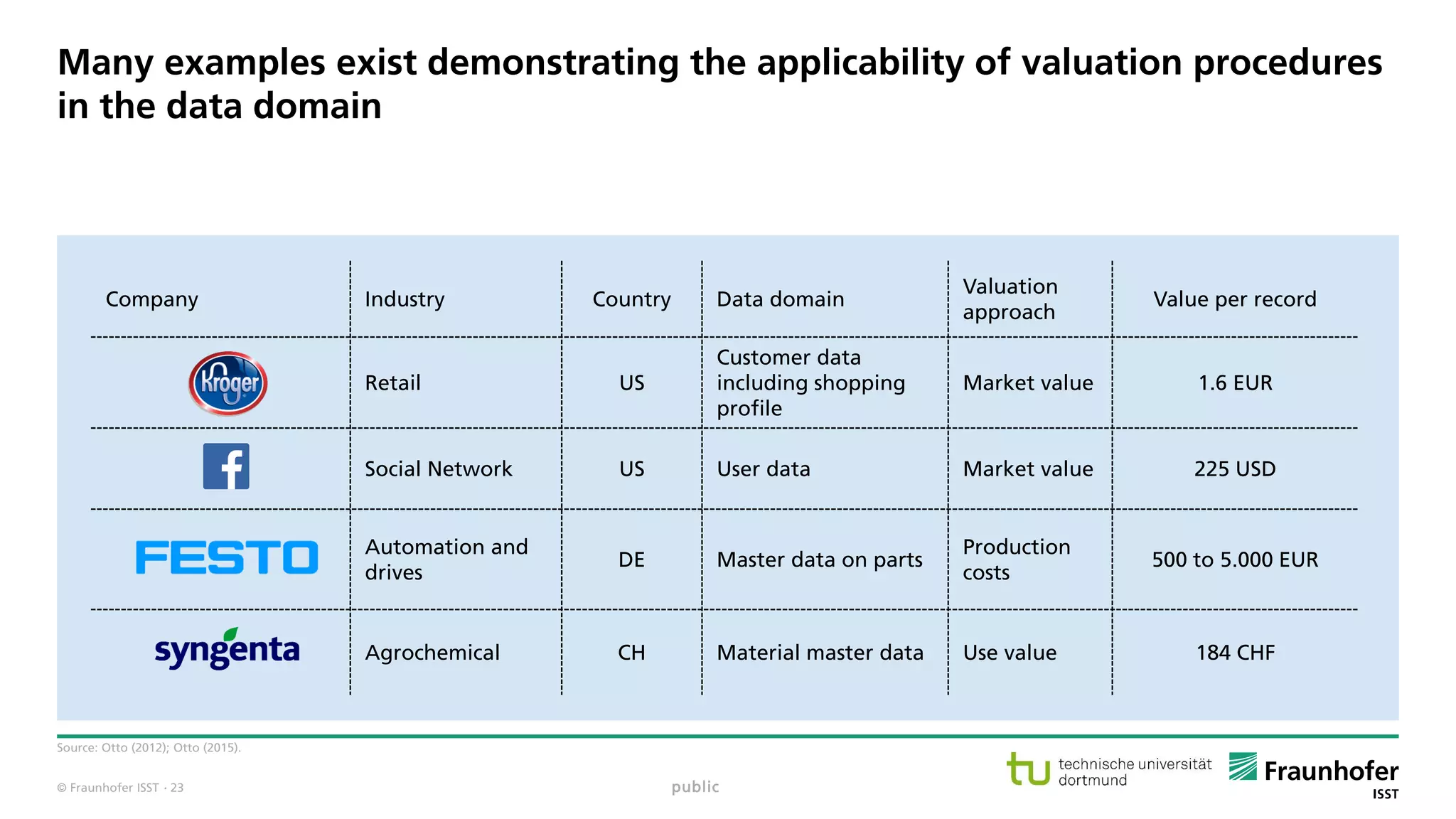
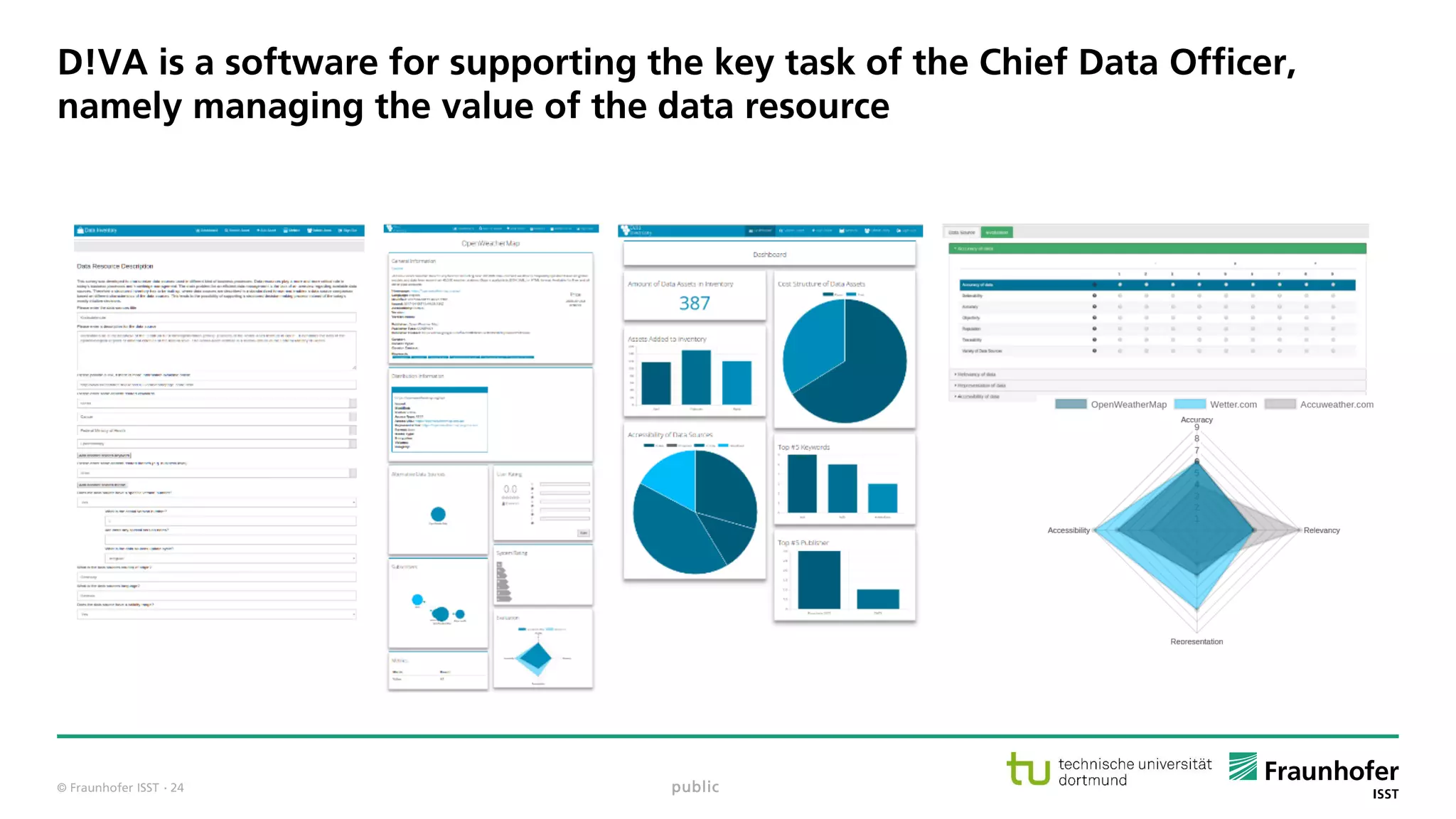
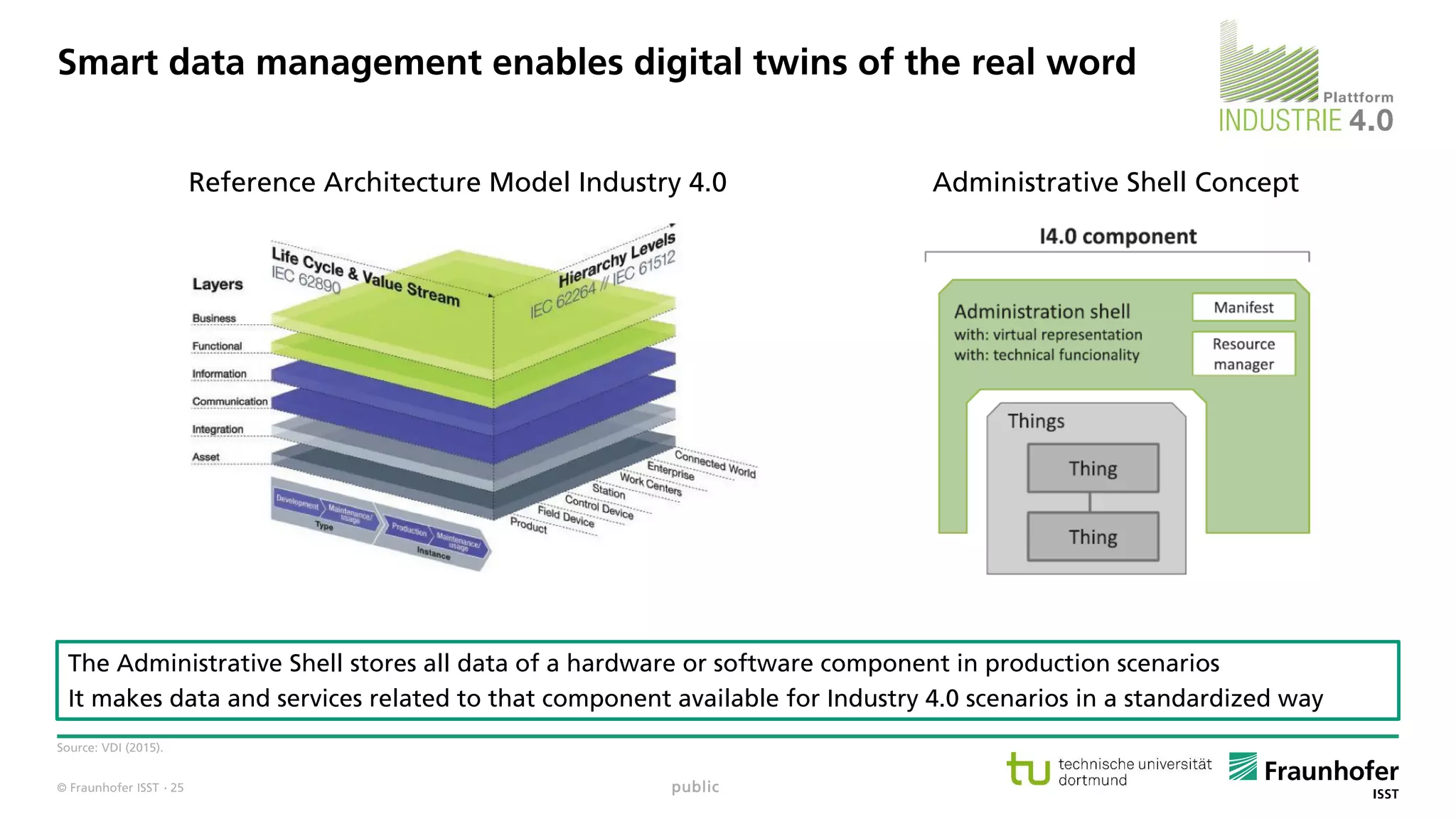
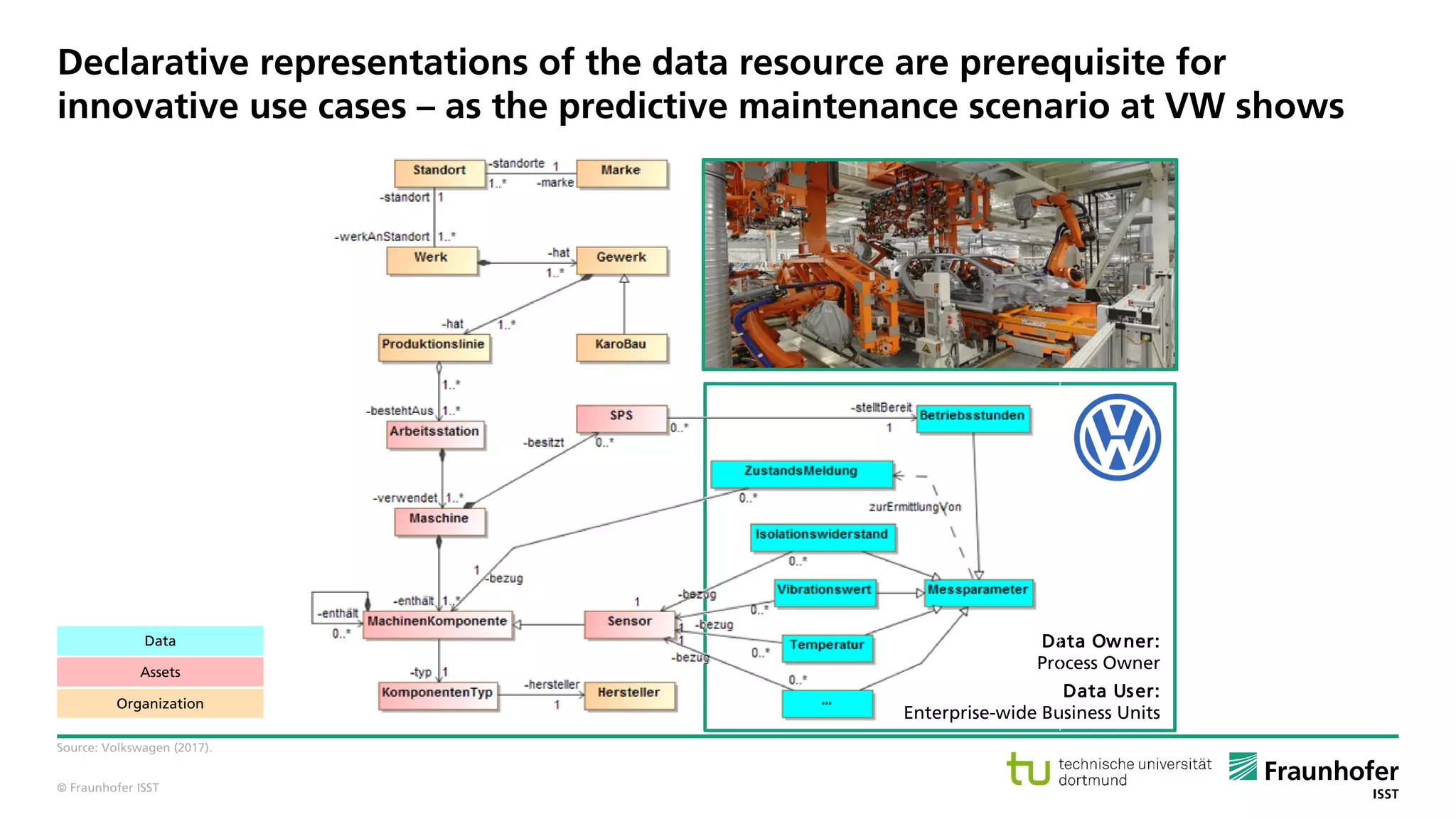
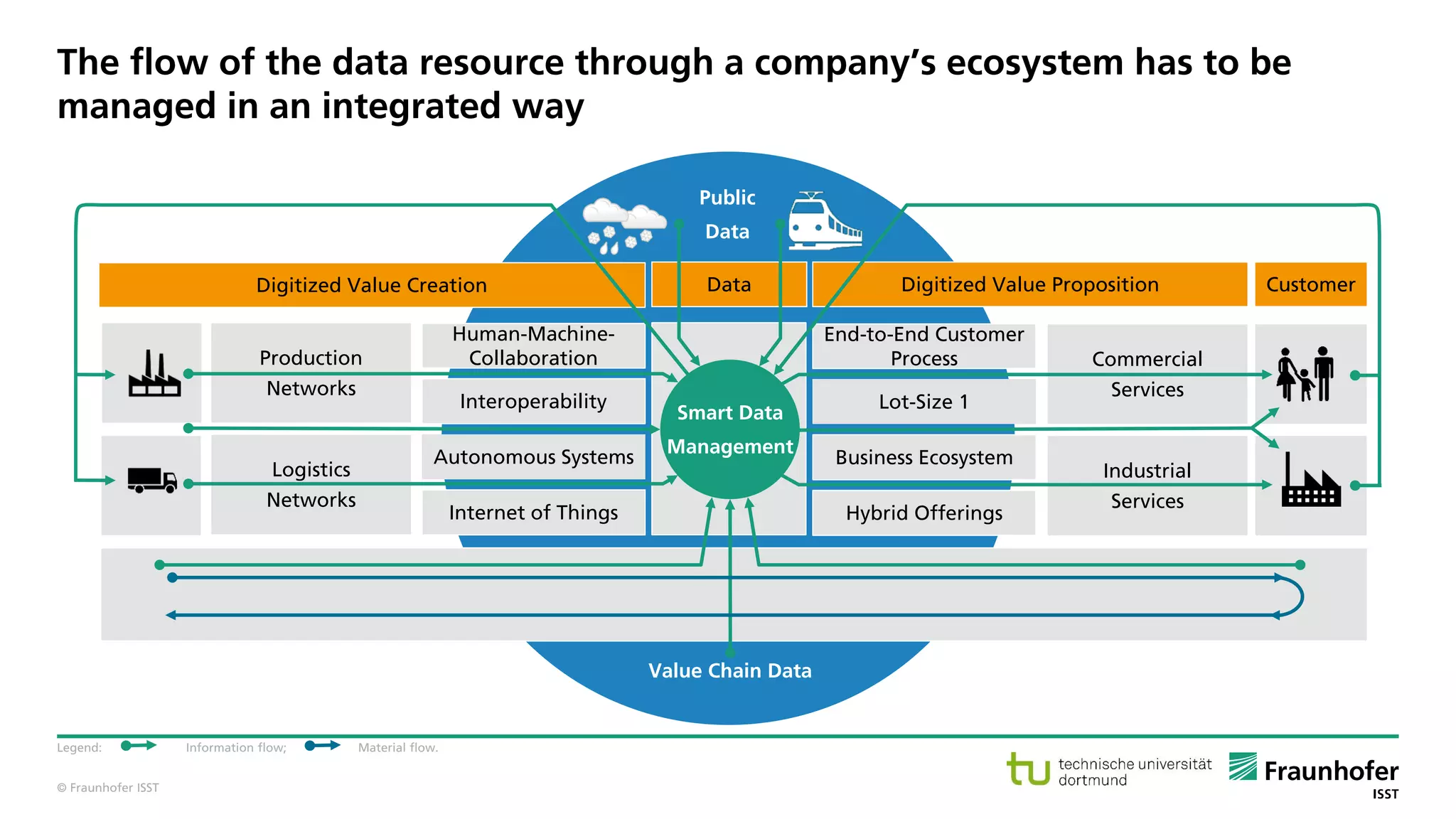
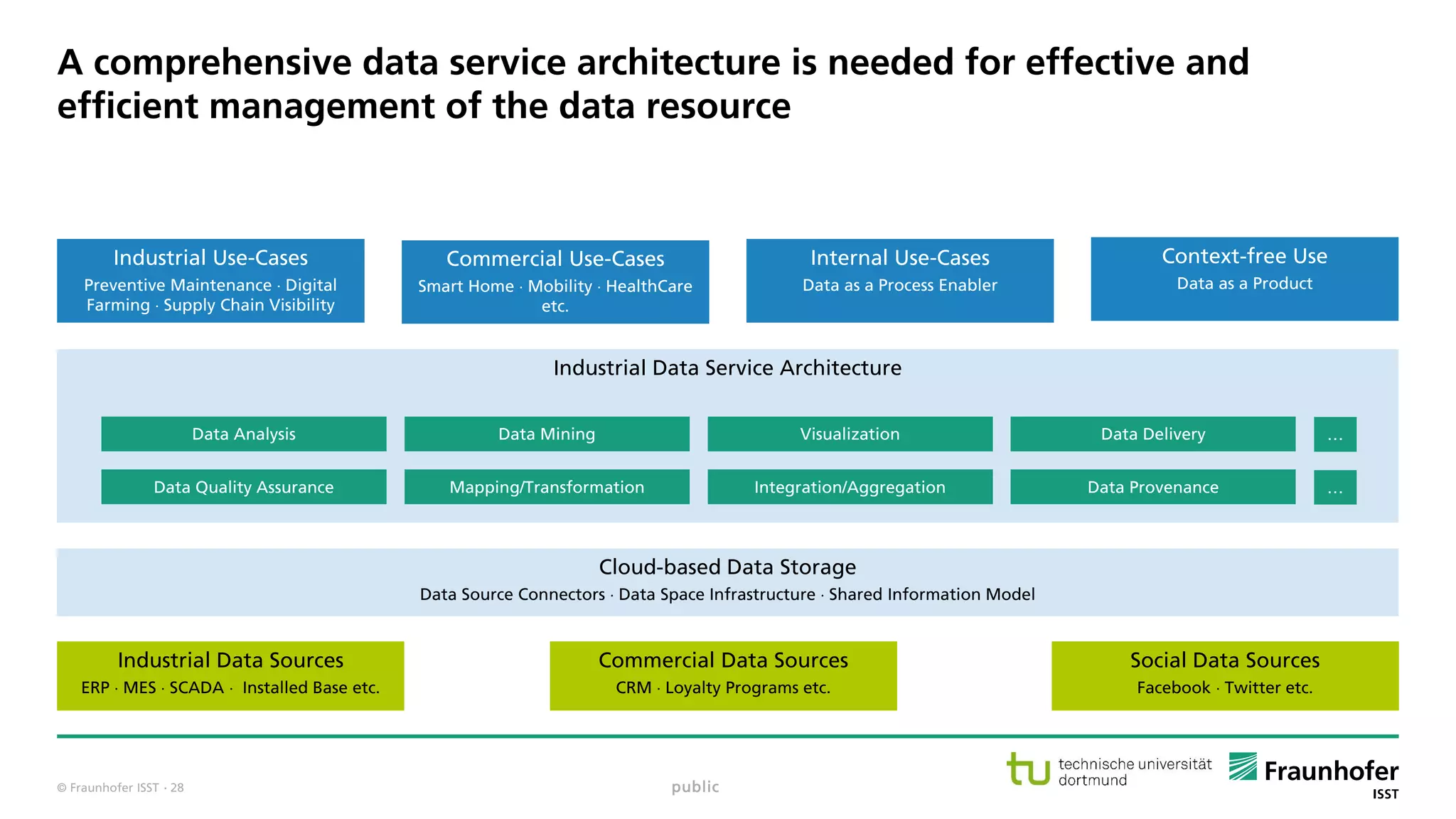
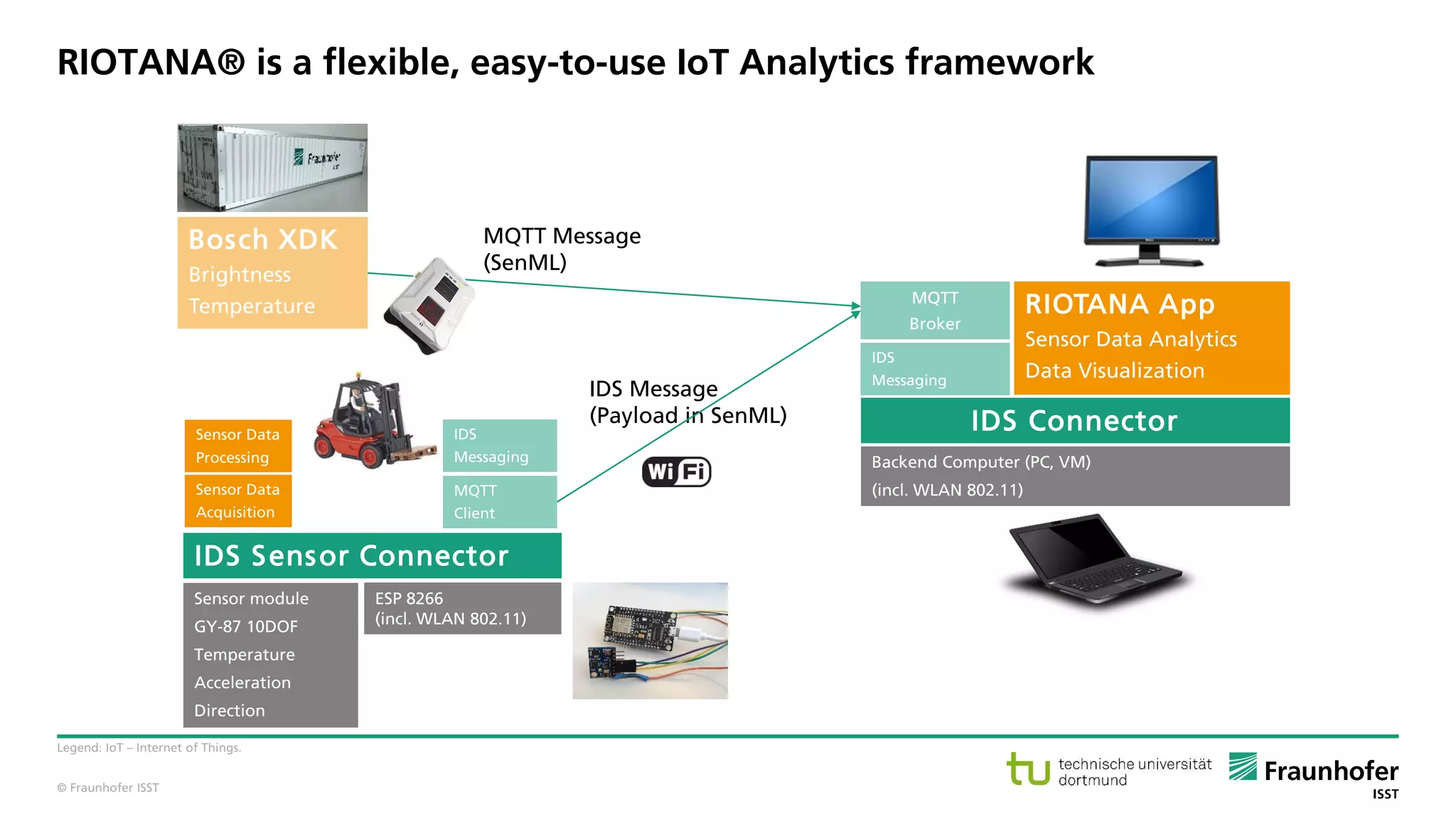
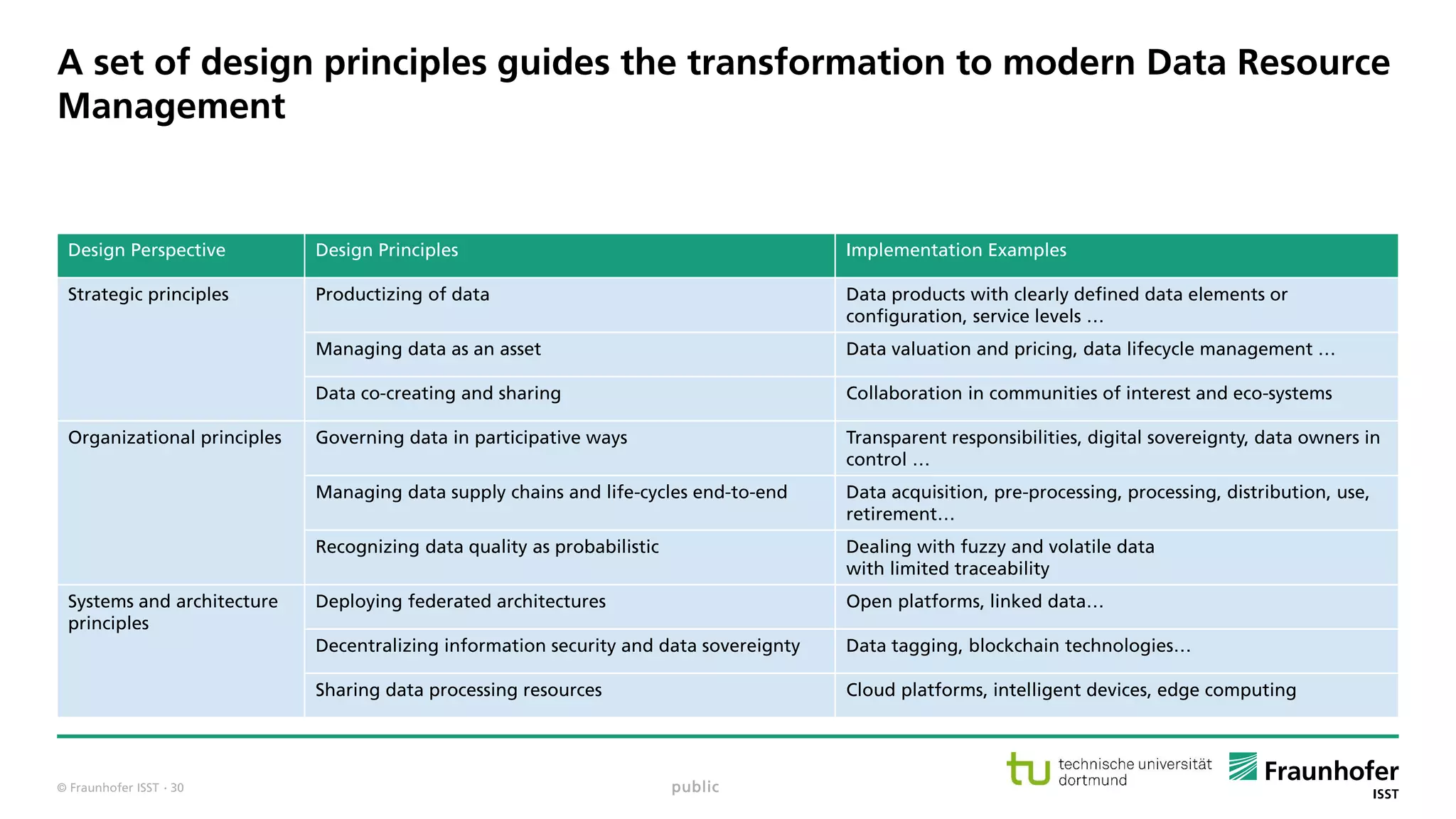
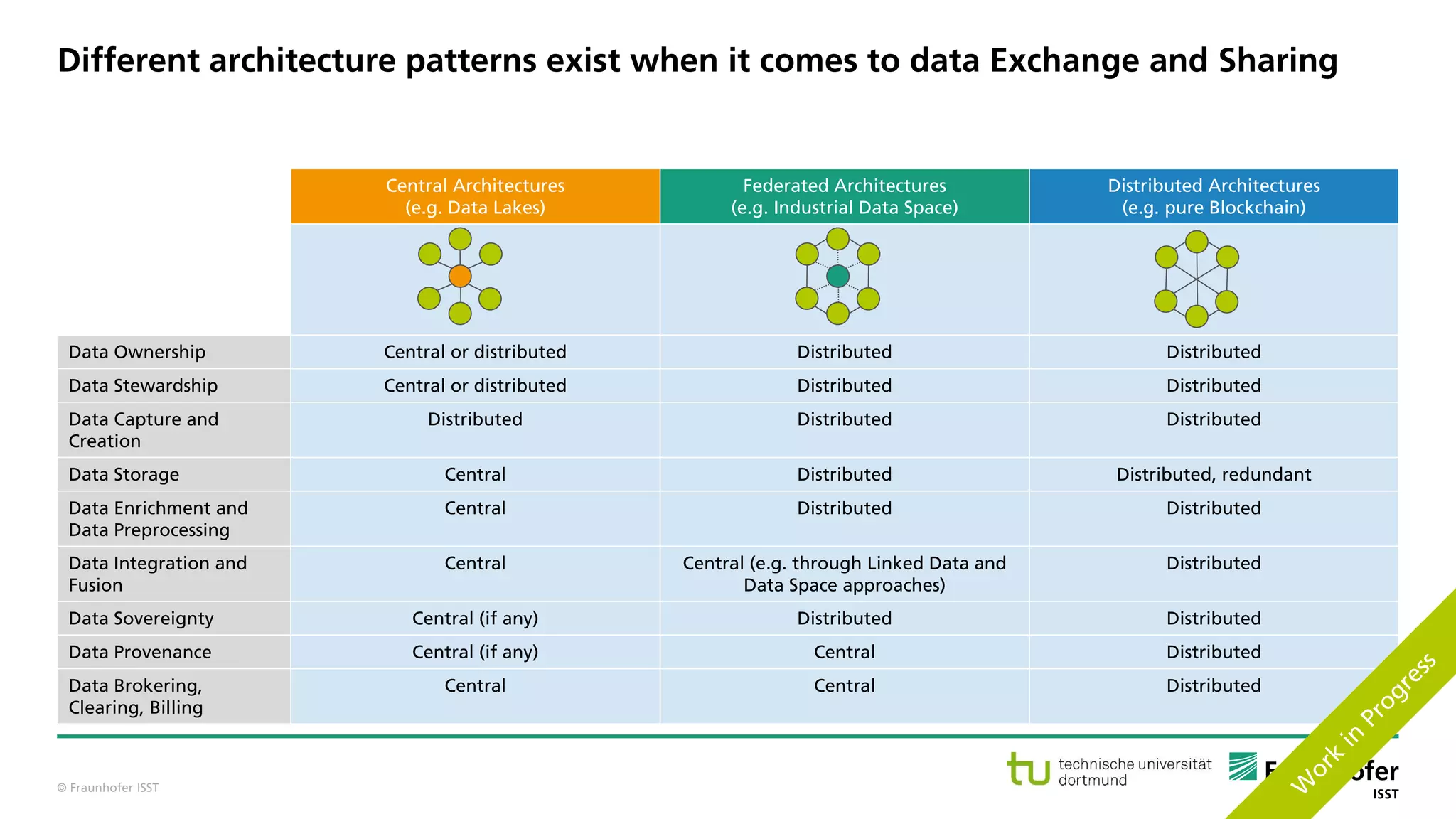
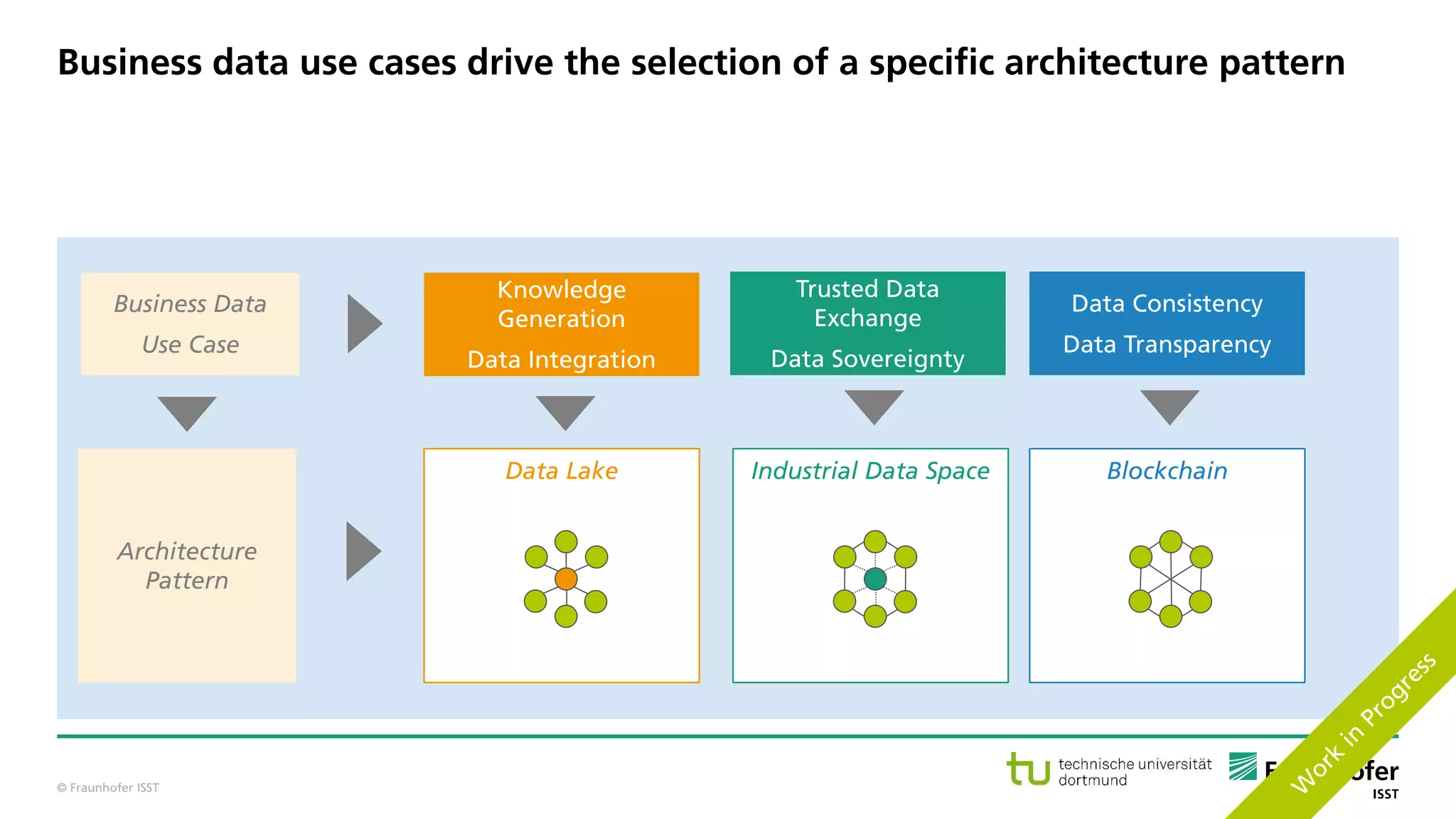
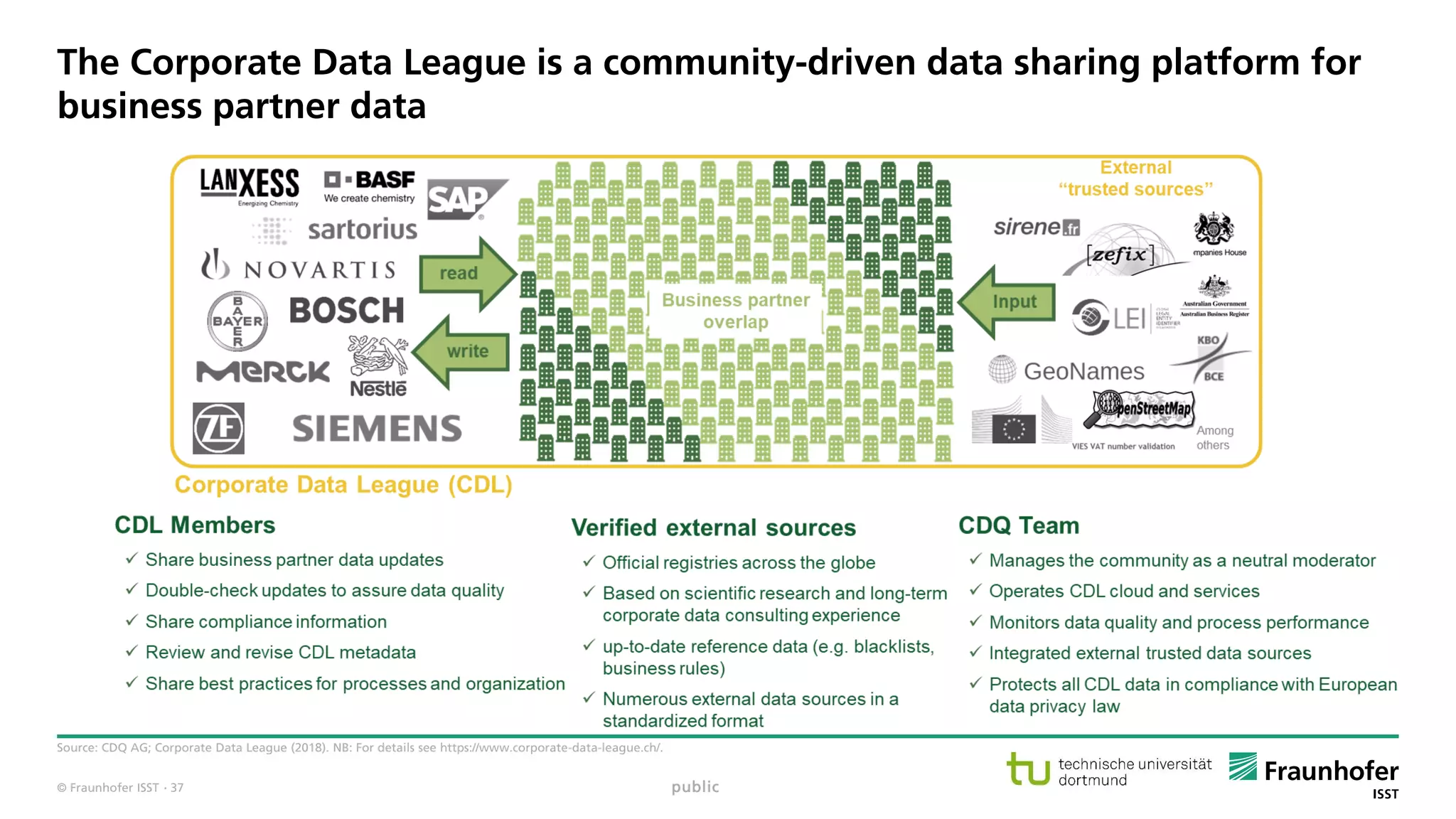
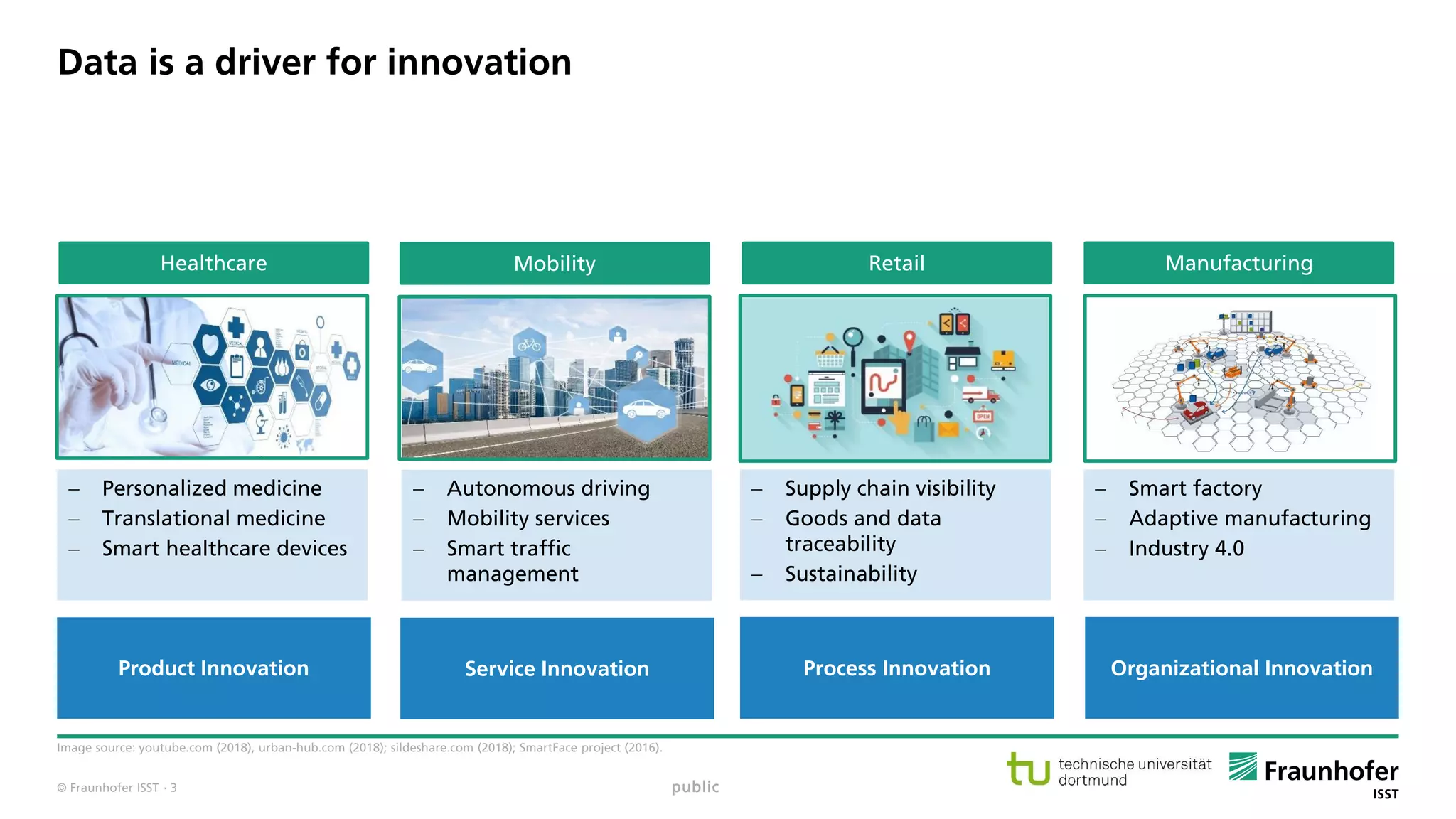
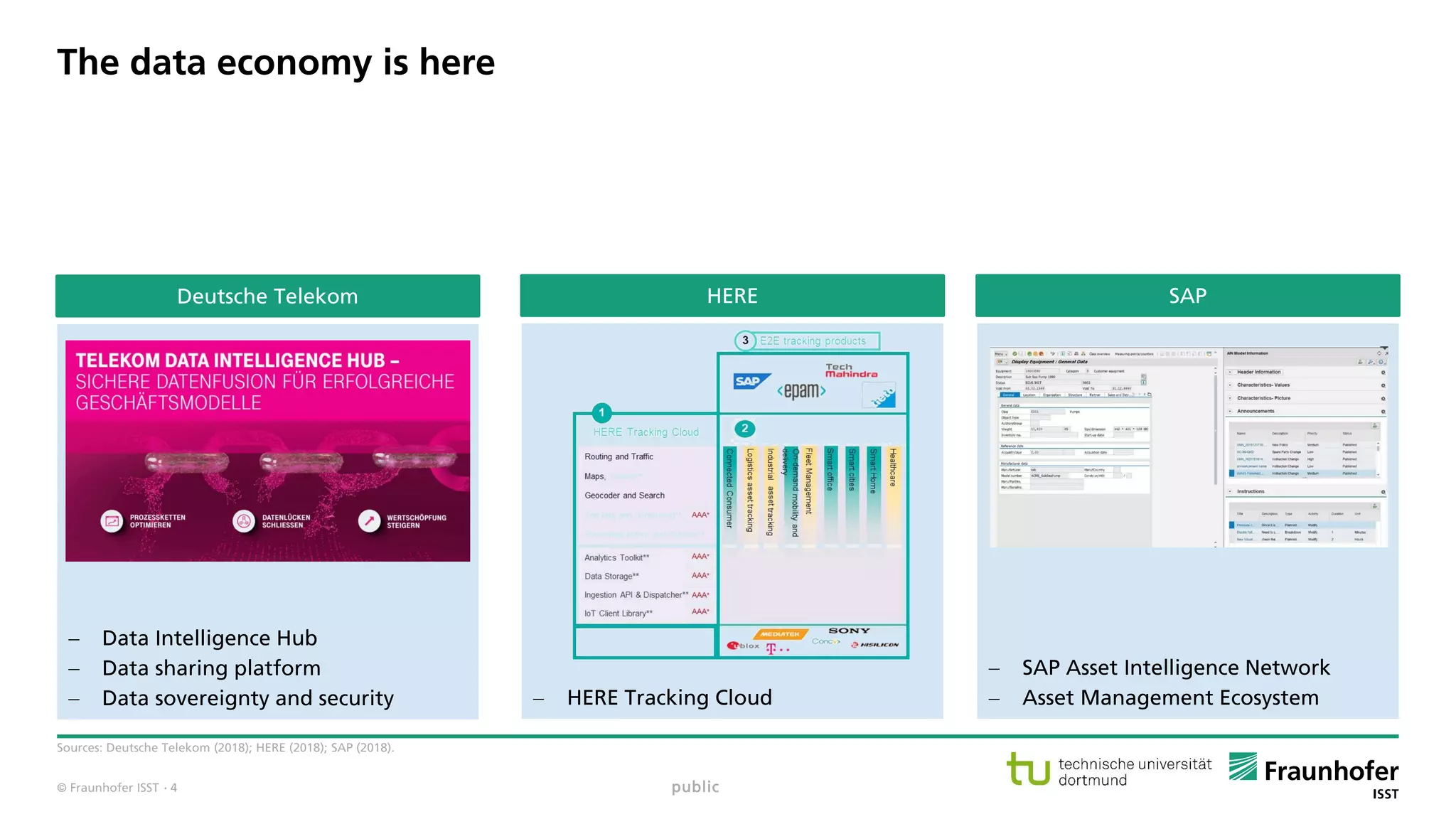
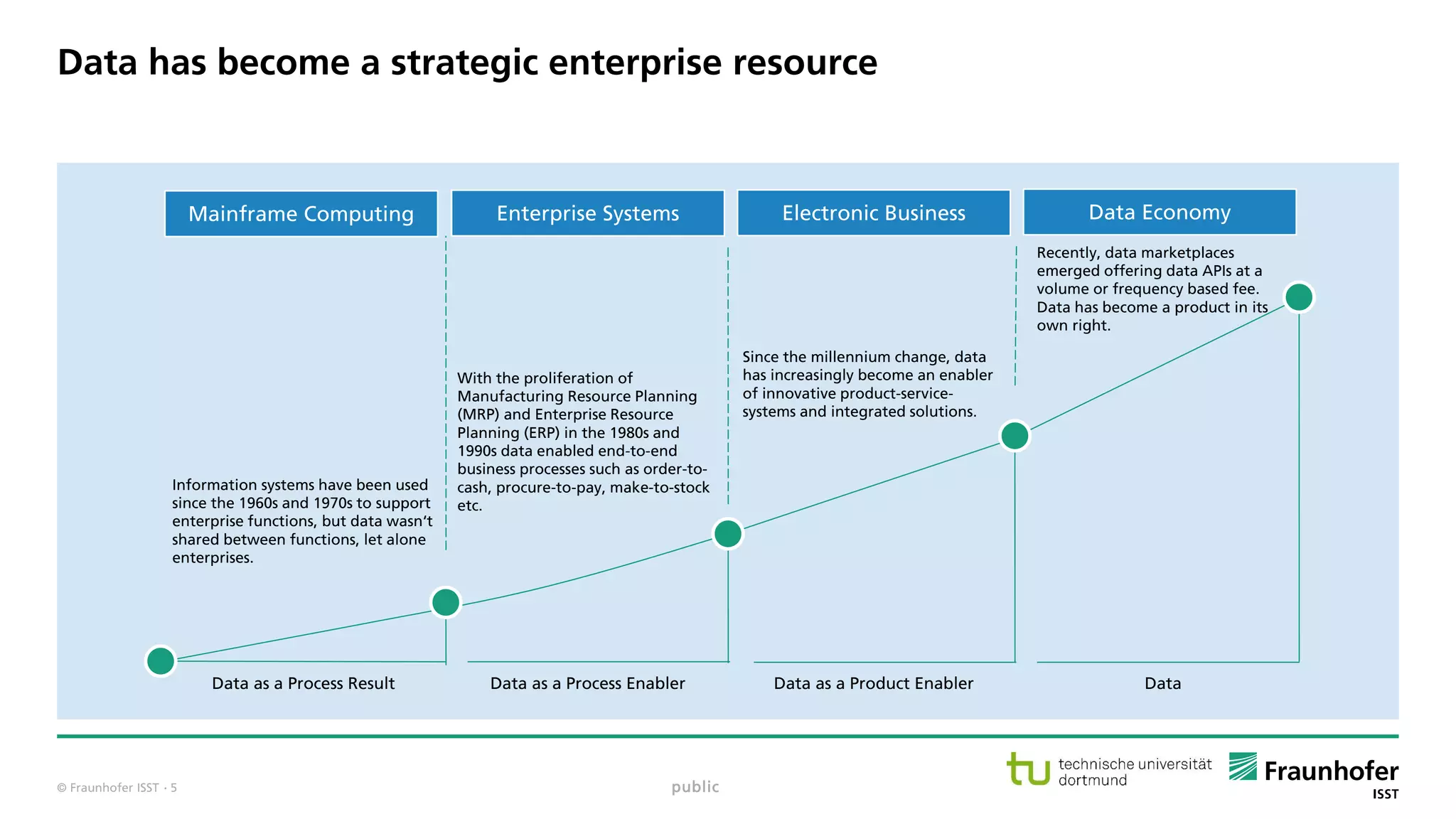
The document discusses best practices for data resource management, emphasizing that data is a strategic enterprise resource driving innovation across various sectors including healthcare and manufacturing. It highlights the importance of proactive data management to enhance data quality and reduce costs related to poor data quality. Furthermore, it outlines principles for effective data governance and the establishment of data ecosystems to facilitate data sharing and maximize value.

![© Fraunhofer ISST
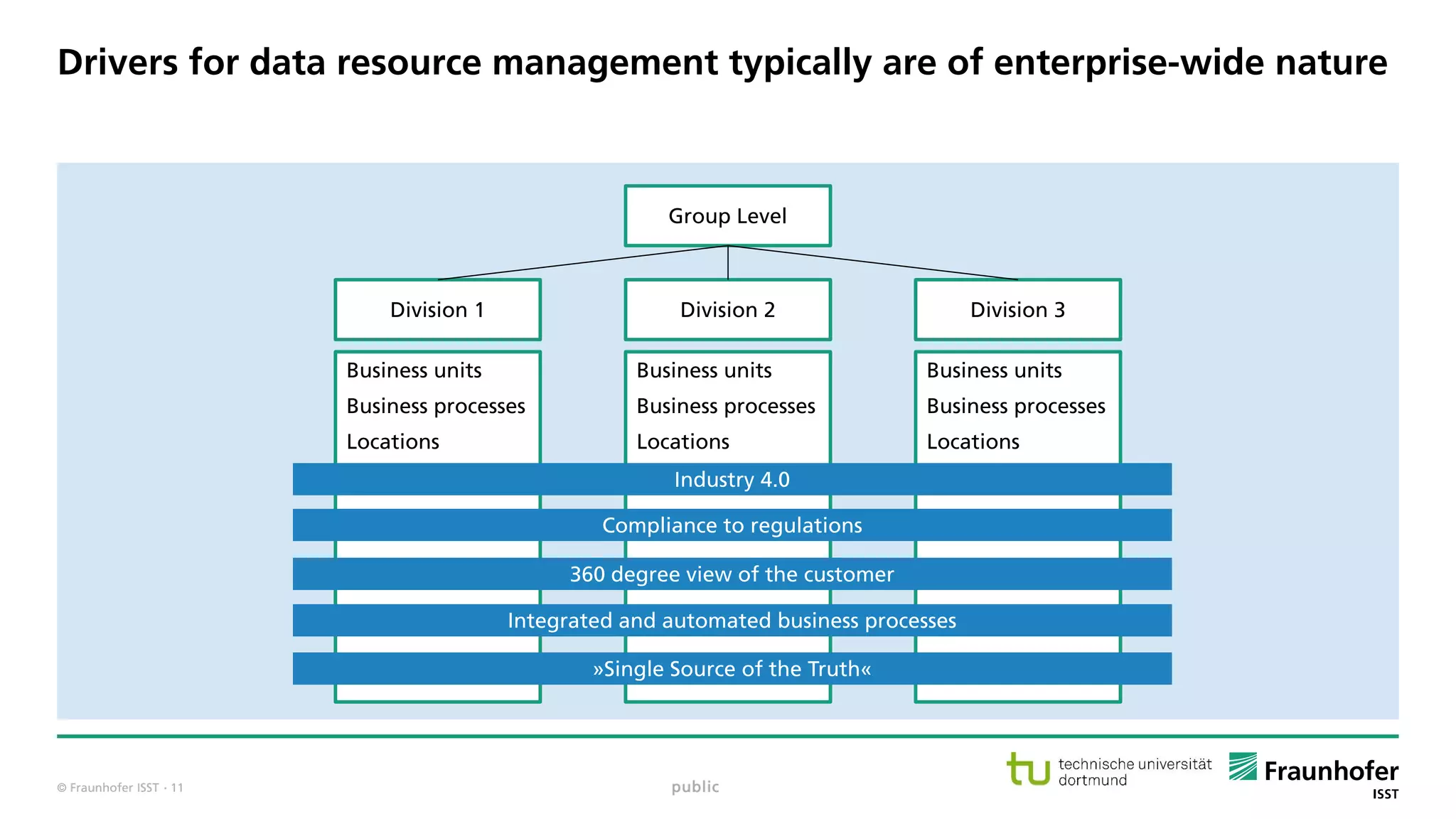
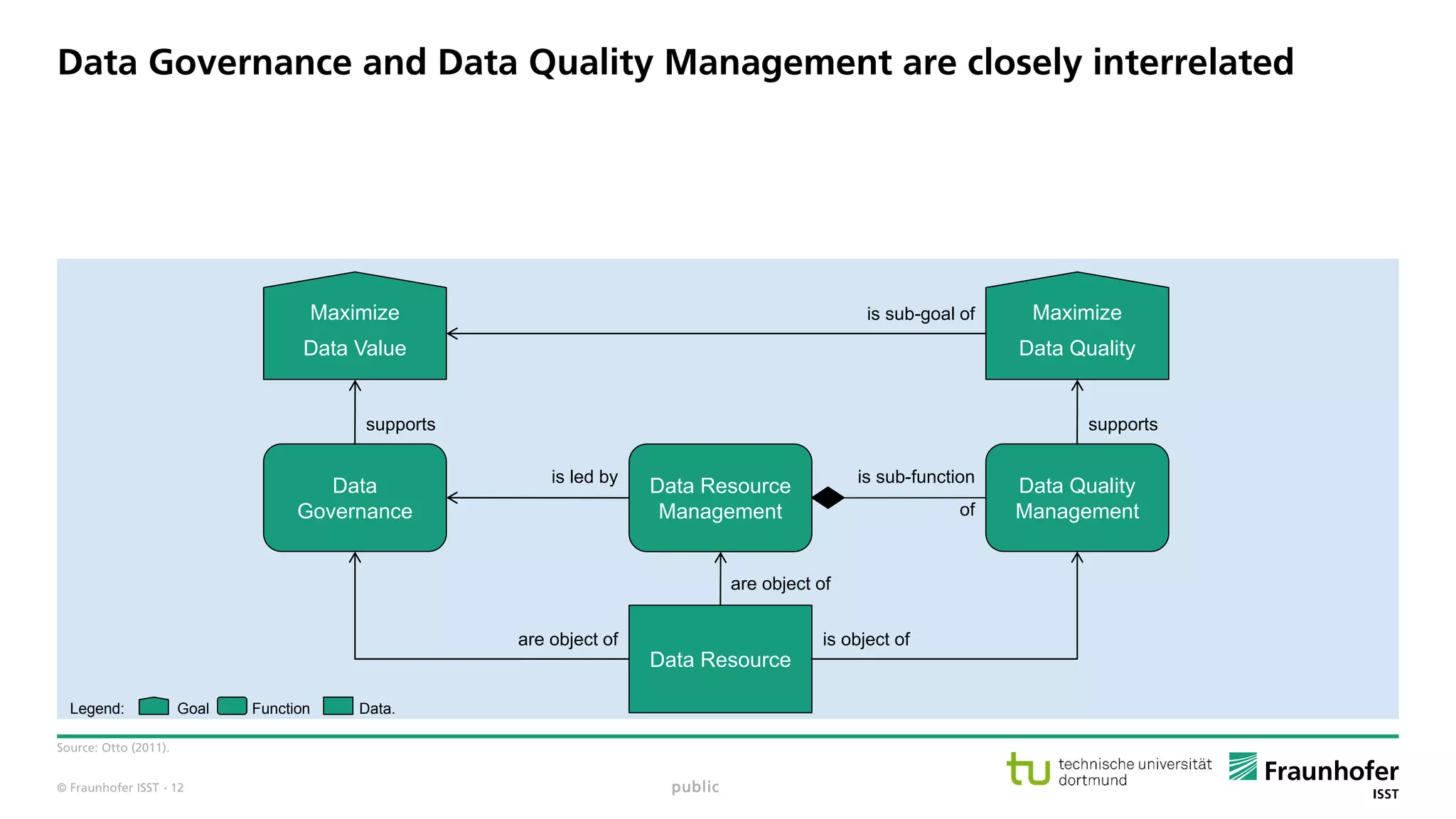
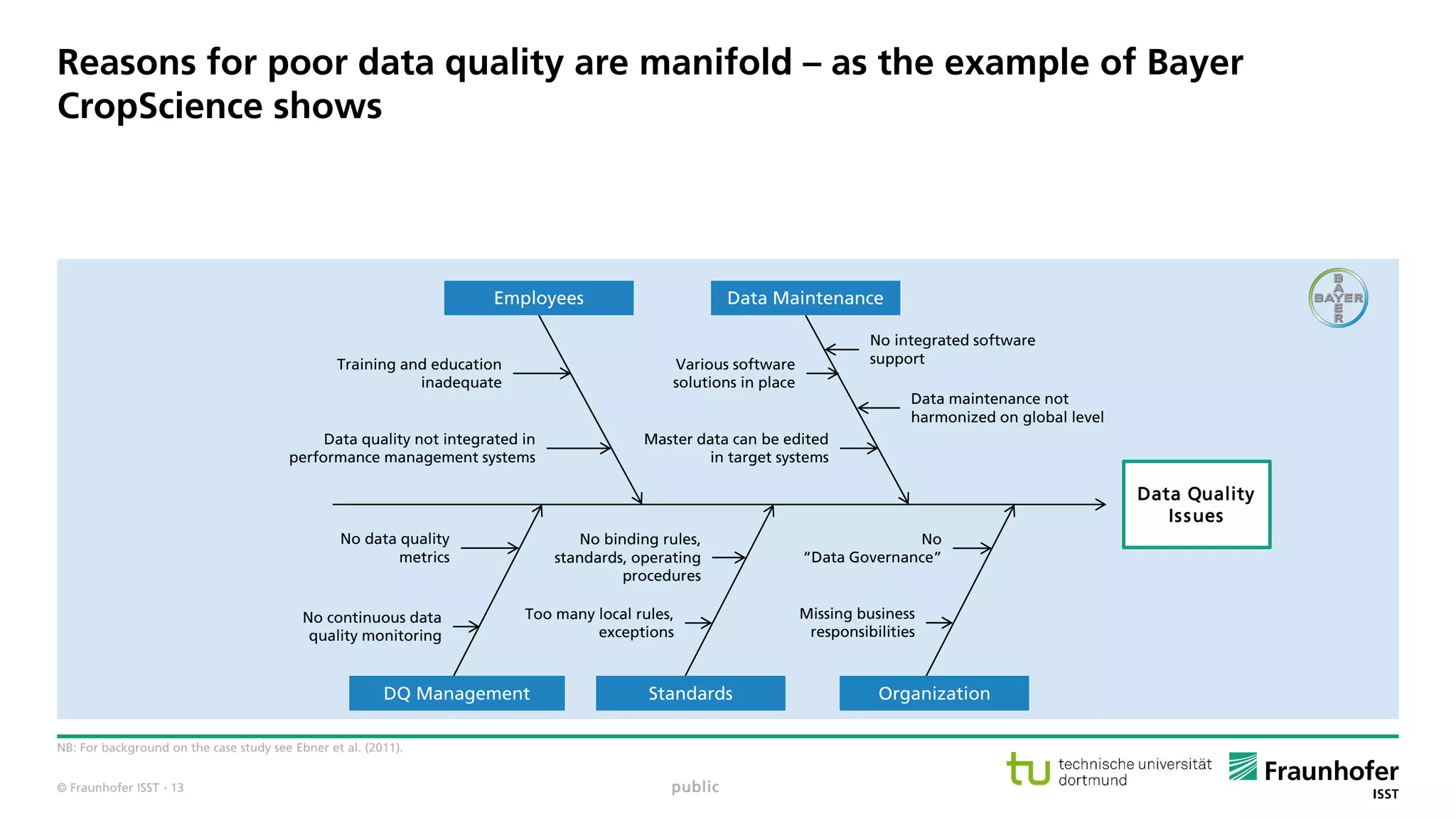
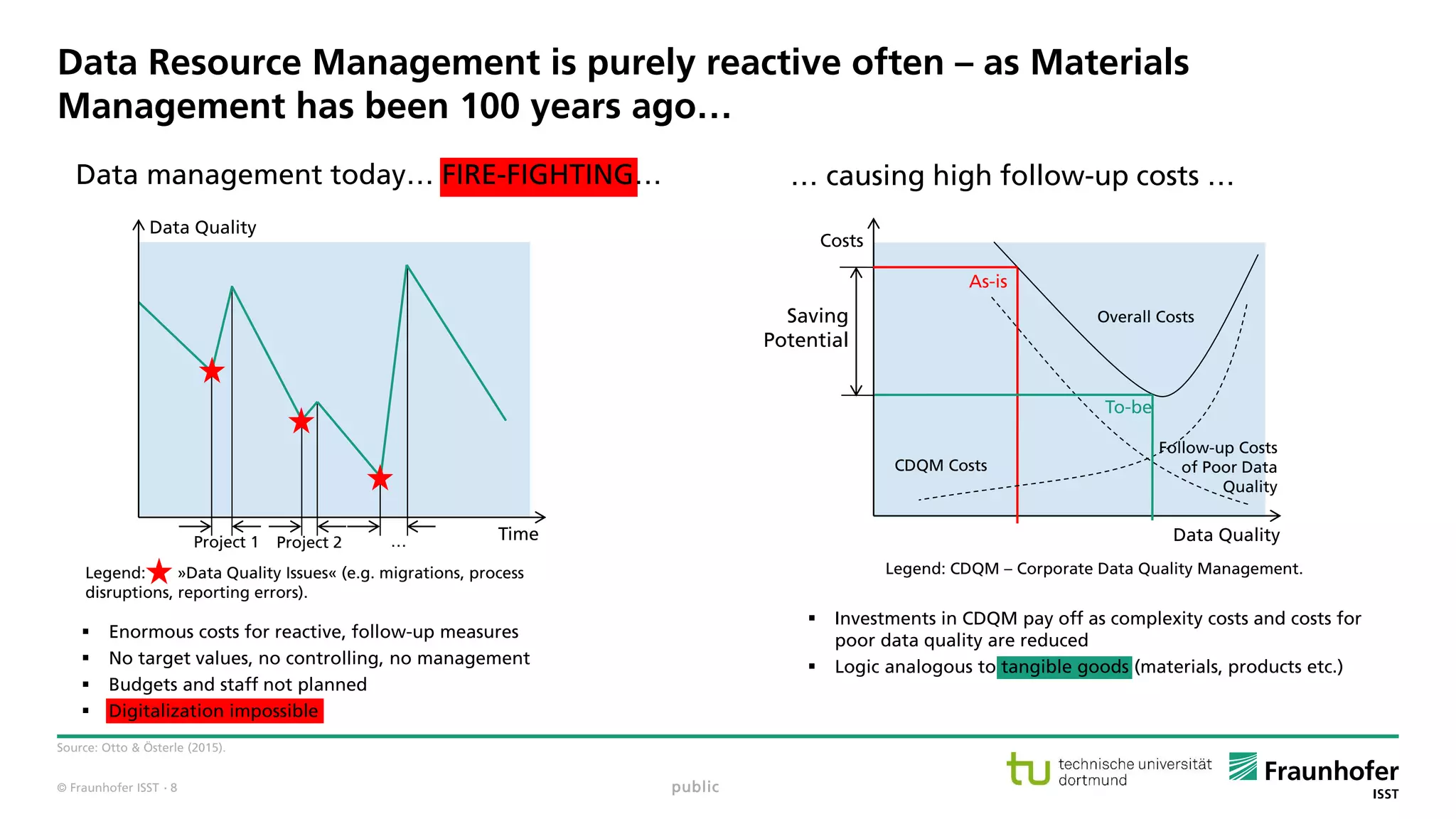
Data resource management has to be planned, monitored, executed as
materials and asset management
Source: Womack et al. (1991).
»Our findings were eye-opening. The Japanese plant requires
(less effort the American and European plants). At the same
time, the Japanese plant greatly exceeds the quality level of all
plants execpt one in Europe - and this plant requires four times
the effort […]«
»When we visited the high-quality but low productivity
European plant […] we didn‘t have to go far to find the basic
problem […]. At the end of the assembly line was an enormous
rework and rectification area where armies of technicians in
white laboratory jackets labored to bring the finished vehicles
up to the company‘s fabled quality standard.«
public· 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180712drmgslv1-180918053751/75/Data-Resource-Management-Good-Practices-to-Make-the-Most-out-of-a-Hidden-Treasure-9-2048.jpg)