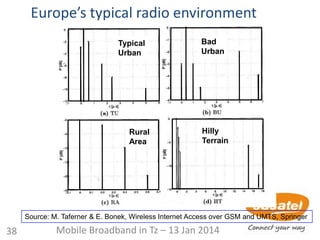
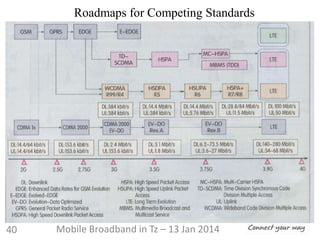
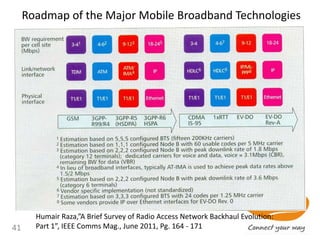
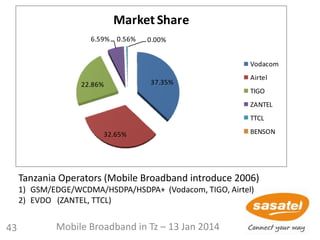
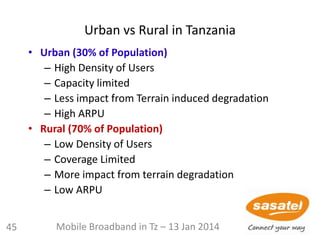
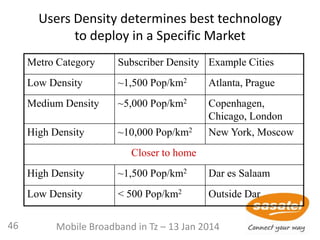
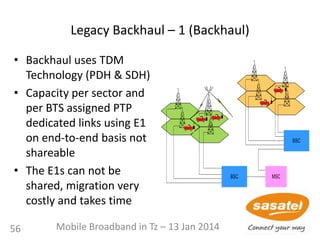
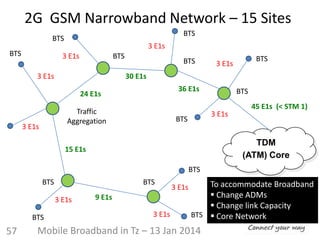
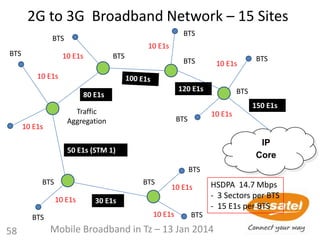
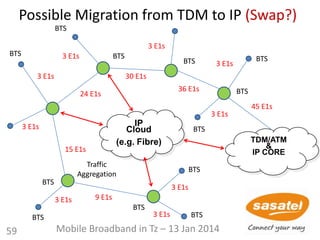
This document discusses the development of mobile broadband in Tanzania. It provides background on Tanzania's demographics and telecommunications statistics. It then covers the various mobile broadband services and technologies available in Tanzania, noting the main operators and the standards they use (GSM, CDMA, WCDMA, etc.). It also discusses some of the operational challenges in deploying mobile broadband across Tanzania given the differences between urban and rural areas in terms of population density, terrain, and other factors.







![Effect of Multipath
23
exp,][, n
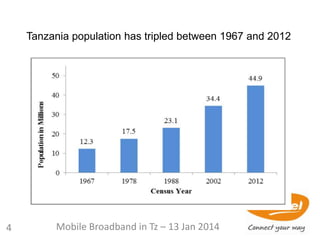
njnECPE
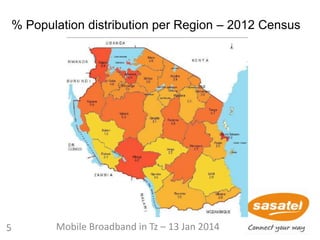
23
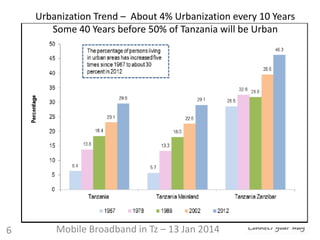
1
,, exp][
n
nnC jEPE
Non-Coherent Vector Sum
Coherent Vector Sum
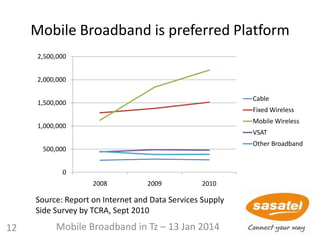
Delay (s)
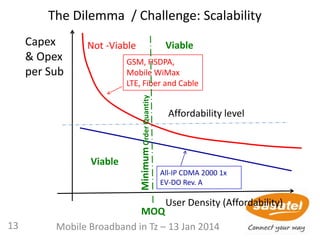
Real
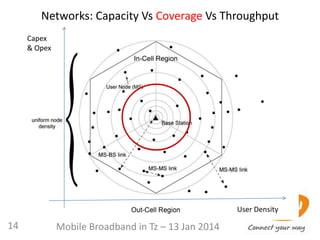
0
Coherent Vector sum
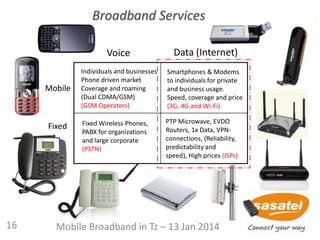
1
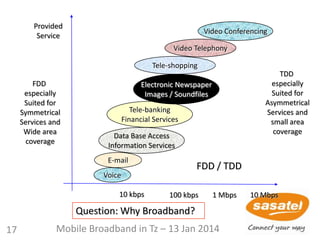
2
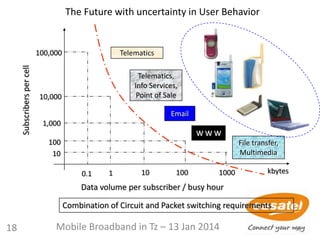
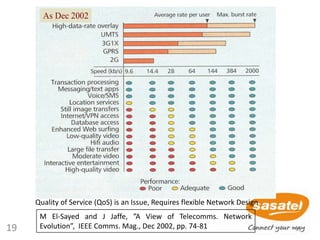
3
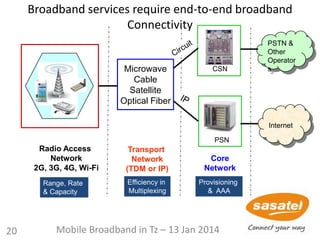
2
3
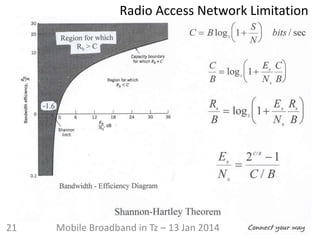
I II III
Delay
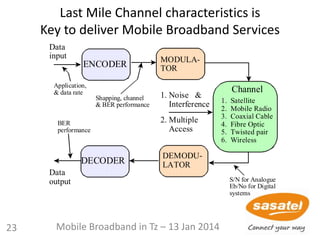
Resolution
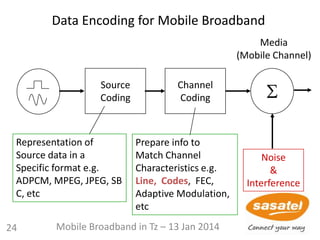
1 2
3
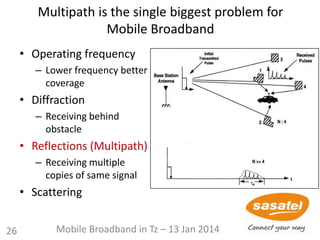
Imaginary
Real
0
(Fading)
Delay ( λ)
27 Mobile Broadband in Tz – 13 Jan 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mobilebroadbanddevelopmentintz-13jan2015-150222053154-conversion-gate01/85/Mobile-broadband-development-in-tz-13-jan-2015-27-320.jpg)
![Multipath Fades
x1(t) + x2(t)
x t t
x t t
where
C
C
1
1
0 180
( ) sin( )
( ) sin( )
0 45 90 135 180
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
Phase Difference [ degrees ]
Effect of phase difference
CDMA handles this situation better than other mobile networks
Using RAKE receiver and other techniques
28 Mobile Broadband in Tz – 13 Jan 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mobilebroadbanddevelopmentintz-13jan2015-150222053154-conversion-gate01/85/Mobile-broadband-development-in-tz-13-jan-2015-28-320.jpg)





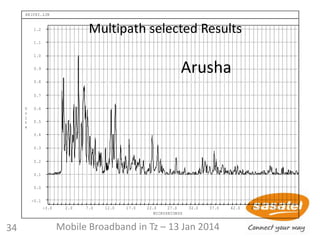
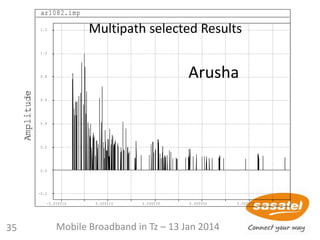
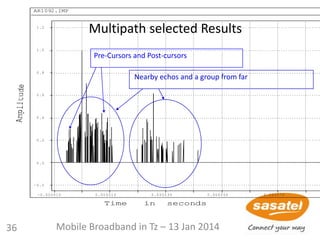
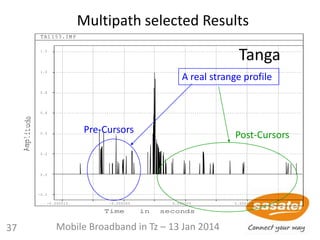











![61
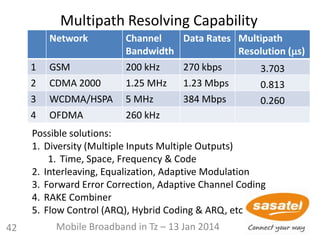
Impact of Operating Frequency
0.0 4.0 8.0 12.0 16.0 20.0 24.0 28.0
80.0
85.0
90.0
95.0
100.0
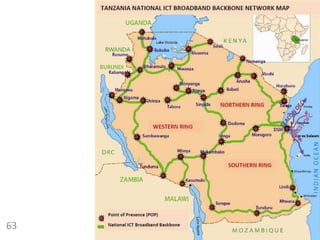
105.0
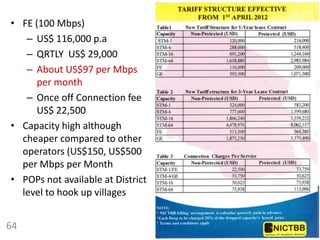
110.0
115.0
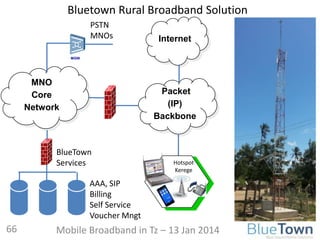
120.0
125.0
130.0
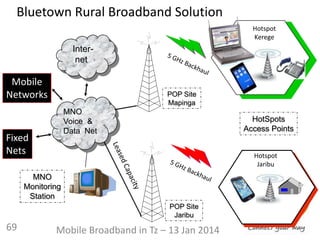
Distance [ 1 -30 km ]
900 MHz
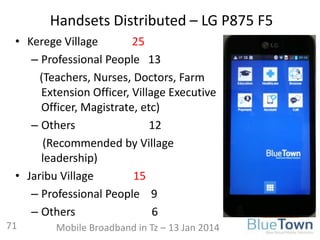
400 MHz
1800 MHz
About 8 km gained
61 Mobile Broadband in Tz – 13 Jan 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mobilebroadbanddevelopmentintz-13jan2015-150222053154-conversion-gate01/85/Mobile-broadband-development-in-tz-13-jan-2015-61-320.jpg)