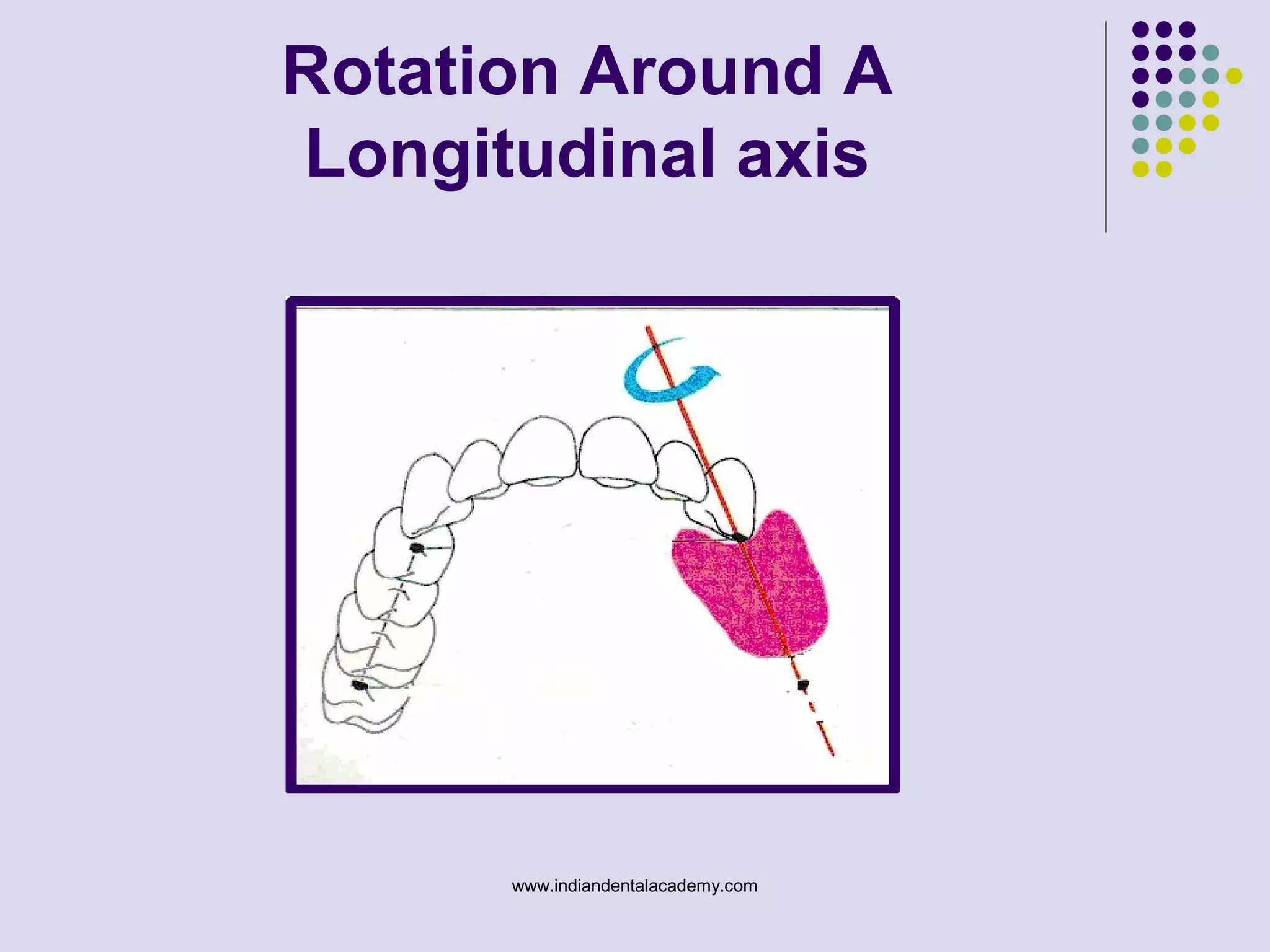
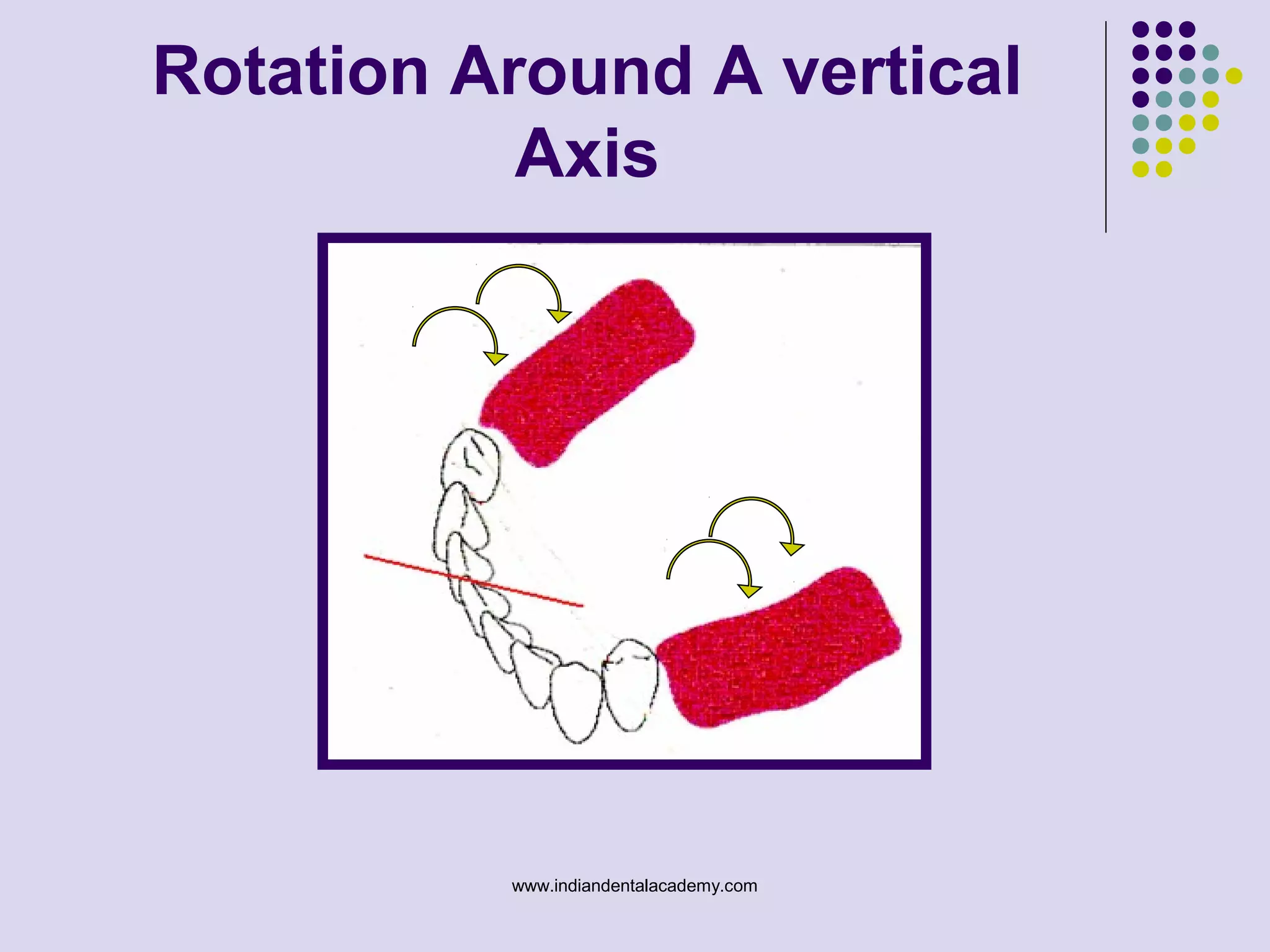
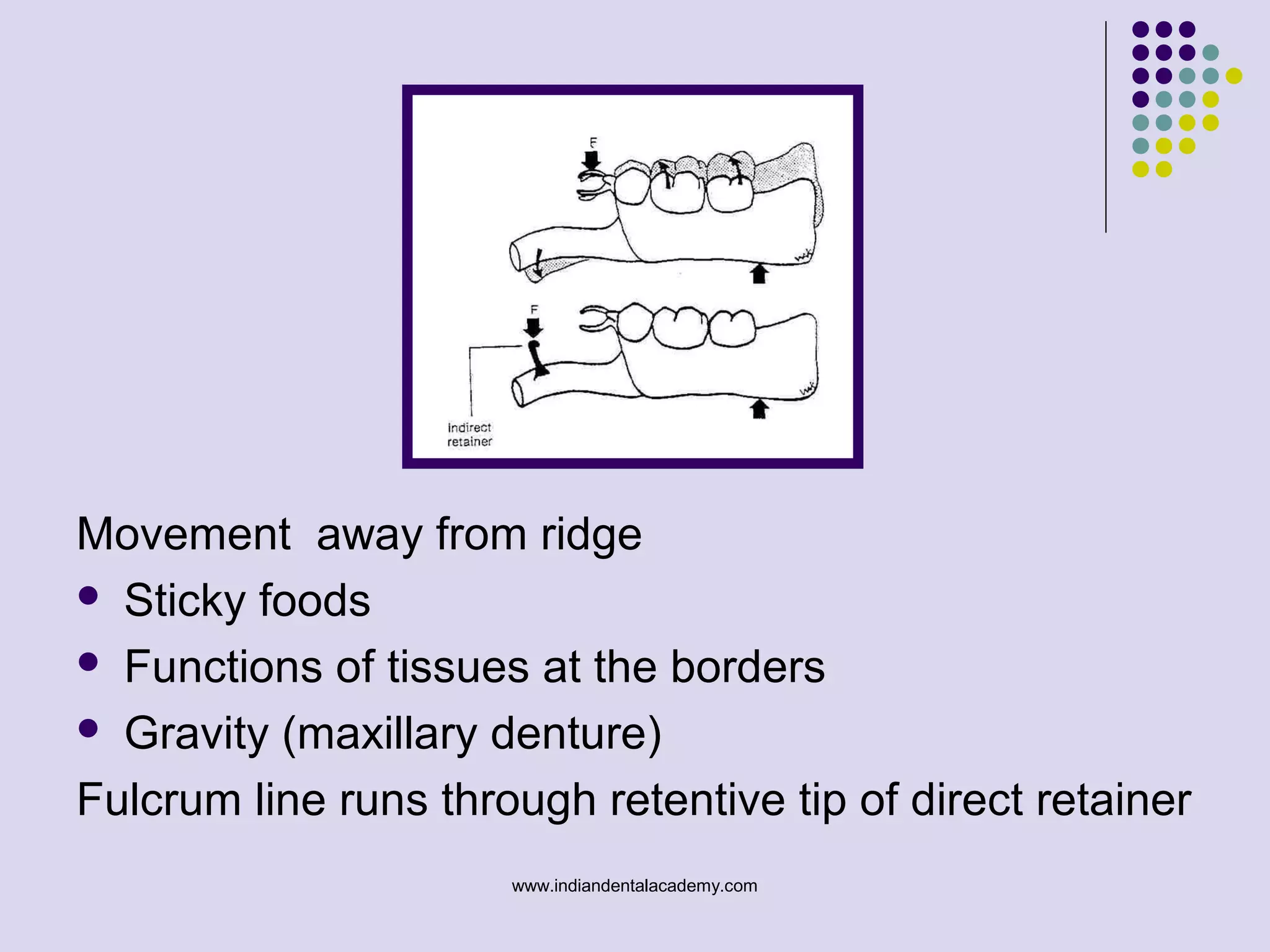
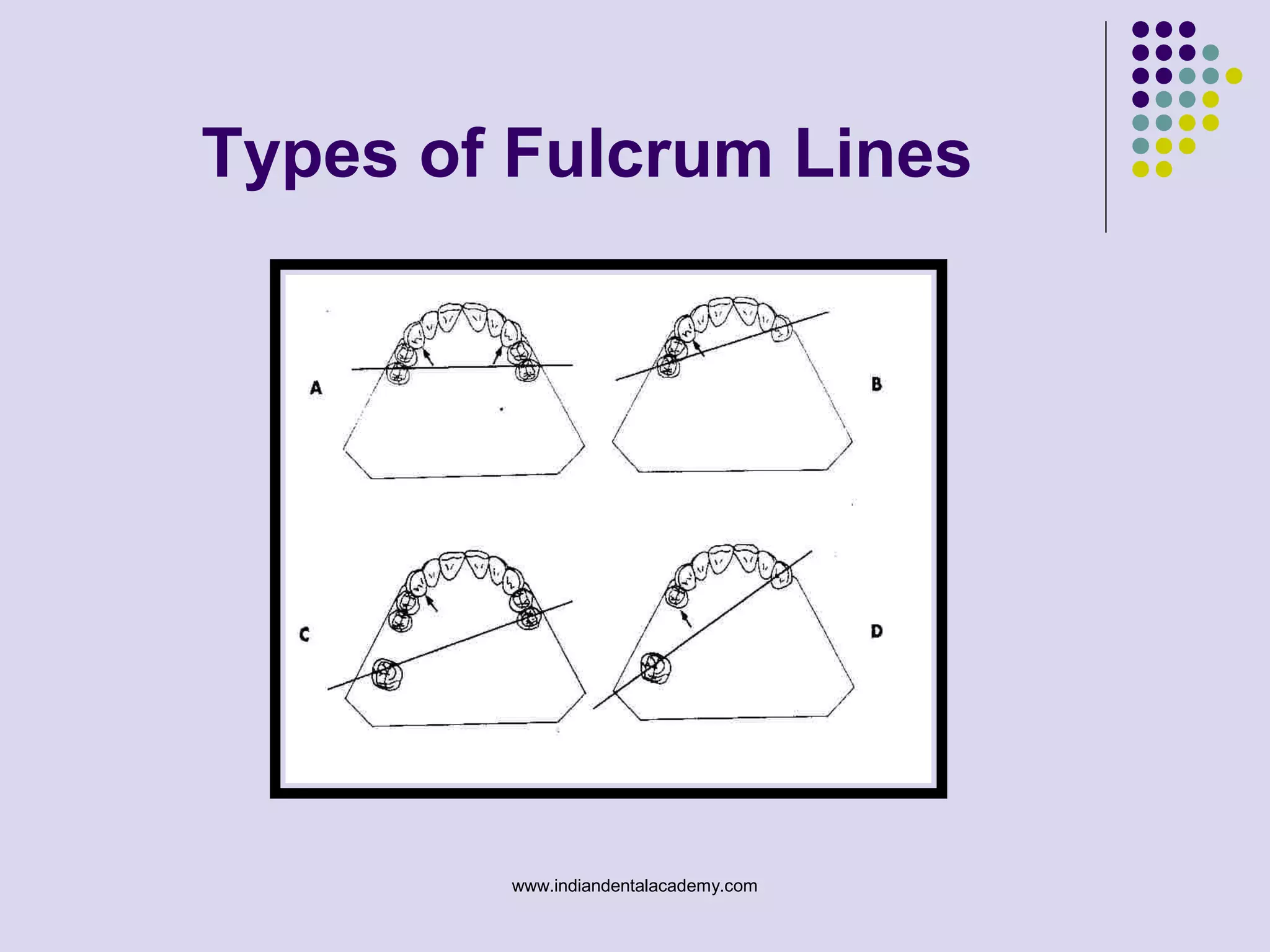
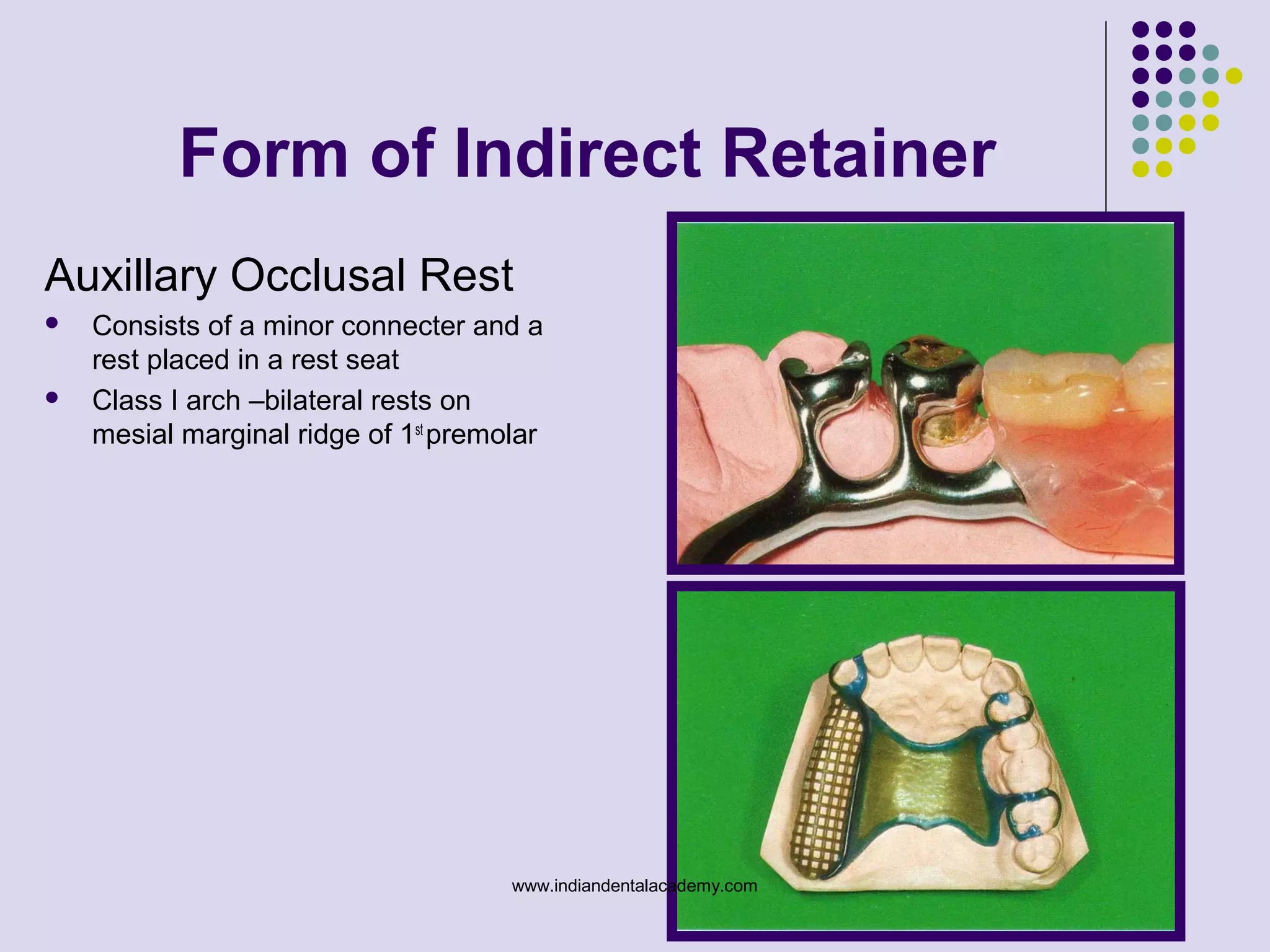
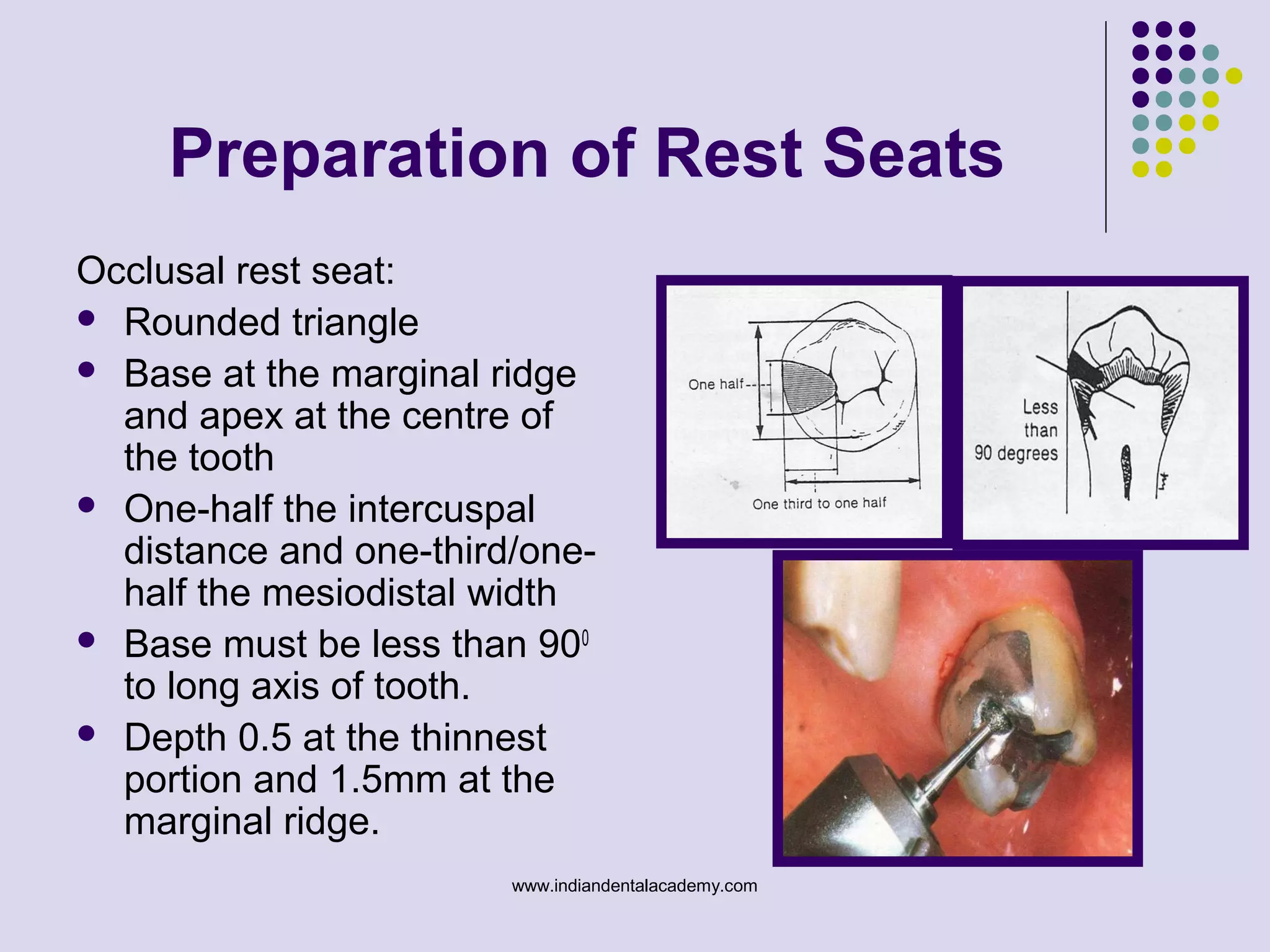
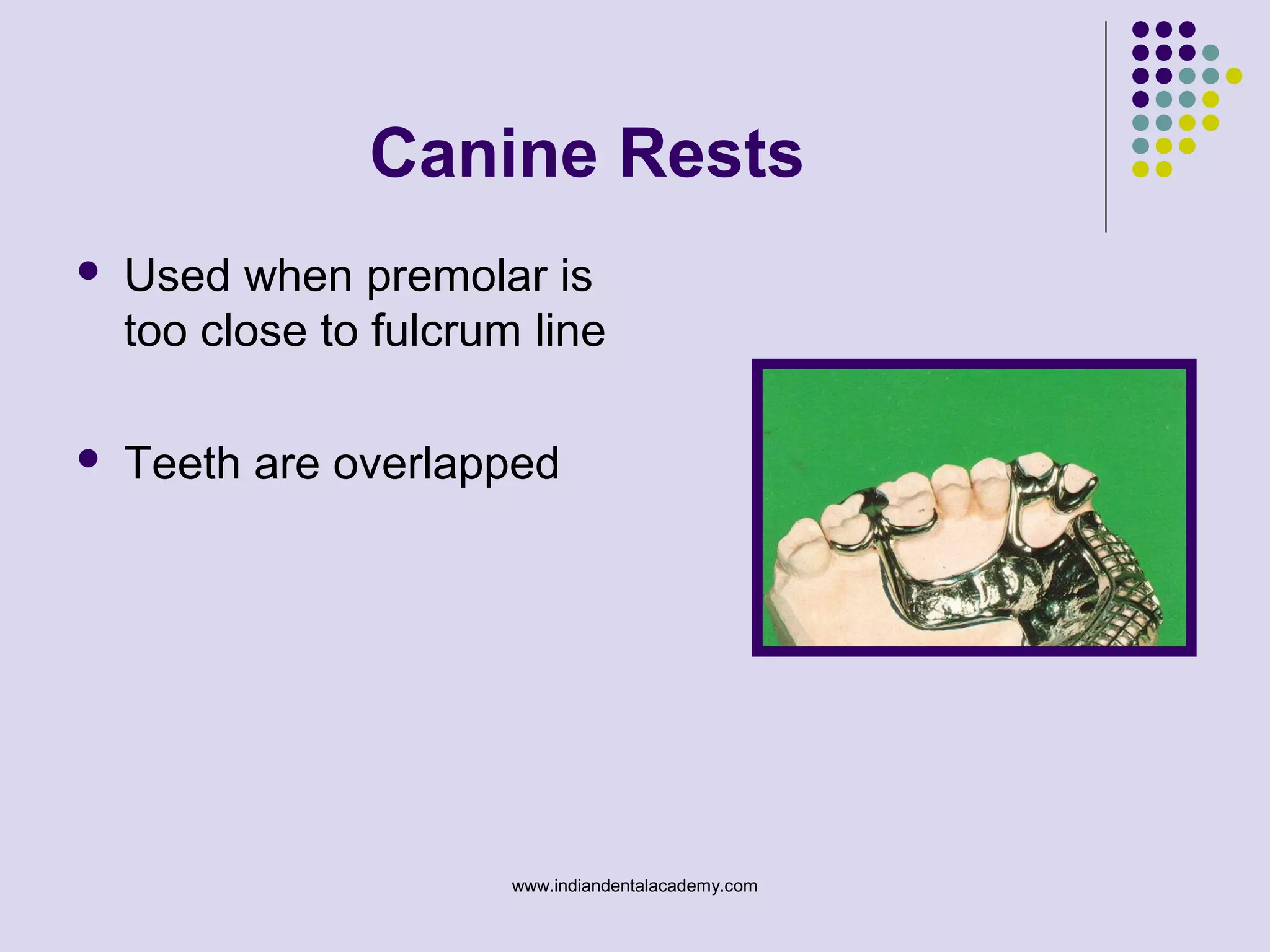
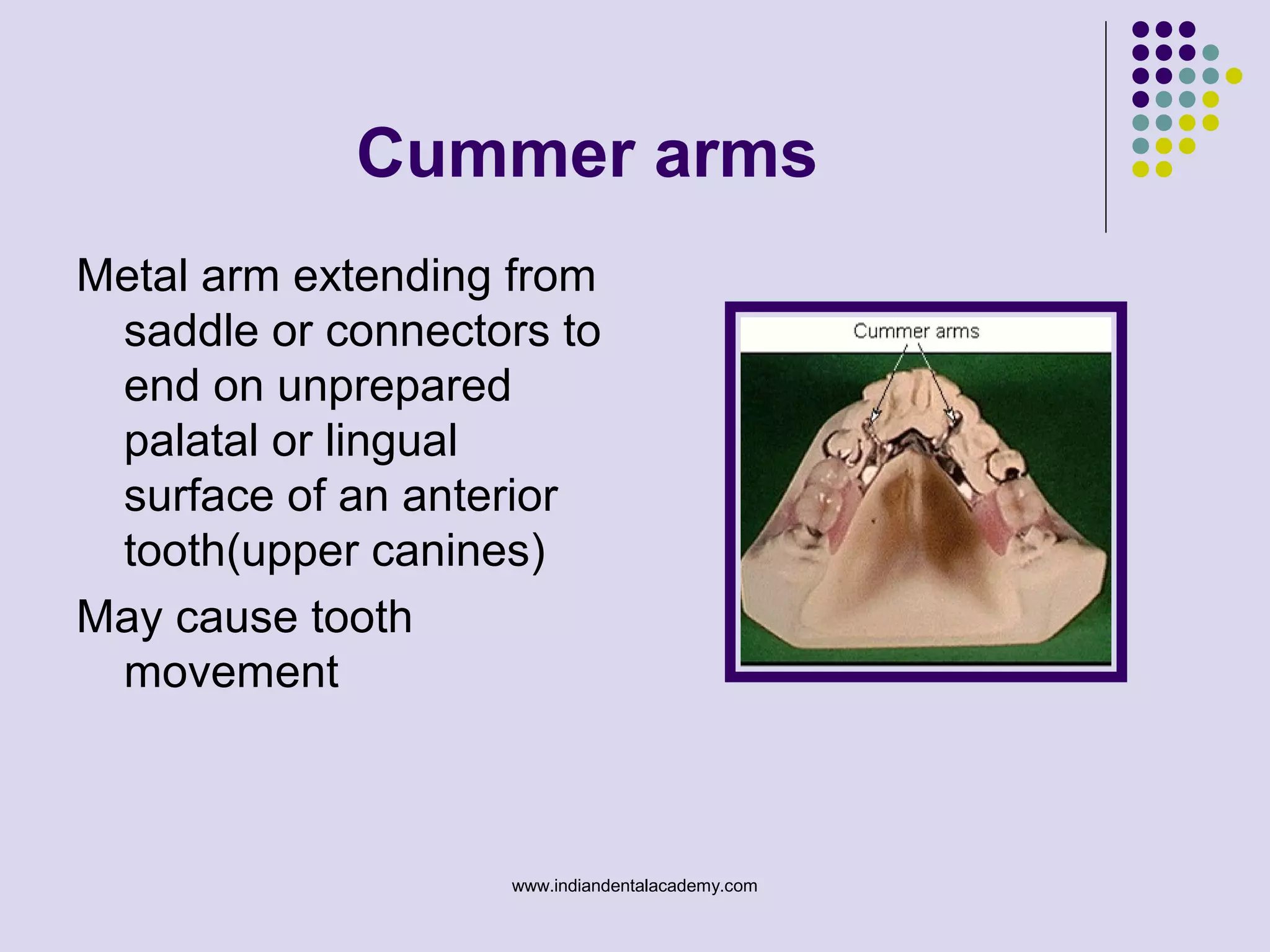
The document discusses indirect retainers in the context of removable partial dentures, emphasizing their importance for stability and retention when direct retainers are insufficient. It outlines the principles of levers, types of fulcrum lines, factors affecting indirect retainers, and various forms and functions they serve. Proper design and placement of these components are essential to minimize displacing forces and ensure the success of dental prosthetics.