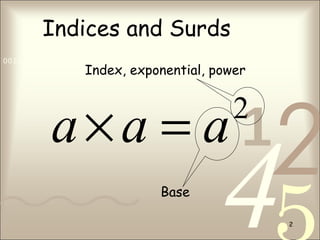
This document discusses indices and surds. It presents 8 rules of indices related to multiplication, division, exponents, and fractions. It also discusses irrational numbers as numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction of integers, such as π. Example problems are given to simplify surd expressions using the rules presented.































![1 1
OR =
Rationalize k 2 31 + 8 15
5+ 3 k First
2
1 31 − 8 15
k2 = = ×
5− 3 31 + 8 15 31 − 8 15
0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011
k2 = [
(
5+ 3
2
]2 ) =
31 − 8 15
( )(
5− 3 5+ 3 ) ( 961 − 64 × 15) 1
2
k + 2
2
(5 + 2 15 + 3) 31 − 8 15 k
1
k2 = [ ]2 =
( 5 − 3) ( 961 − 960)
4
= 31 + 8 15 + 31 − 8 15
8 + 2 15
k2 = [ ]2 = 31− 8 15 = 62
2
k 2 = (4 + 15 ) 2 = 16 + 2 × 4 × 15 + 15
= 31+ 8 15
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indicesandsurds-130128232848-phpapp01/85/Indices-and-surds-33-320.jpg)
