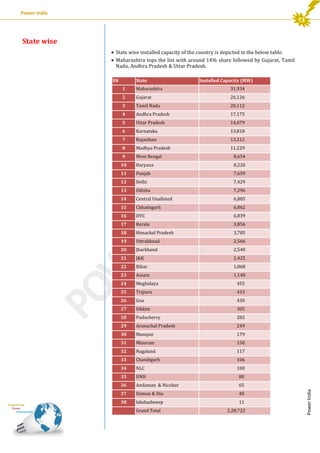
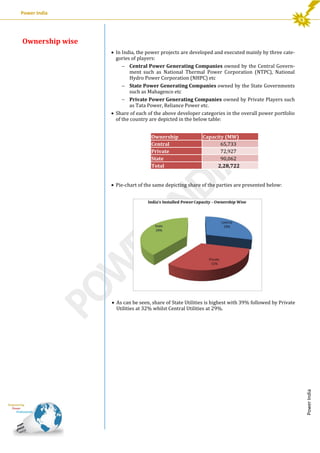
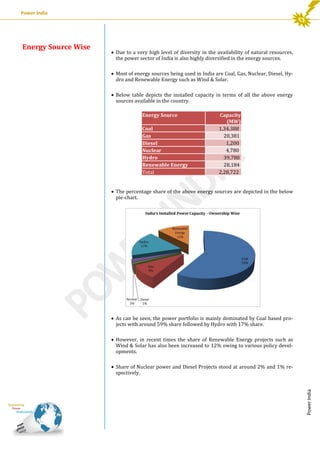
This document provides an analysis of India's installed power generation capacity as of September 2013. It summarizes the total capacity by region, with the Western region having the largest share at 34%. It also analyzes capacity by state, with Maharashtra having the most at 31.9 GW, and by ownership, with state utilities having the largest share at 39%. Finally, it notes that coal-based projects dominate India's energy mix with 59% of capacity, followed by hydro at 17% and renewable energy at 12%.