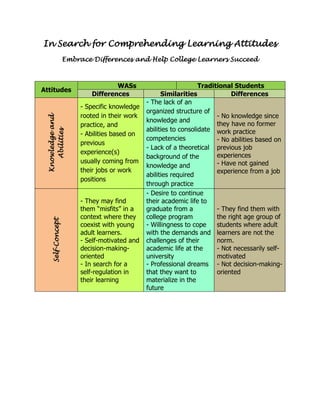
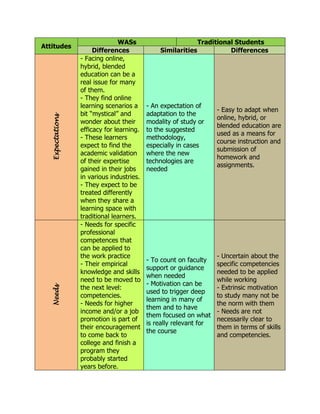
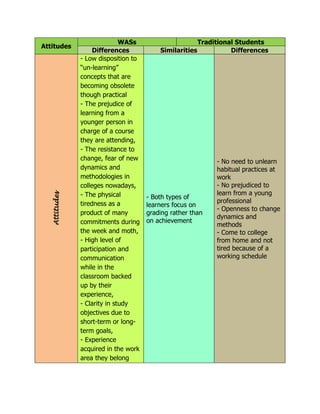
The document discusses some key differences and similarities between working adult students (WASs) and traditional students in terms of their knowledge/abilities, self-concept, expectations, needs, and attitudes towards learning. WASs tend to have specific practical knowledge but lack theoretical backgrounds, see themselves as "misfits", expect validation of work experience, and have needs for professional competencies. They can be resistant to change and tired from work commitments. Meanwhile, traditional students tend to be open to new methods, not tired from work, and focus on grades over achievement. Both groups prioritize short-term goals.