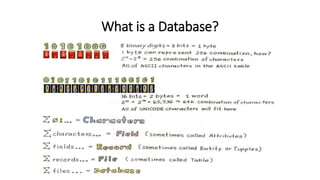
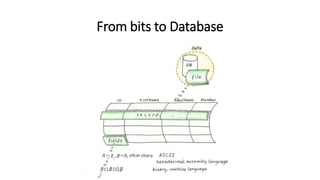
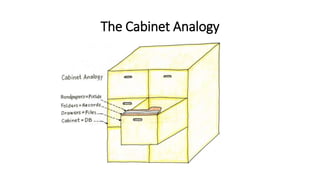
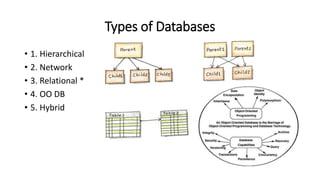
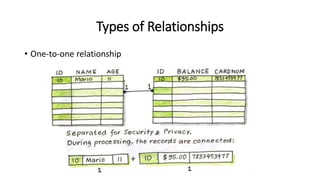
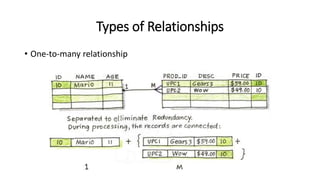
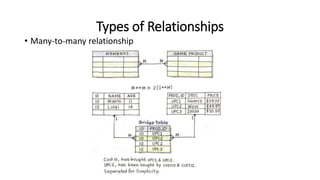
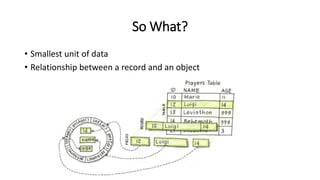
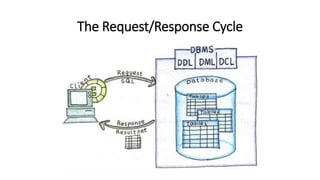
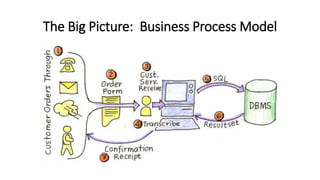
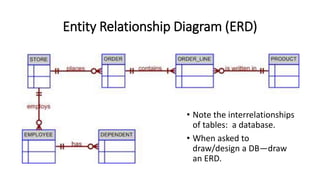
This VoiceThread lecture covers database design and relational databases. It discusses key concepts like bits, binary digits, what a database is, the cabinet analogy, advantages and disadvantages of database management systems, types of databases including relational and object-oriented, types of relationships in relational databases, database normalization process, and entity relationship diagrams. The lecture is intended to make up for a missed class on database design topics.