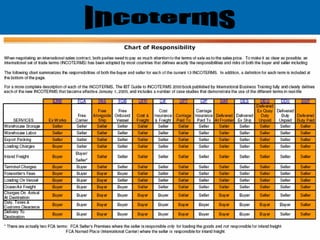
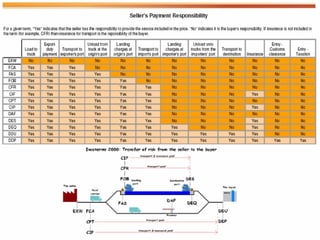
Incoterms are a series of international commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that are used worldwide in international trade transactions. They standardize key aspects of international sales such as determining when delivery is considered complete and who is responsible for transportation costs and cargo insurance. The document discusses the 11 main Incoterms used in international trade including EXW, FCA, FOB, CFR, CIF, CPT, CIP, DAF, DES, DEQ, DDU, and DDP and provides brief descriptions of what obligations each term assigns to the buyer and seller.