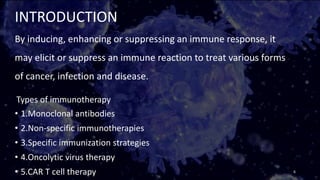
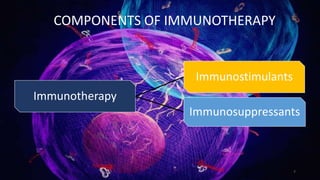
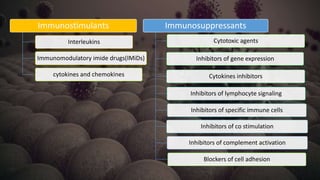
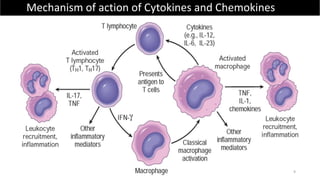
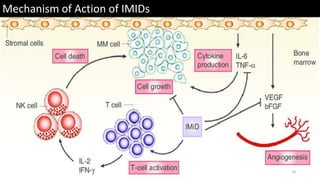
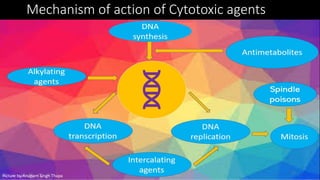
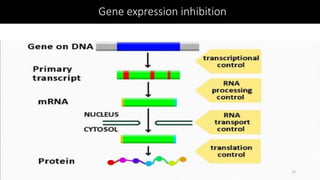
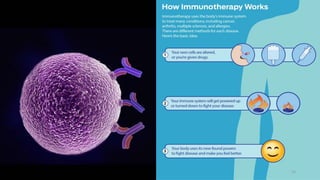
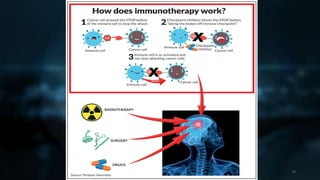
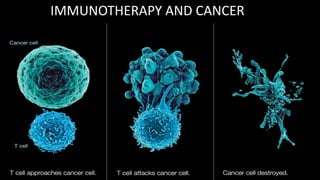
Immunotherapy is a treatment that utilizes biological response modifiers to bolster the immune system's ability to combat cancer and other diseases. It represents an innovative approach to medicine, providing targeted therapies with fewer side effects compared to traditional treatments. Despite its effectiveness and growing use in cancer treatment, challenges such as variability among patient responses and high costs remain.