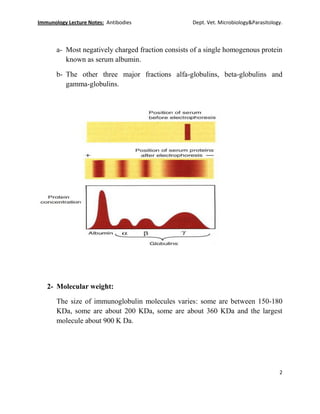
Antibodies are proteins produced by B cells and plasma cells in response to antigens. They bind specifically to antigens and help destroy or eliminate them. Antibodies form the B cell antigen receptor and are found in highest concentration in blood serum. Immunoglobulins are the proteins that have antibody activity and are classified based on their electrophoretic mobility, molecular weight, and antigenic structure. The major immunoglobulin types are IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE, which vary in size and epitope structure.