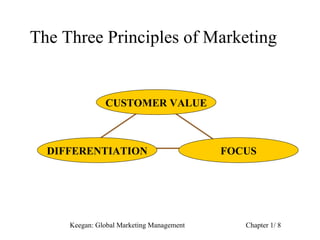
The document introduces concepts in global marketing. It discusses how marketing has evolved from a product focus to emphasizing customer value and differentiation. It also outlines three principles of marketing: creating customer value, differentiation, and focus. Additionally, it examines management orientations in global marketing and driving and restraining forces that impact global integration and marketing.