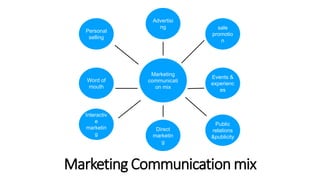
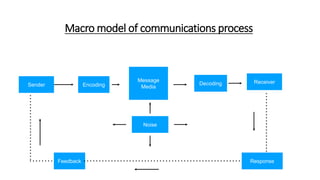
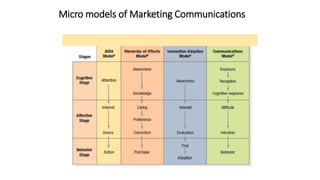
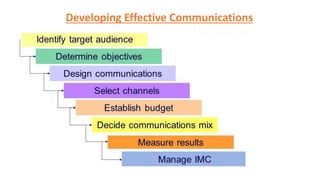
This document discusses marketing communications and developing effective communications. It begins by defining marketing communications and noting how integrated marketing played a role in the success of the movie 3 Idiots. It then discusses the marketing communications mix and various channels including advertising, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, and more. The document outlines models of the communications process including the macro and micro models. It emphasizes the importance of identifying the target audience and setting objectives. It also provides guidance on designing communications through message strategy, creative strategy, and selecting a message source and channels. The document concludes by discussing measuring communication results and integrated marketing communication.