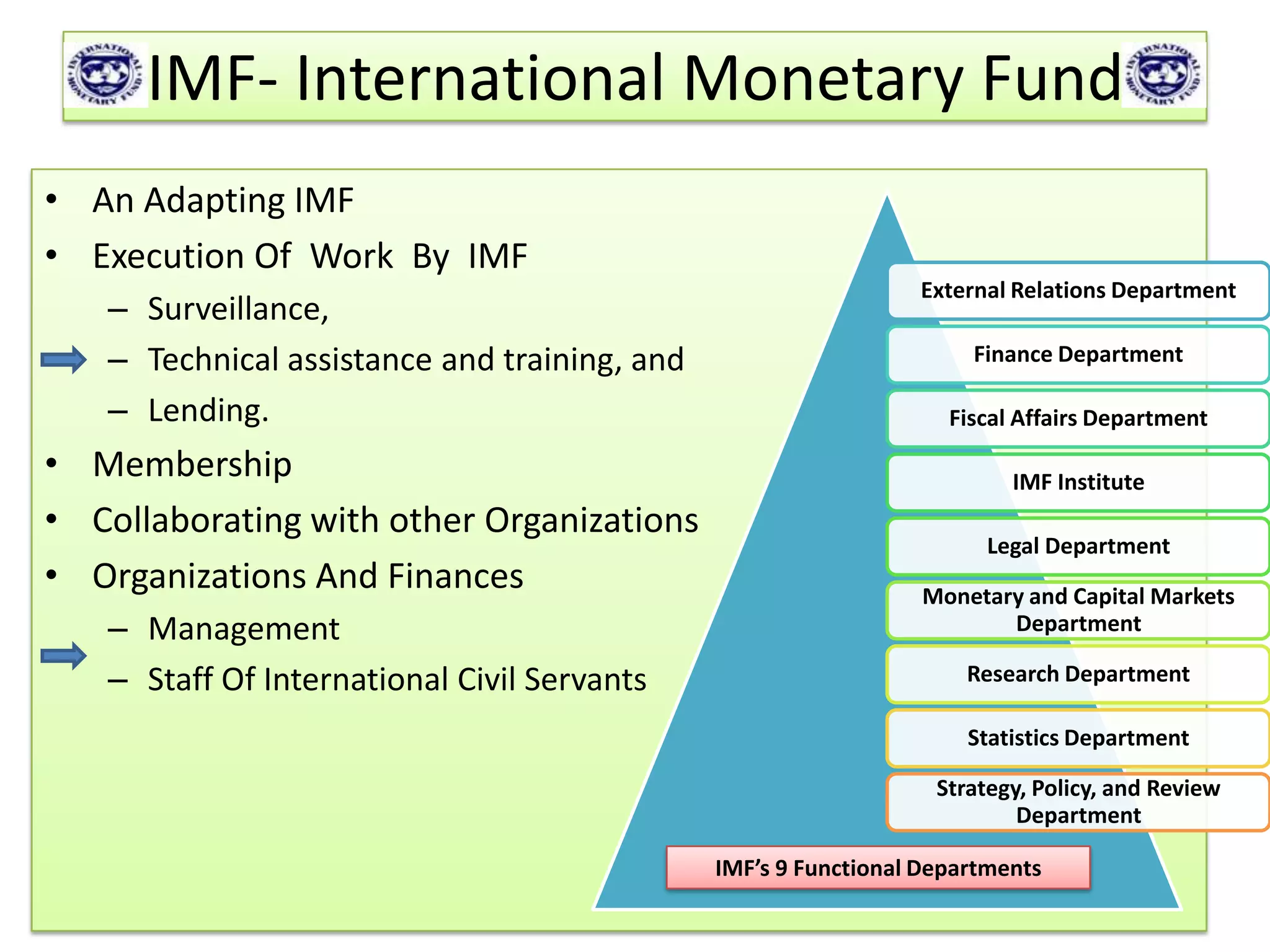
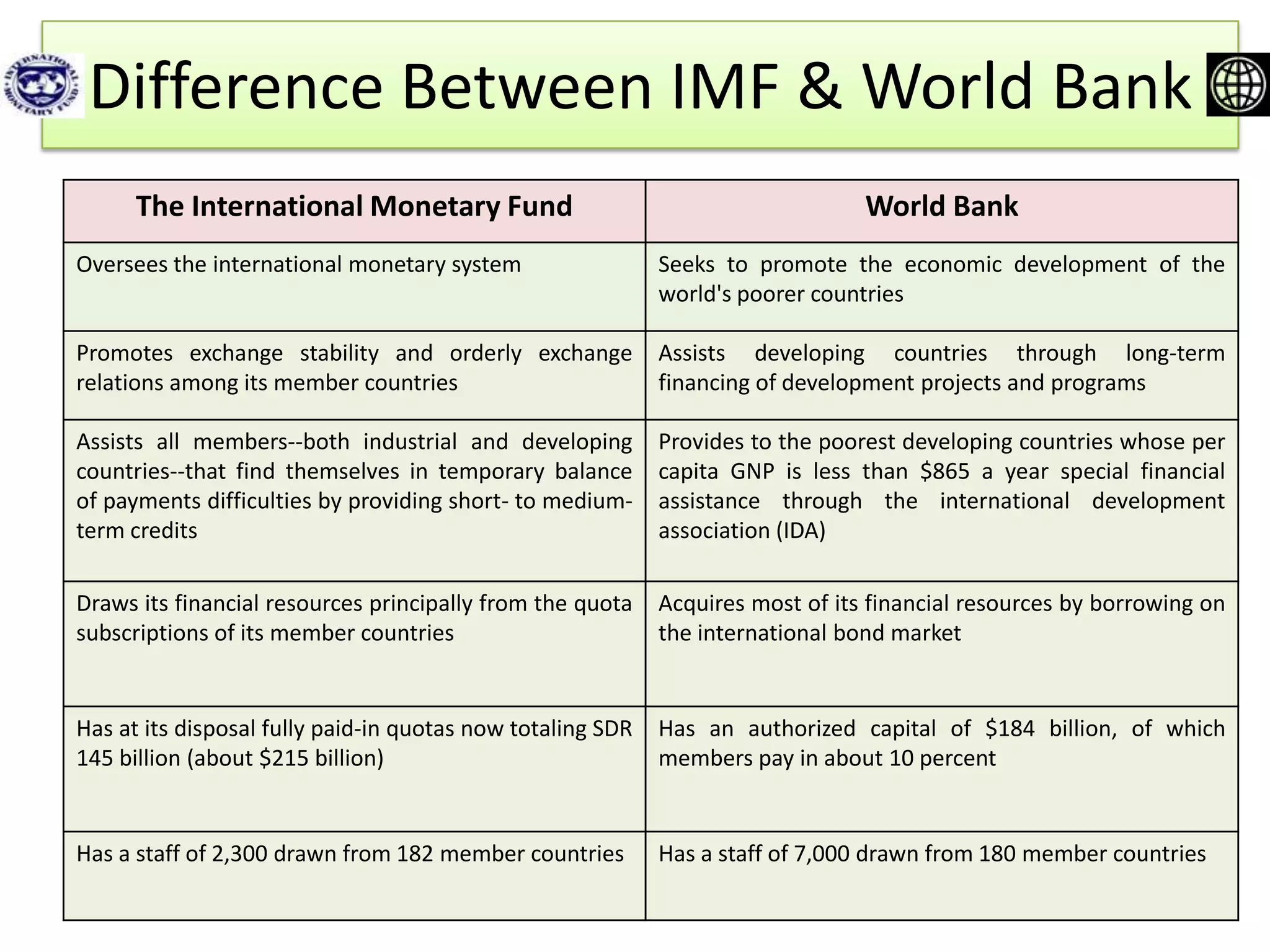
The document summarizes information about the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank. The IMF tracks global economic trends and provides financing and policy advice to member countries. Its goals are to promote financial stability, international trade, and economic growth. The World Bank provides long-term loans and financing to developing countries for capital programs and development projects, with the goal of reducing poverty. Key differences are that the IMF focuses on short-term balance of payments issues while the World Bank concentrates on long-term economic development projects.