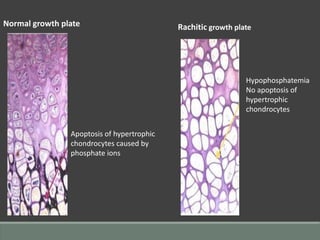
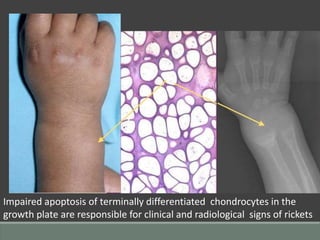
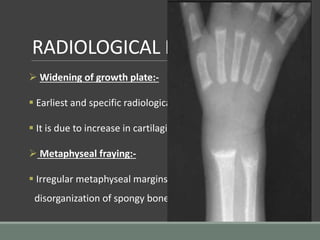
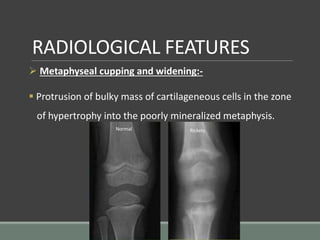
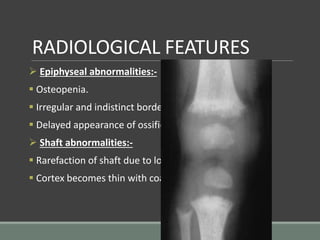
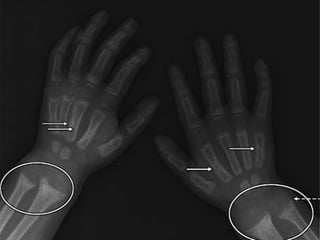
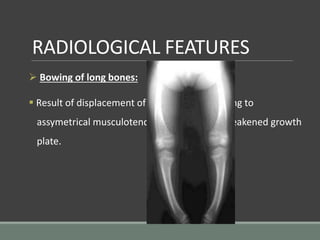
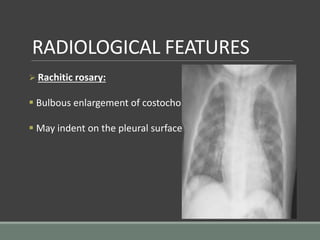
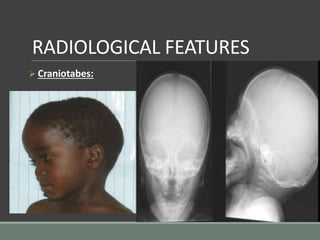
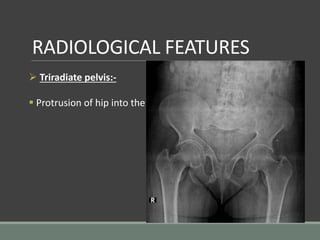
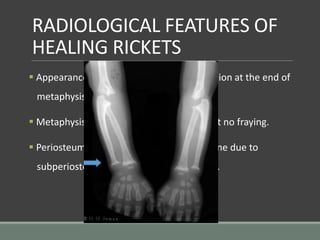
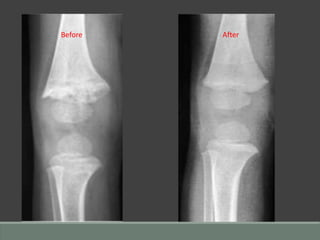
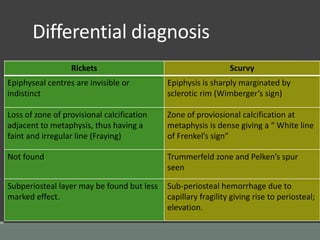
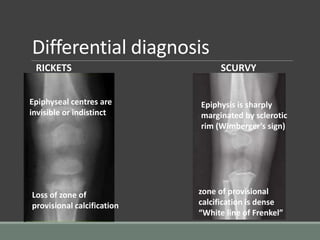
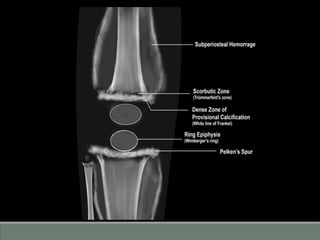
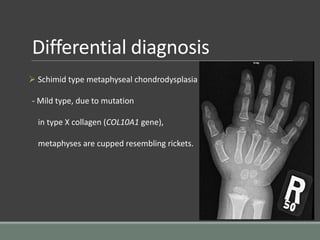
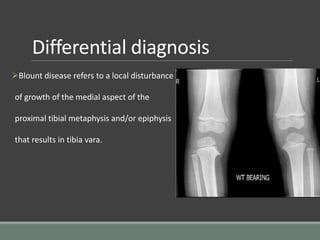
The document discusses rickets, a metabolic disease in children that leads to soft bones and skeletal deformities due to impaired mineralization. It details the patho-radiological features, characteristic radiological signs such as widening of the growth plate and metaphyseal fraying, and the differential diagnosis including conditions like scurvy and Blount disease. The document also describes the features of healing rickets and the specific changes observed in various regions of the skeleton.