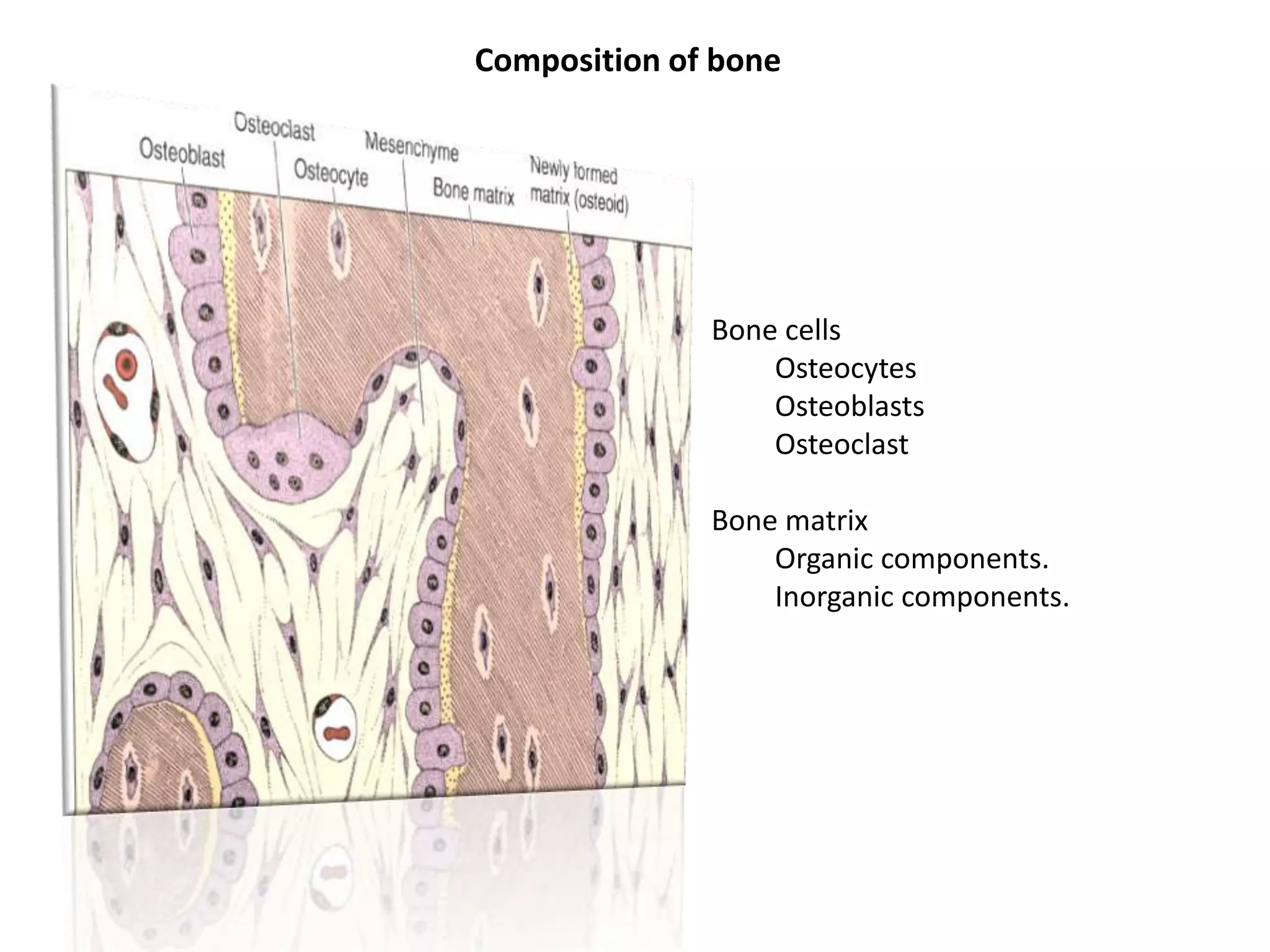
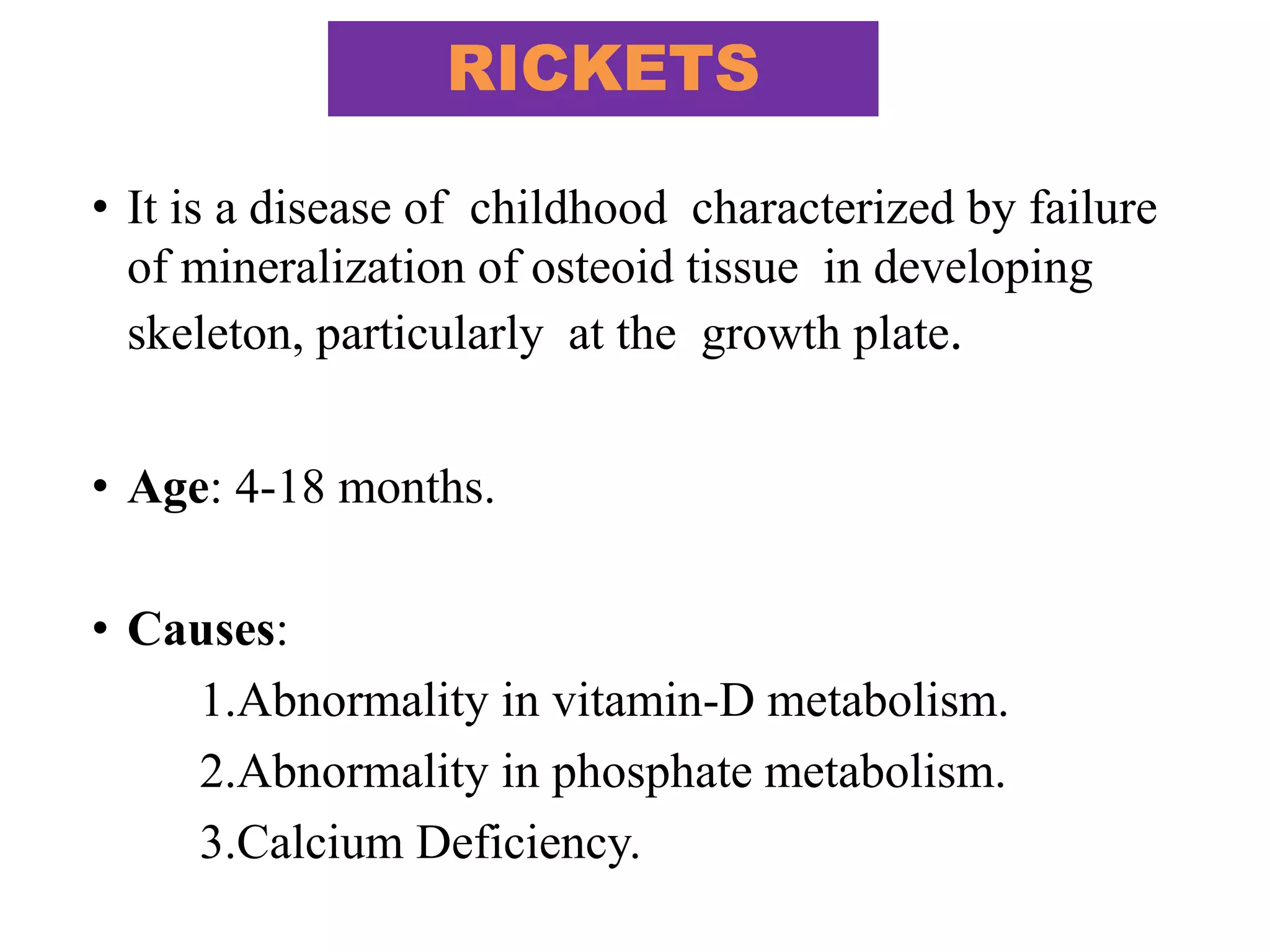
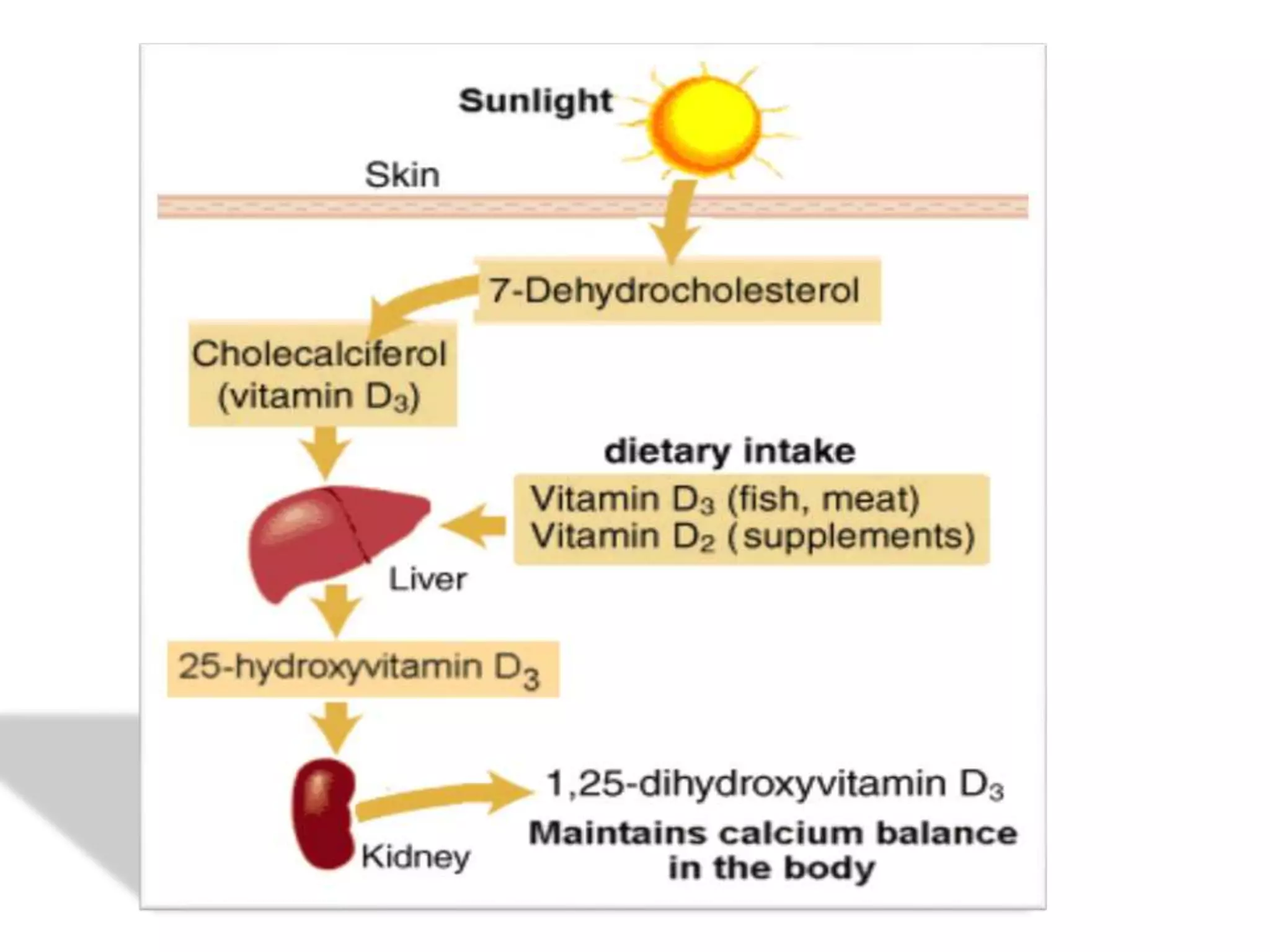
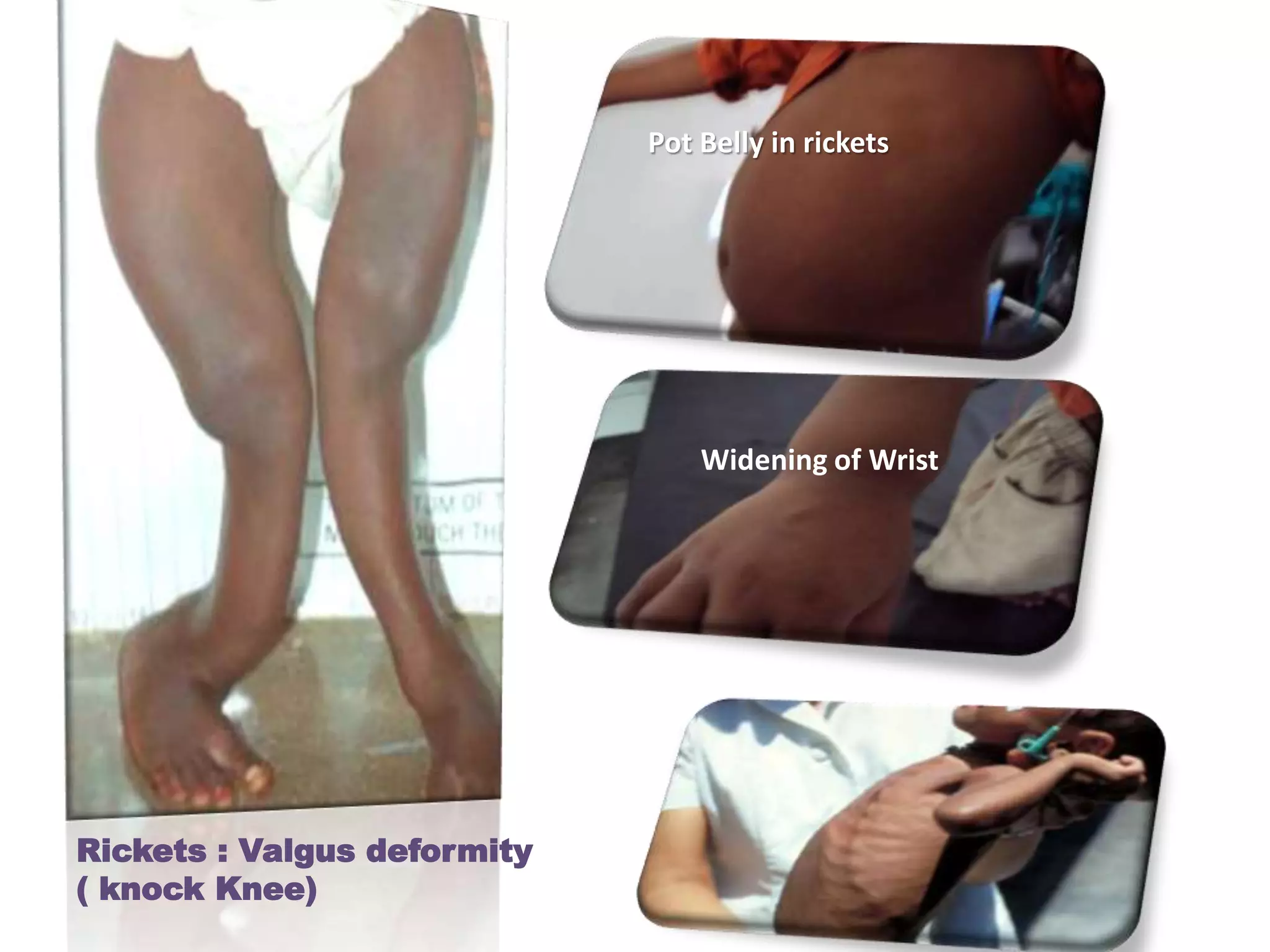
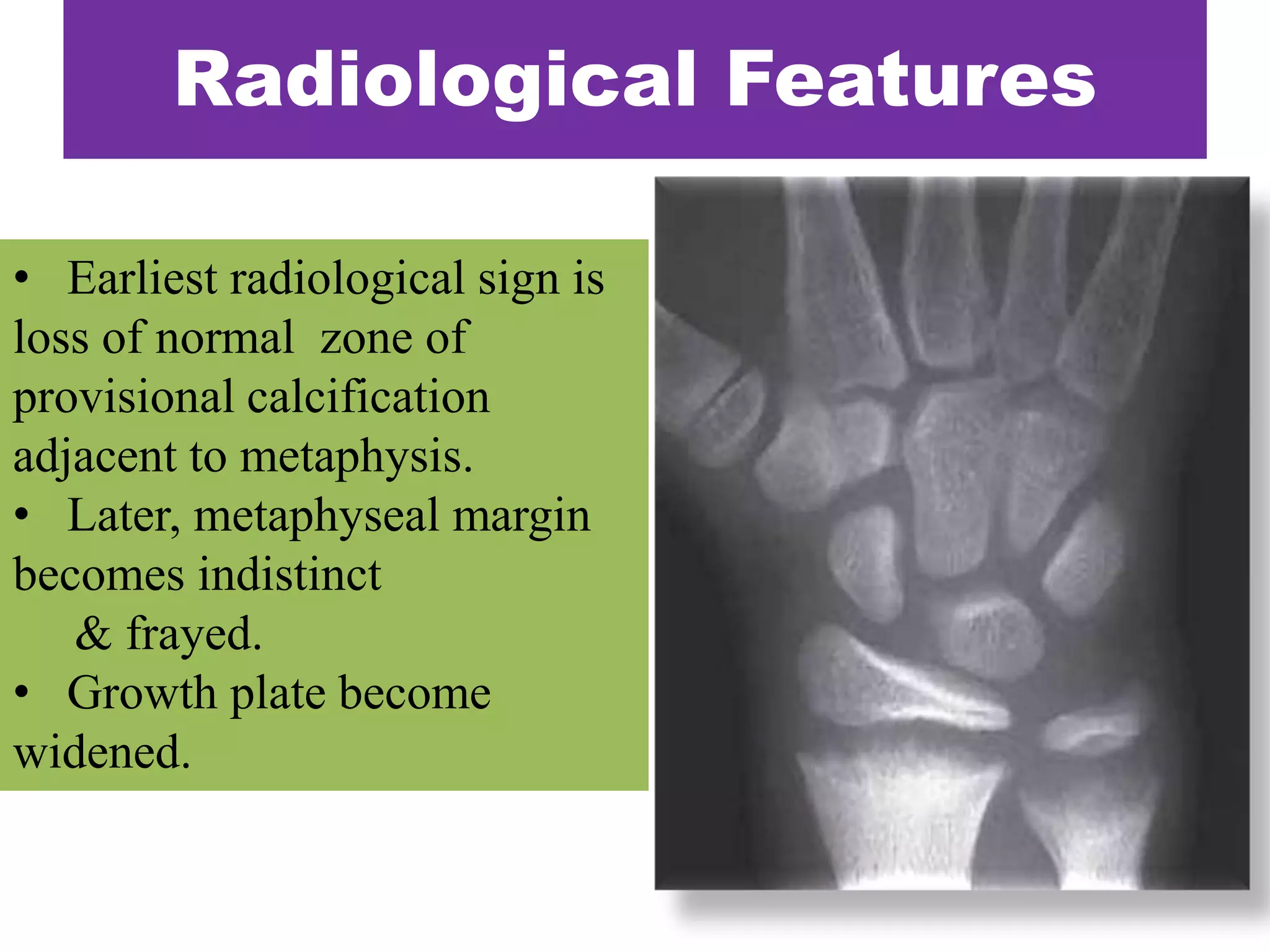
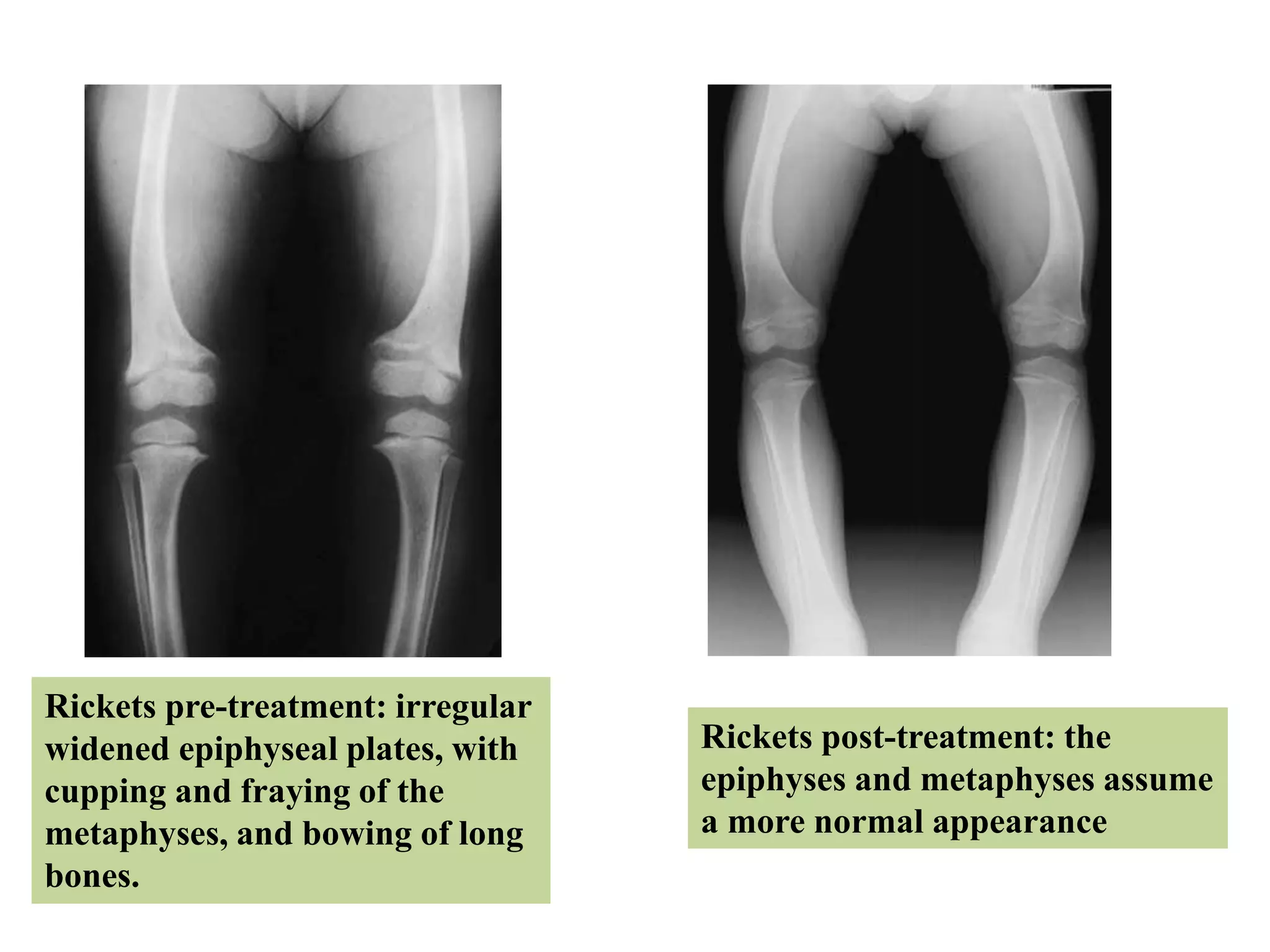
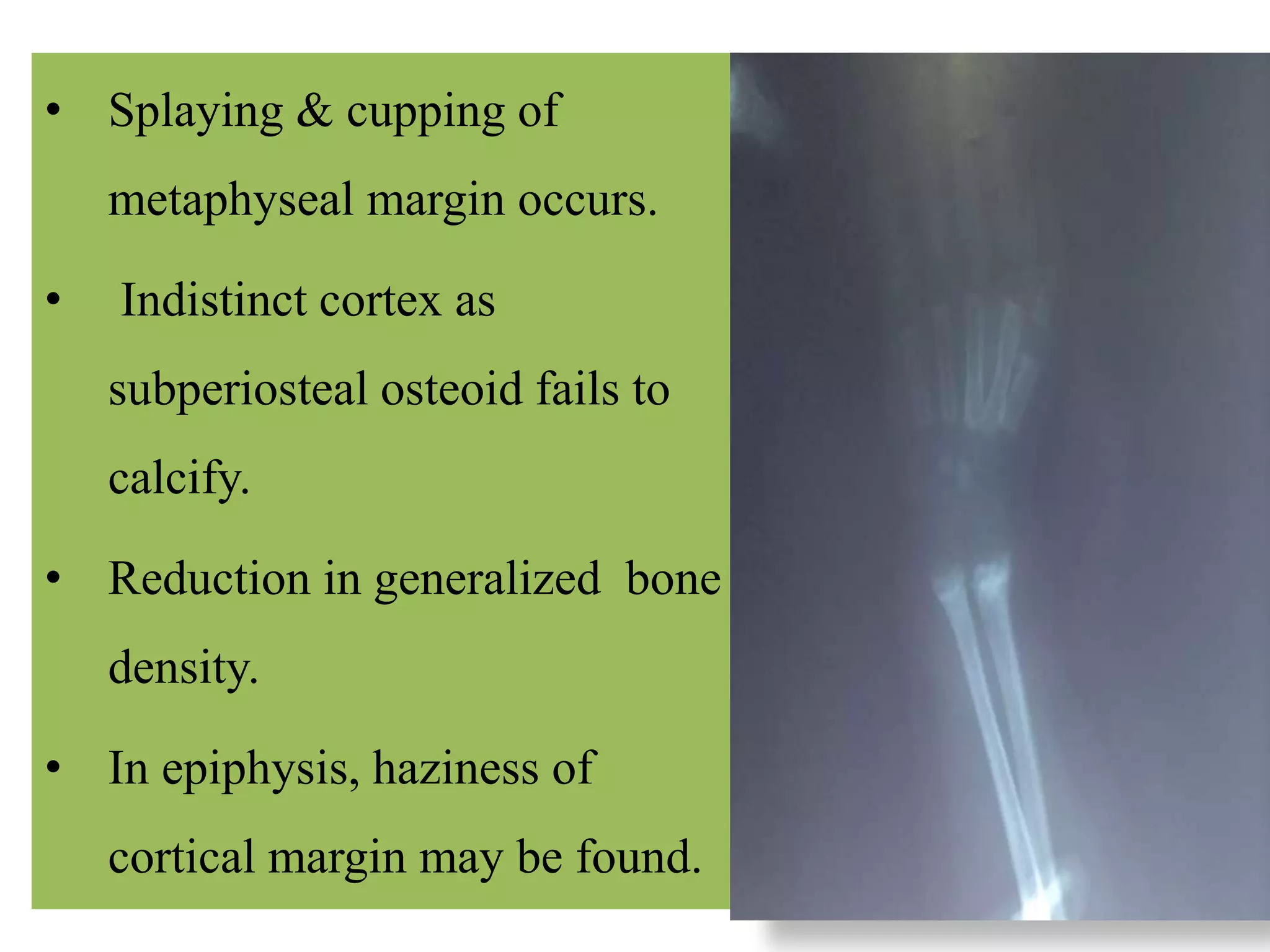
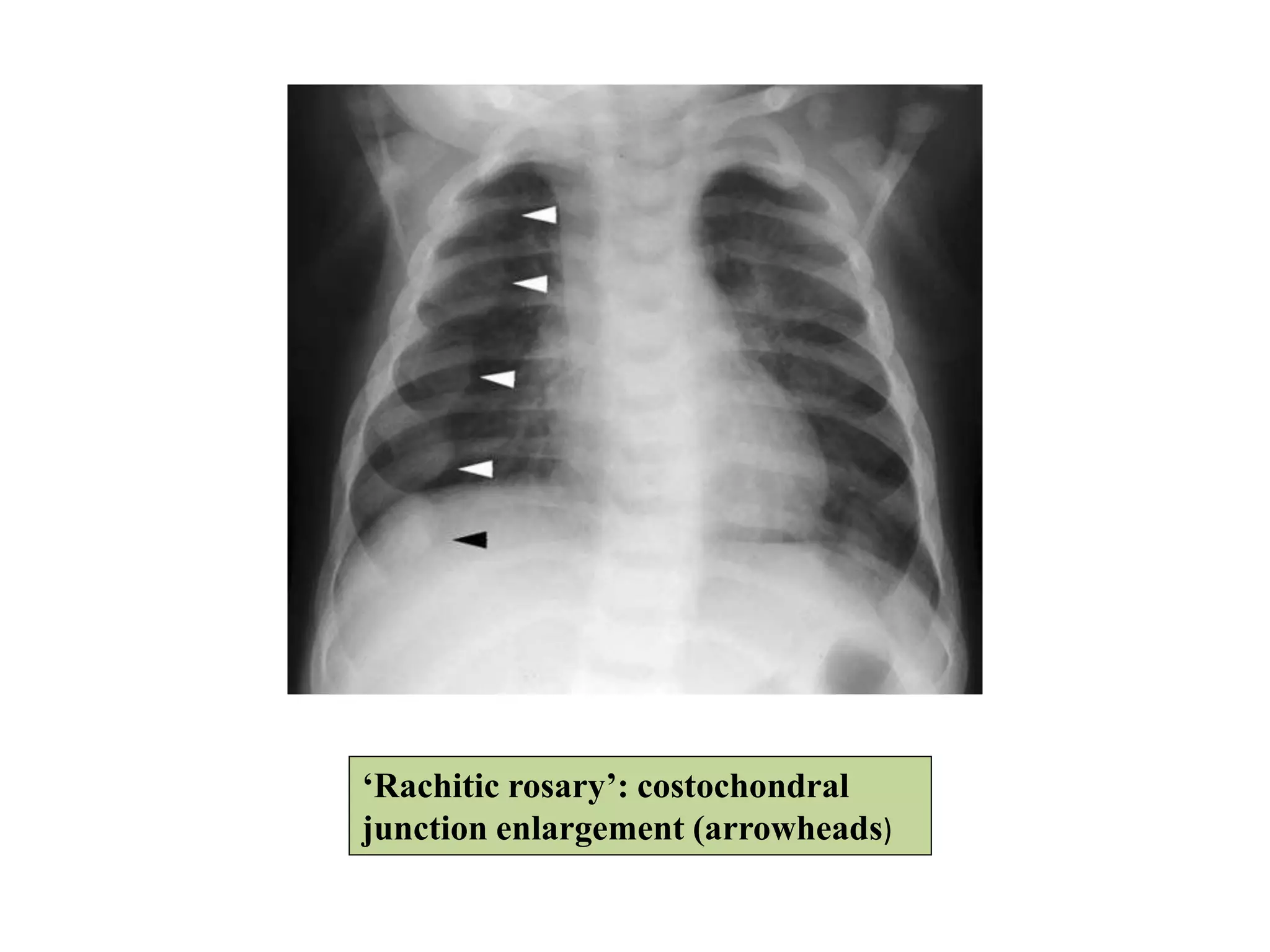
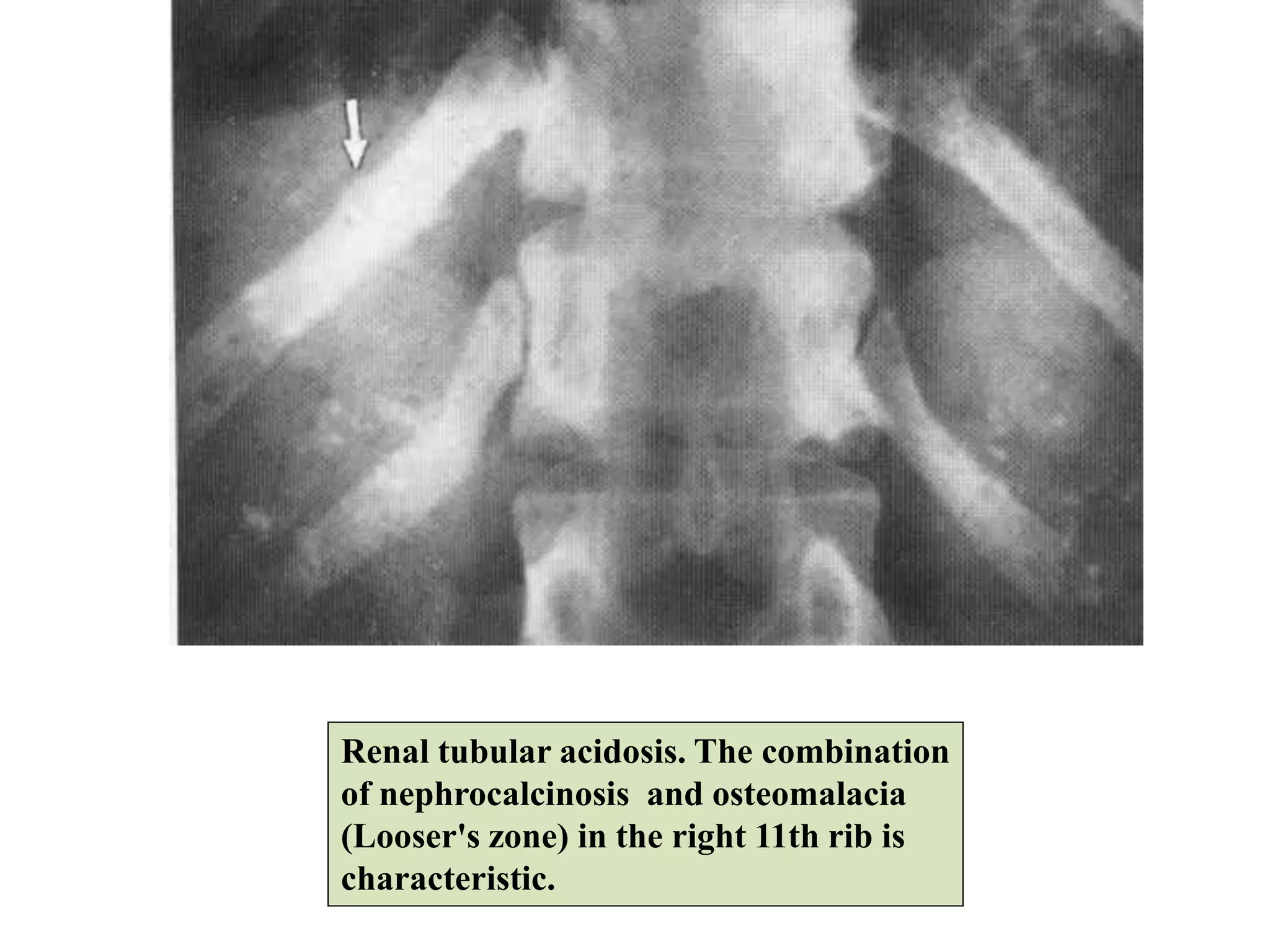
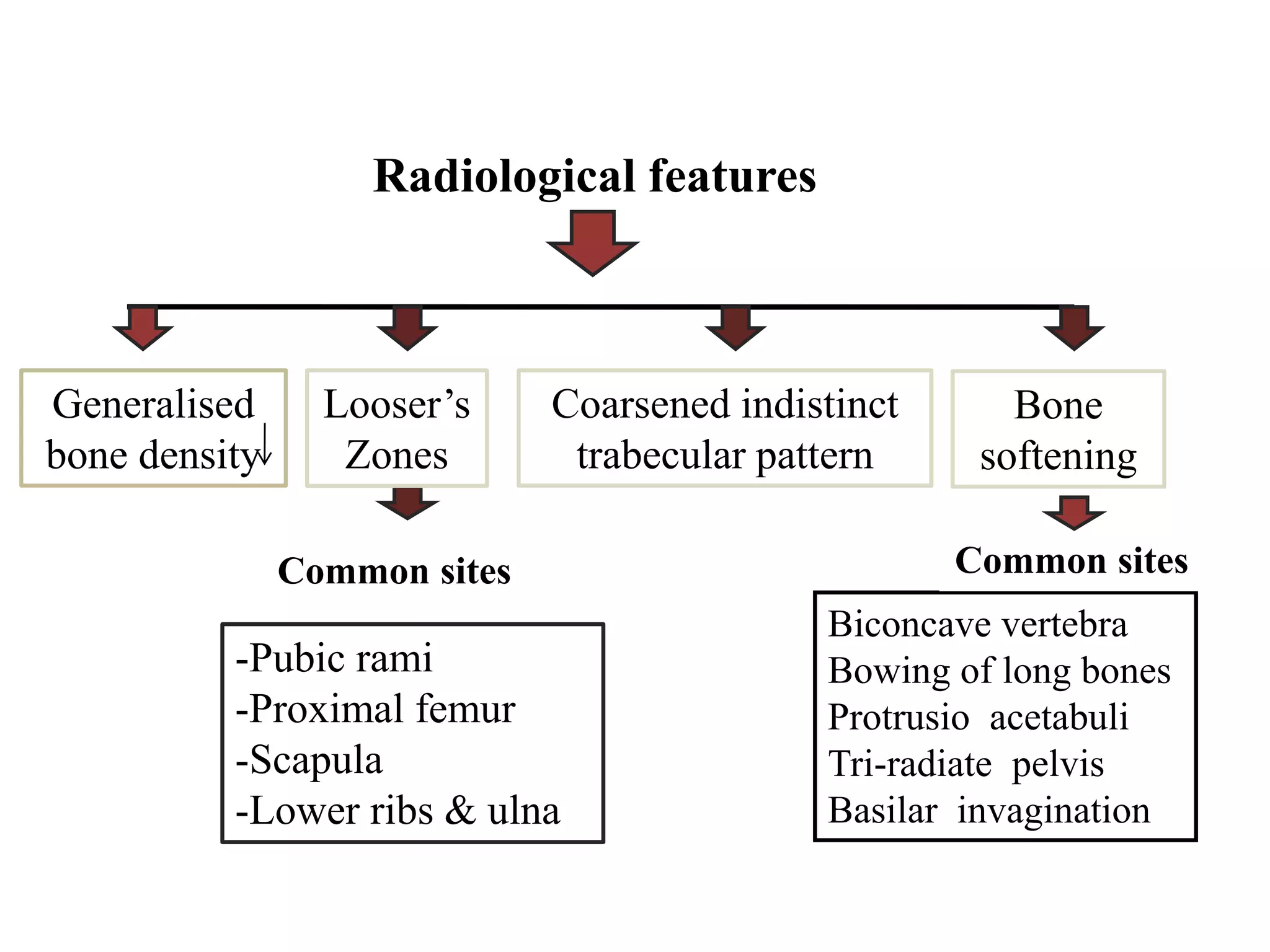
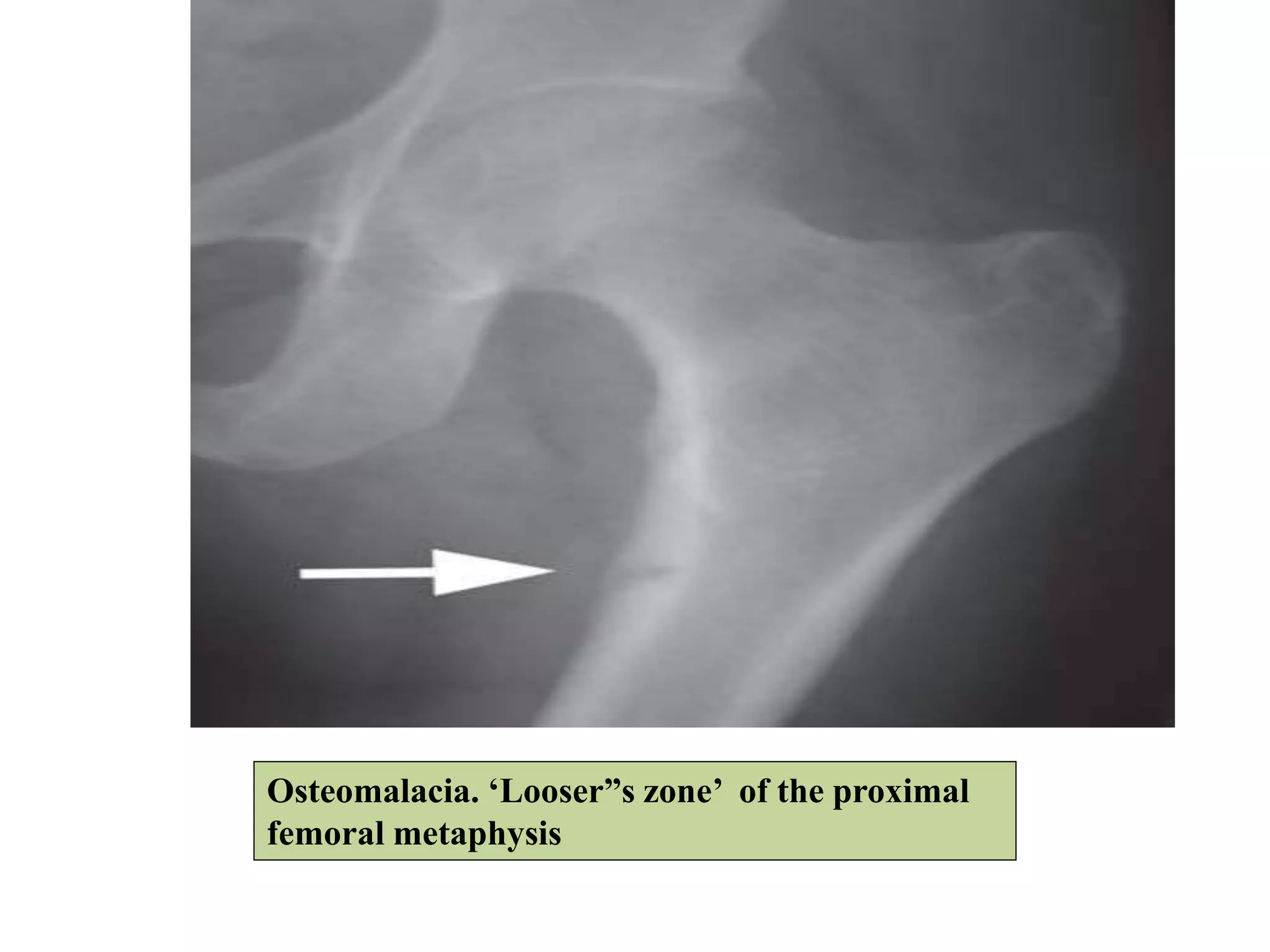
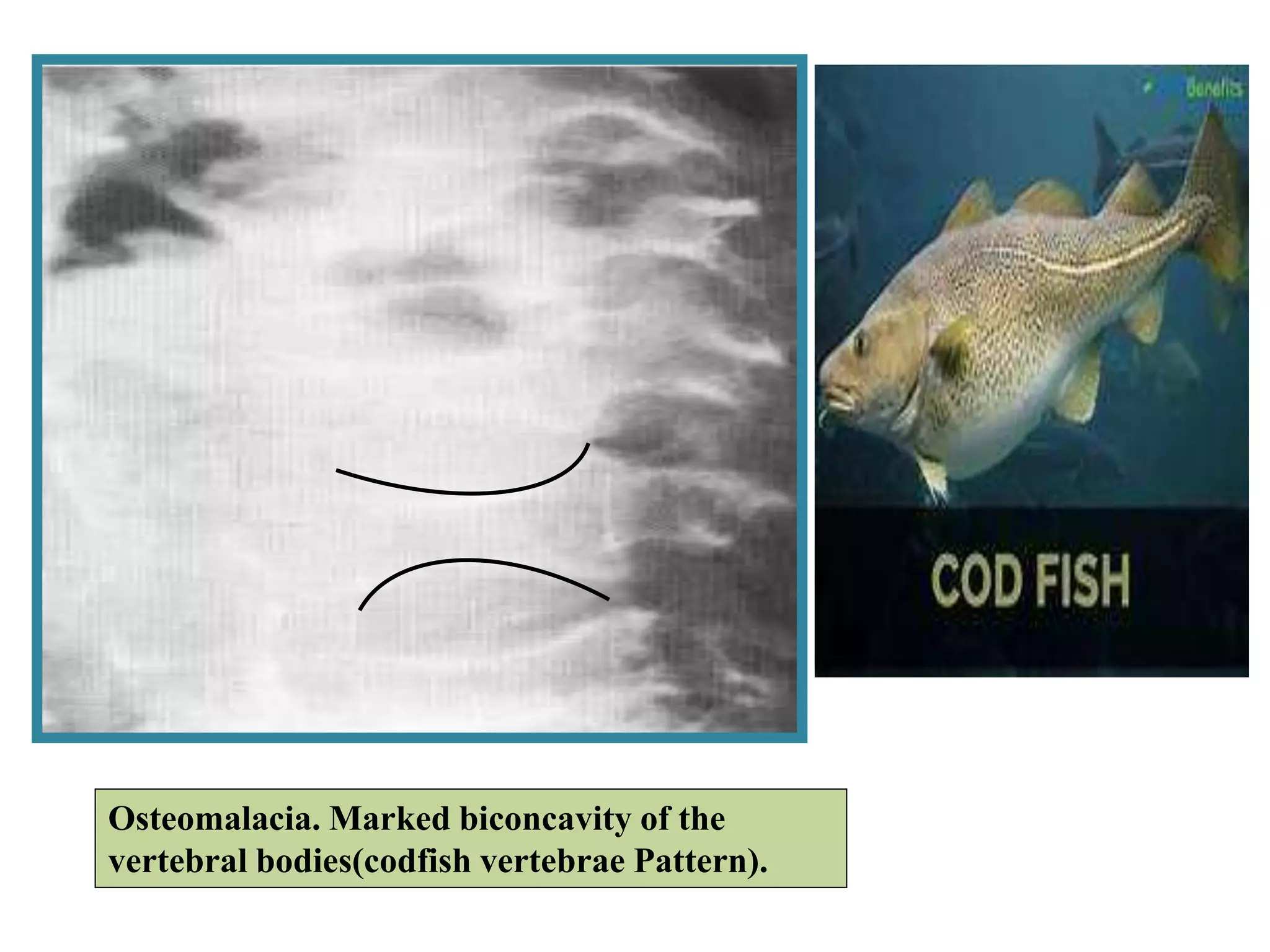
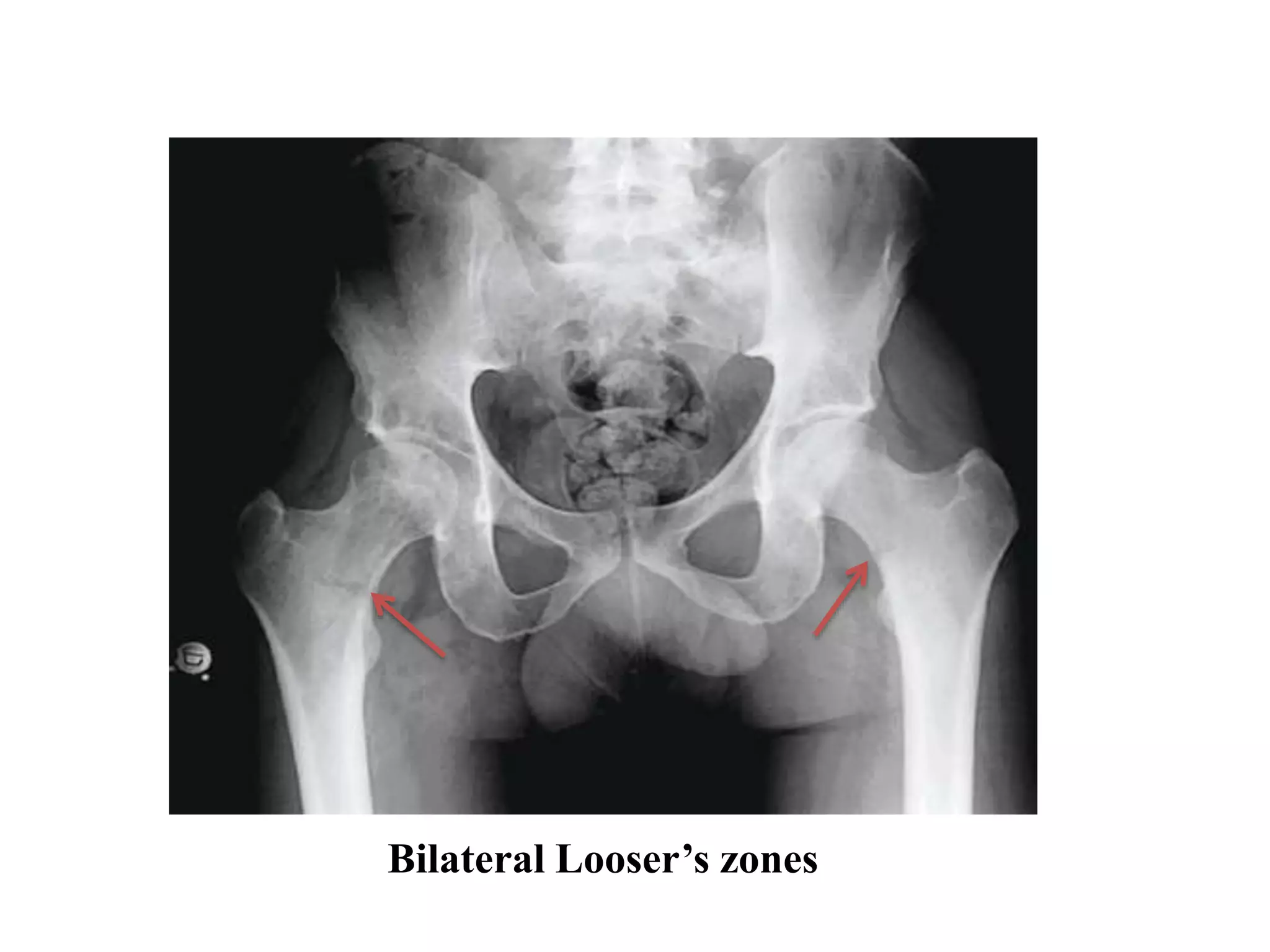
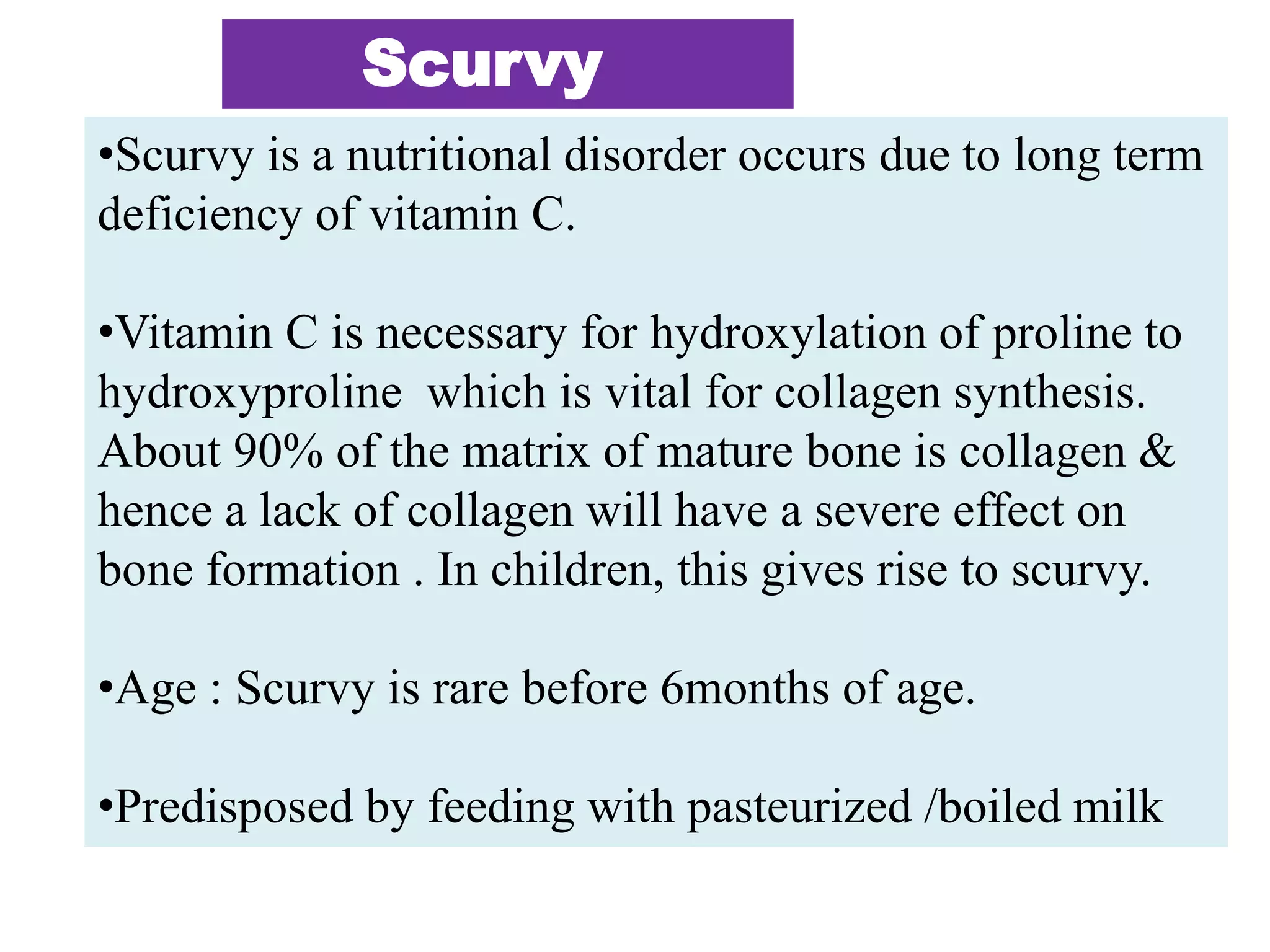
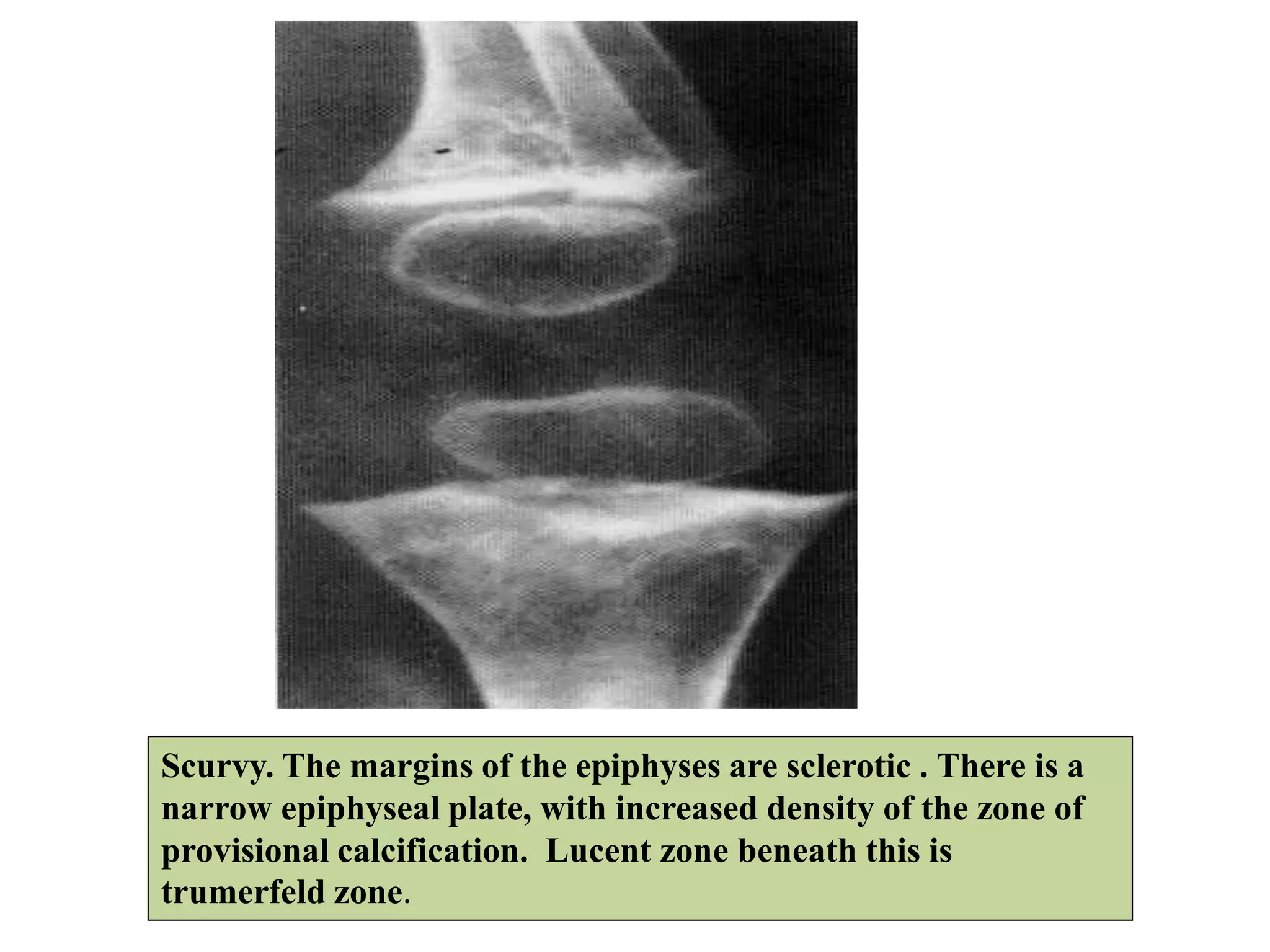
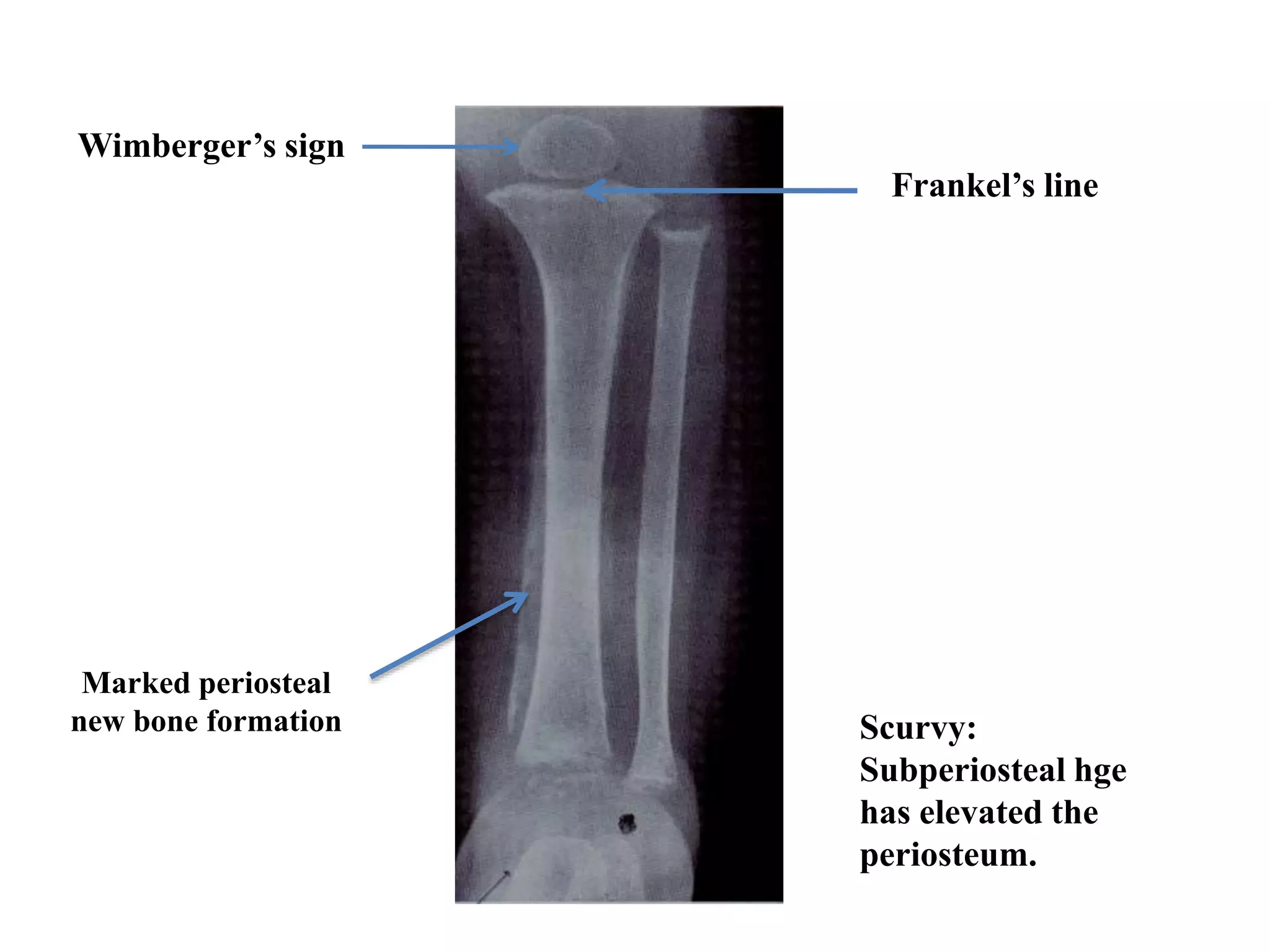
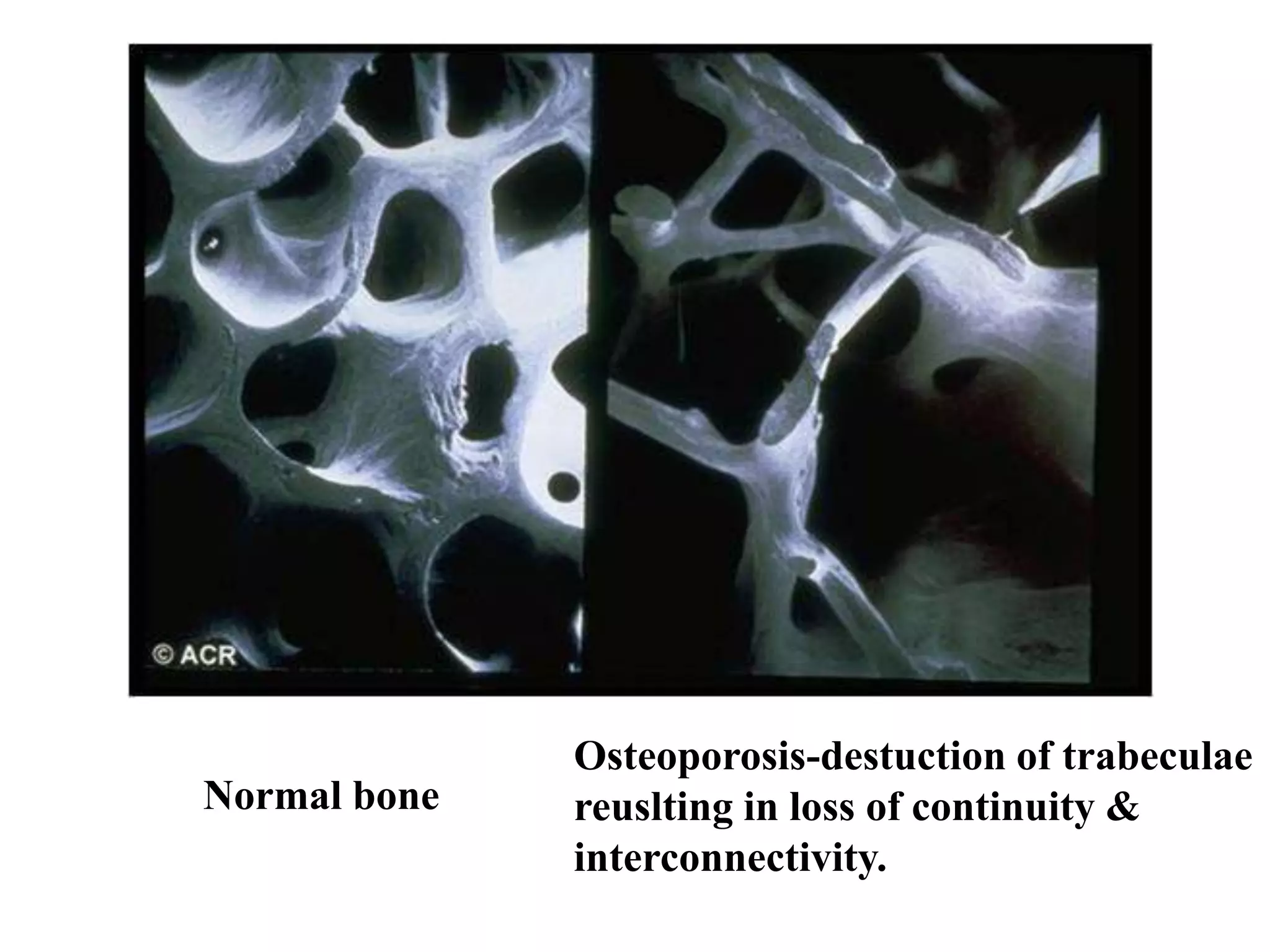
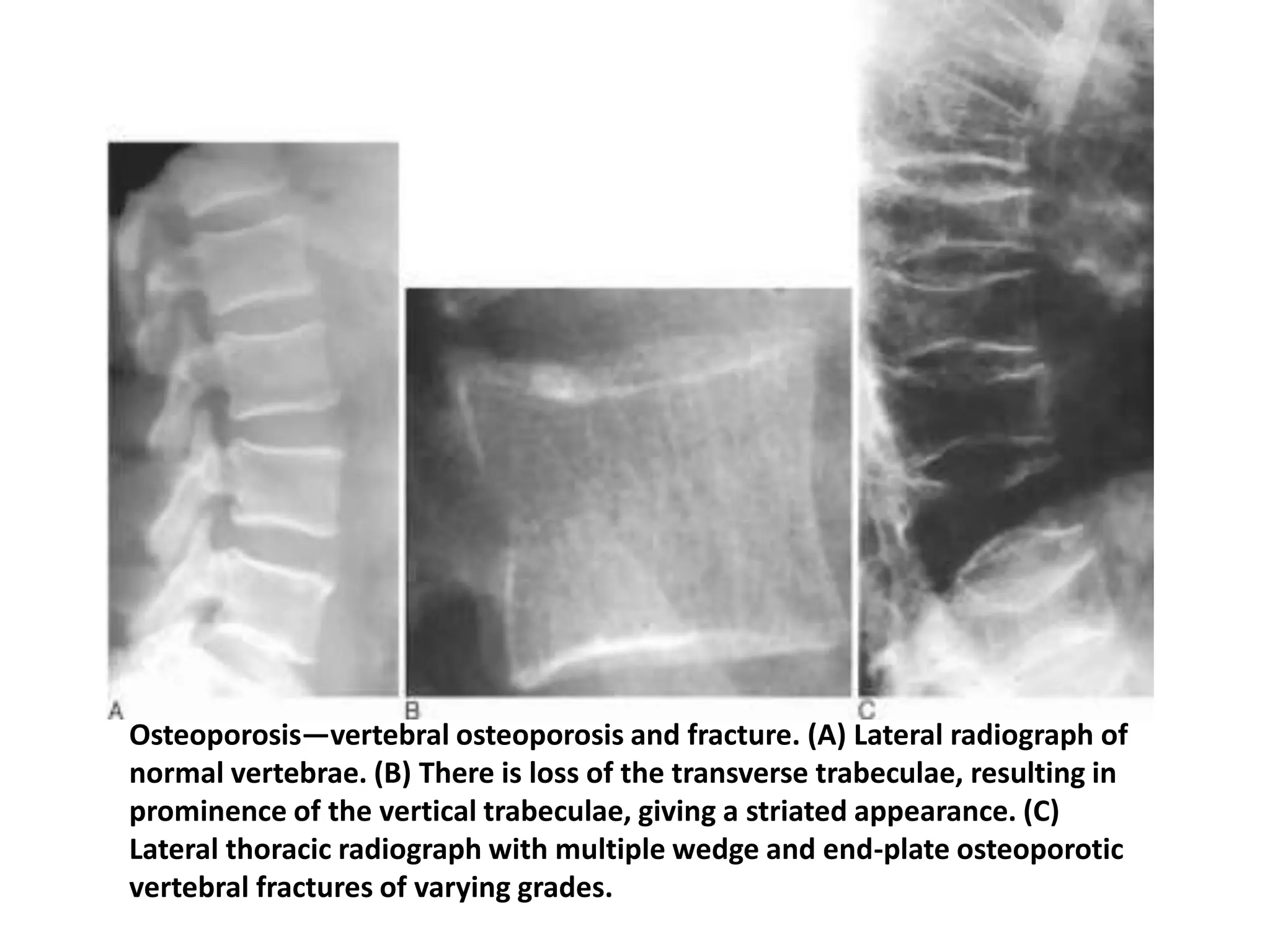
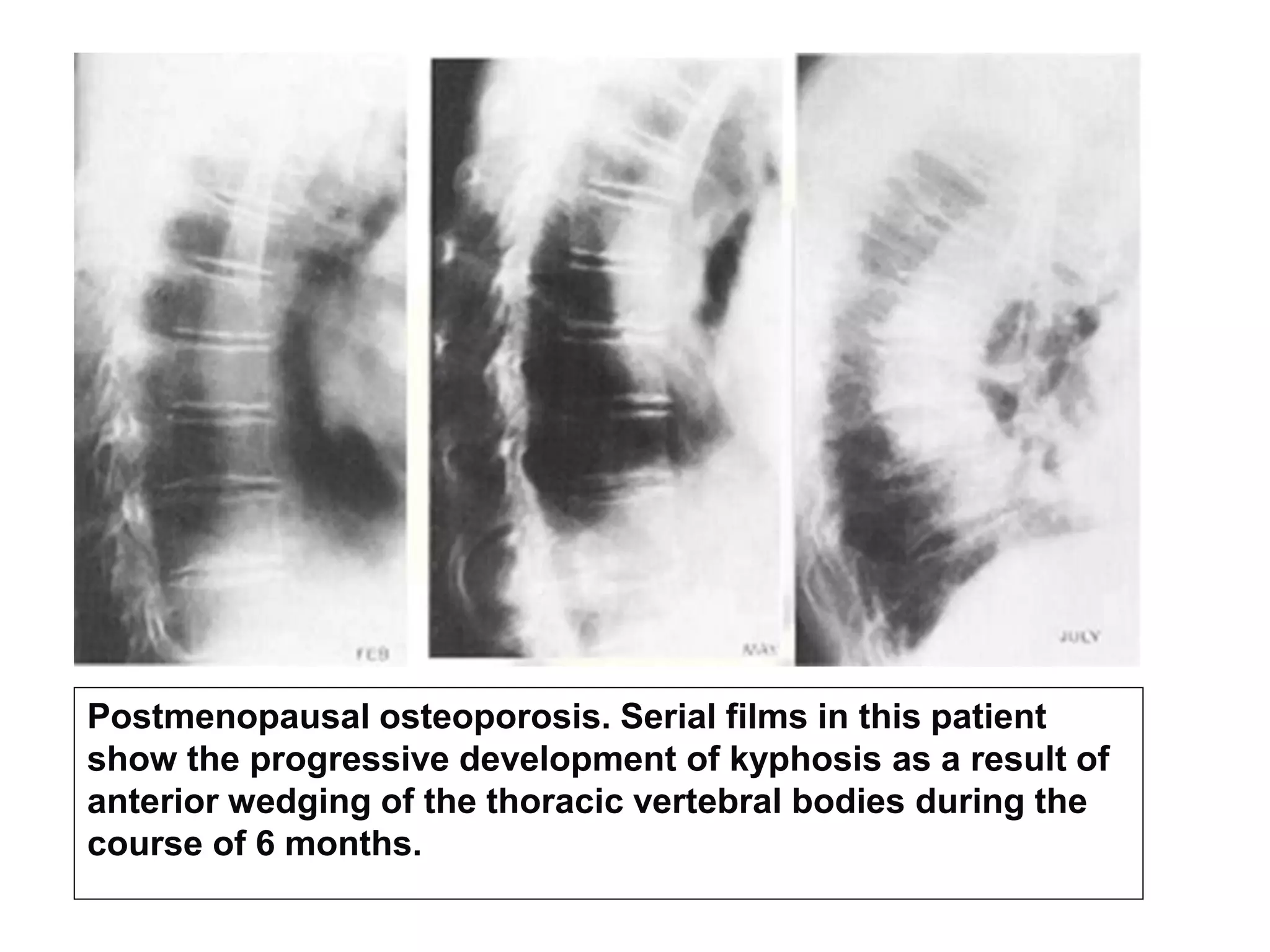
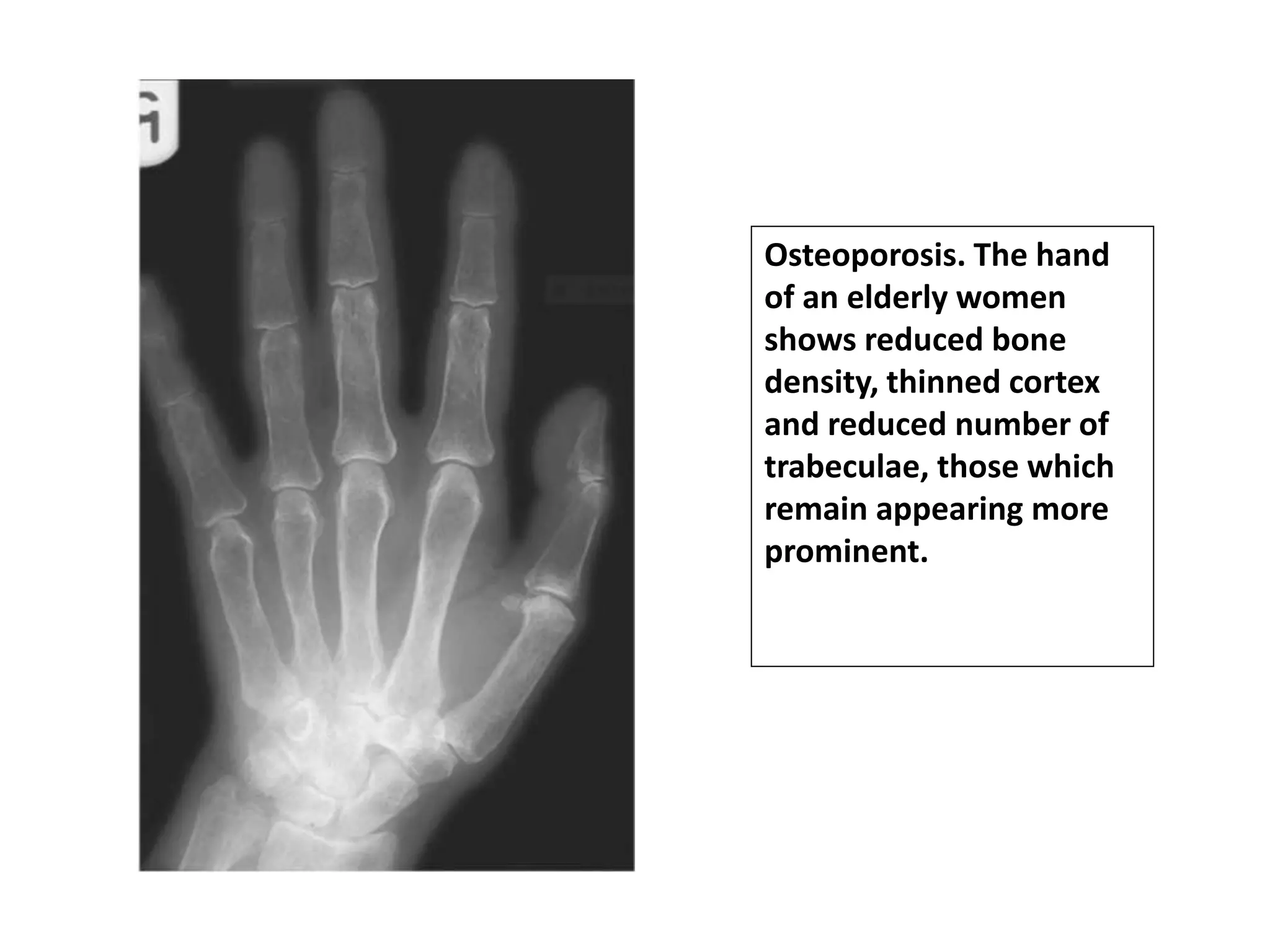
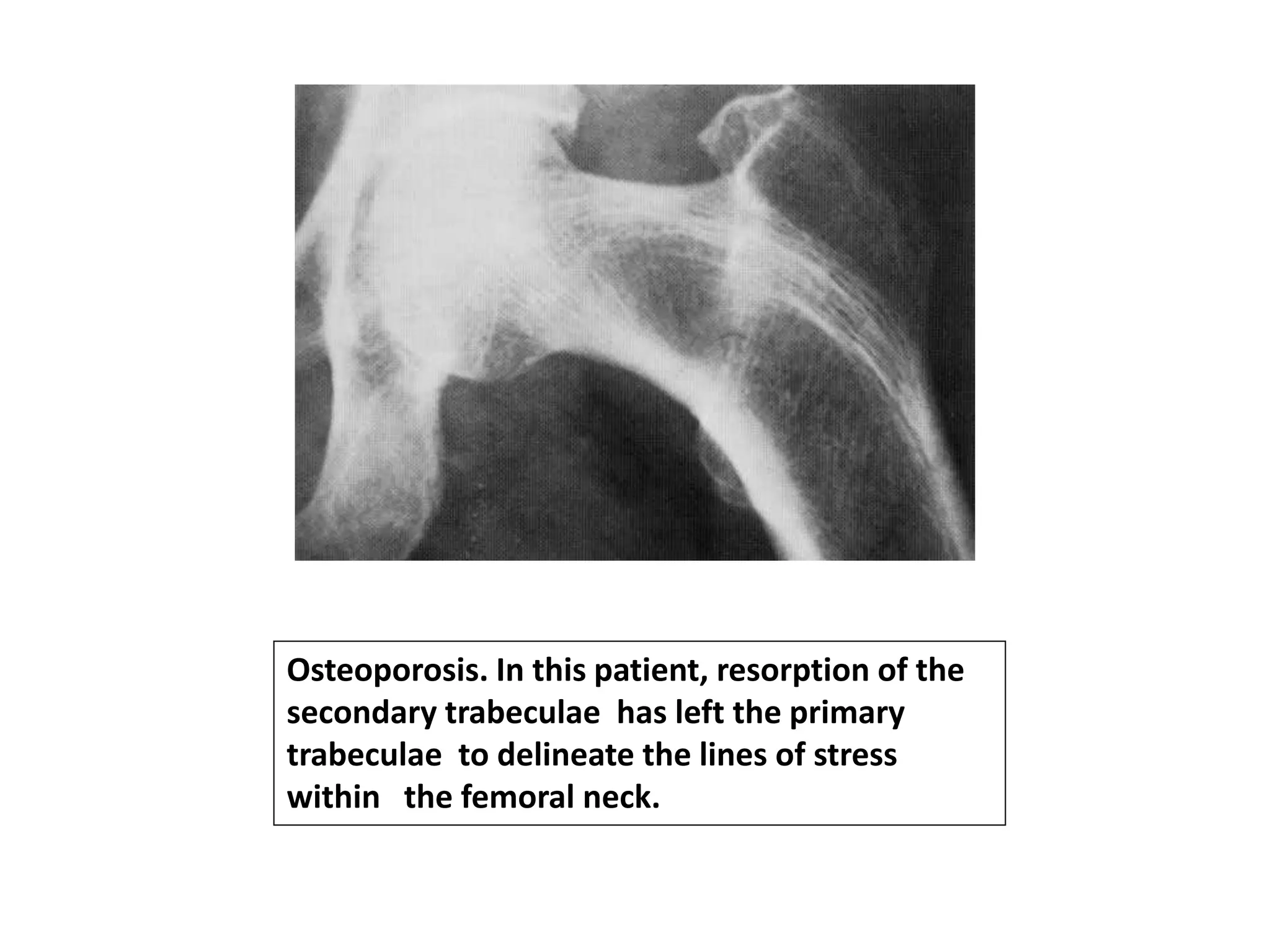
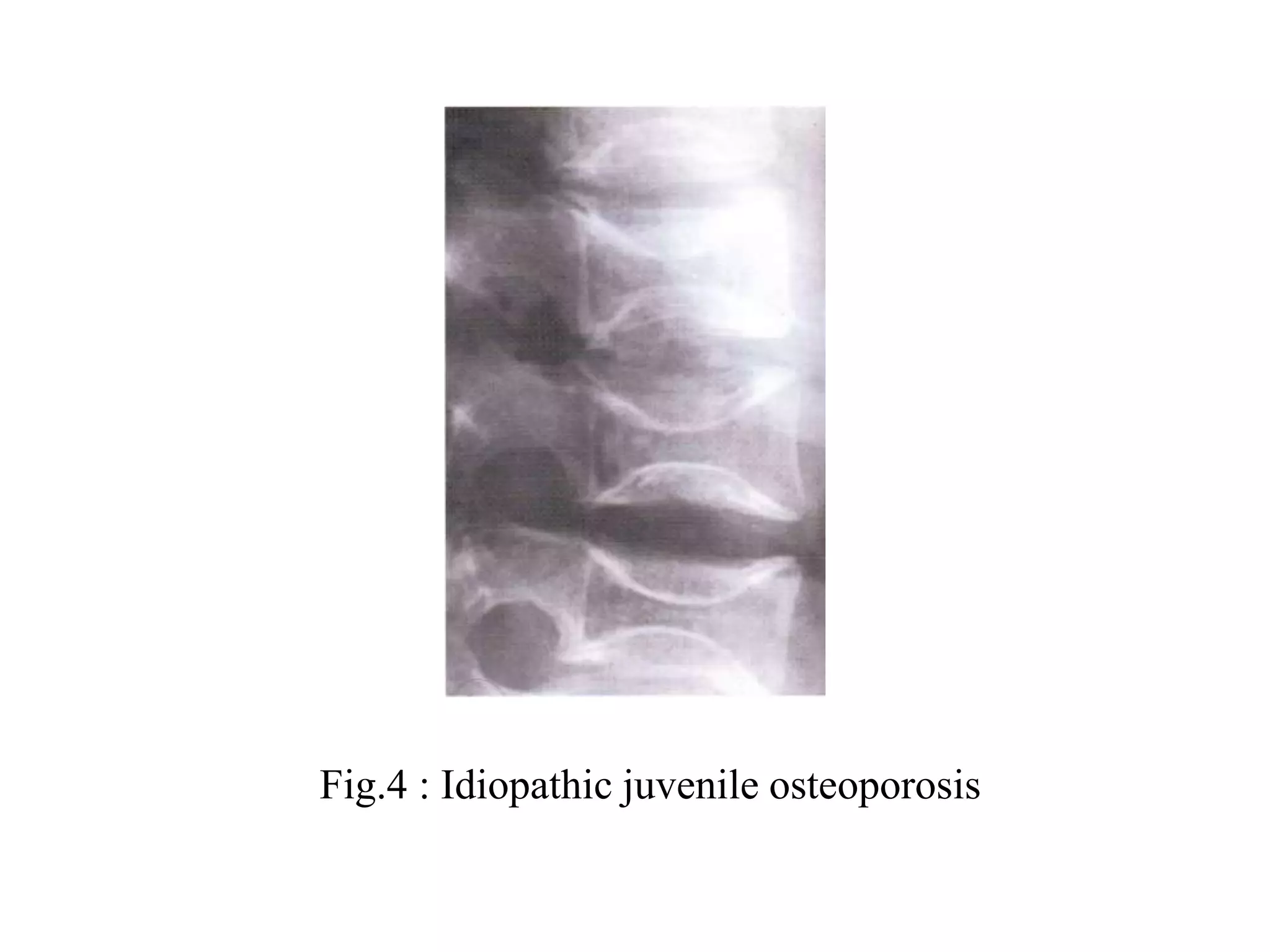
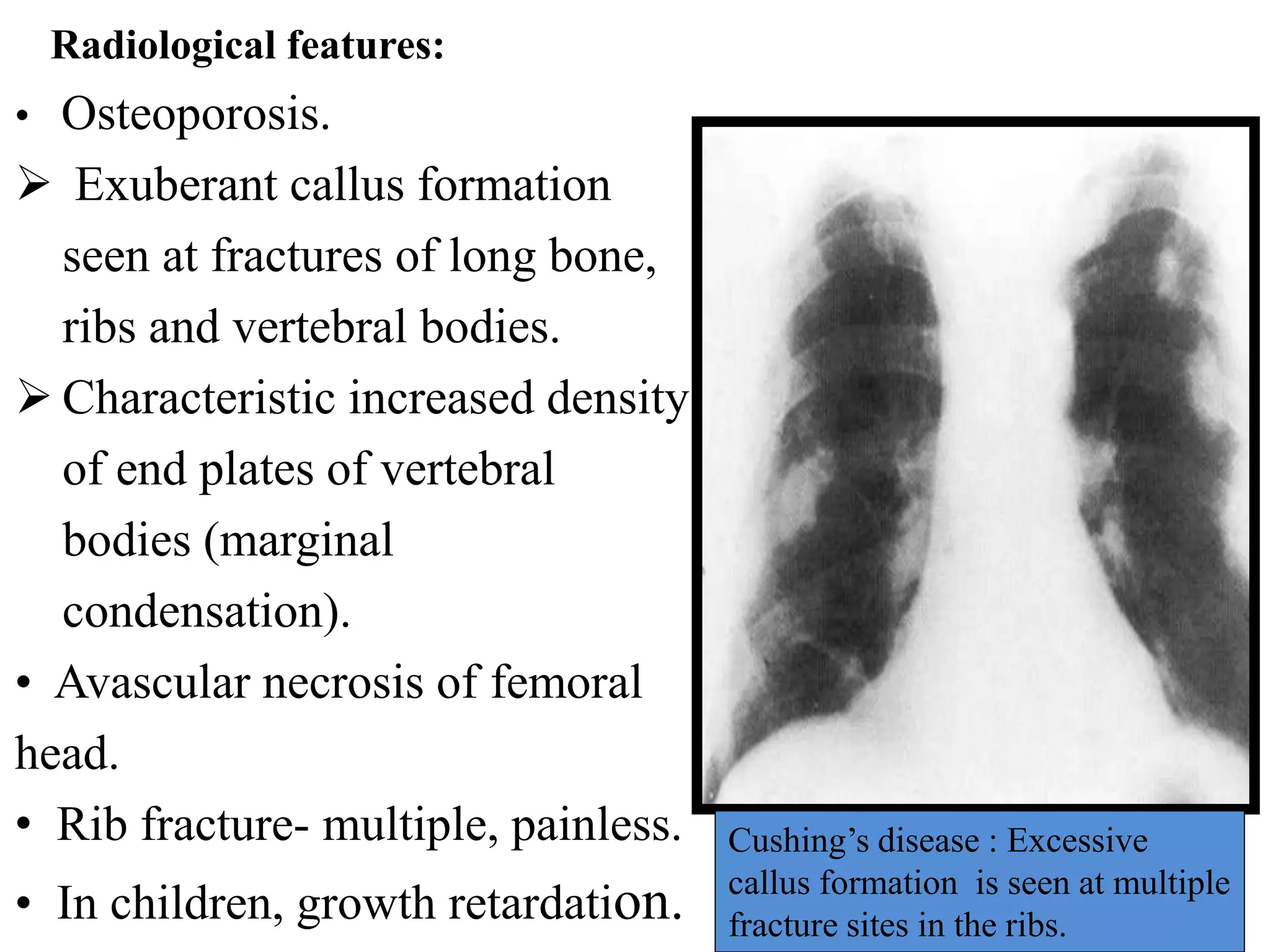
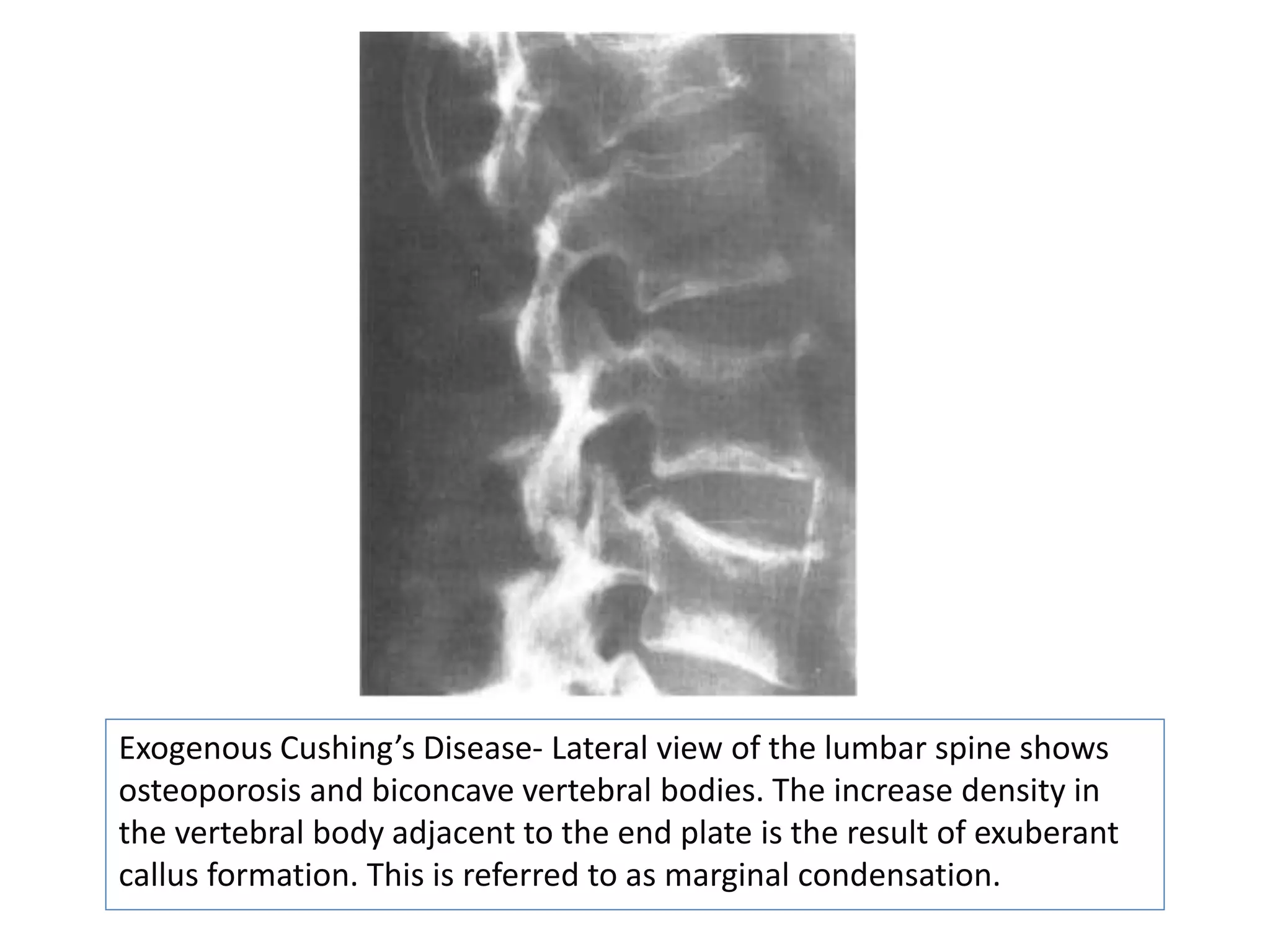
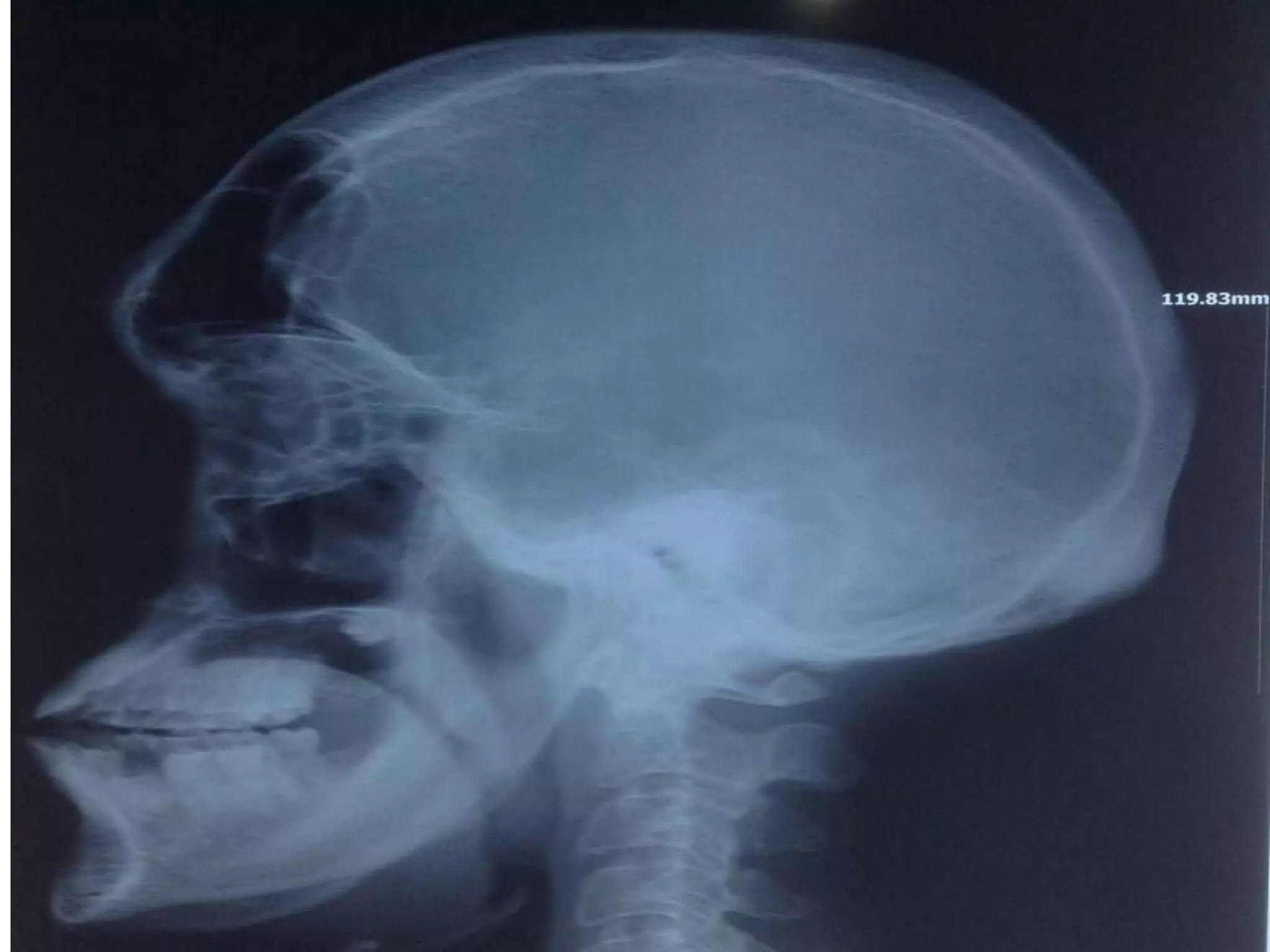
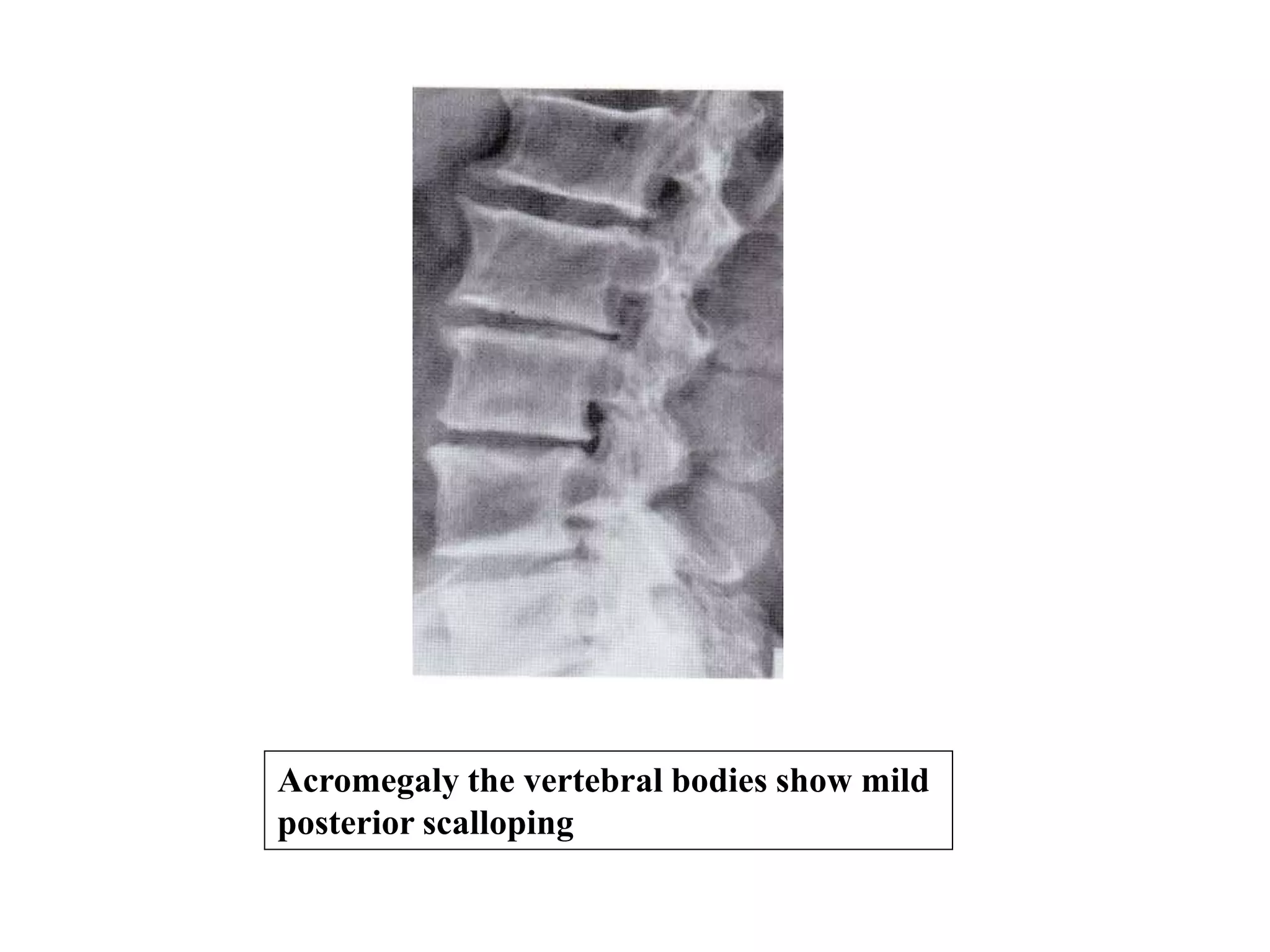
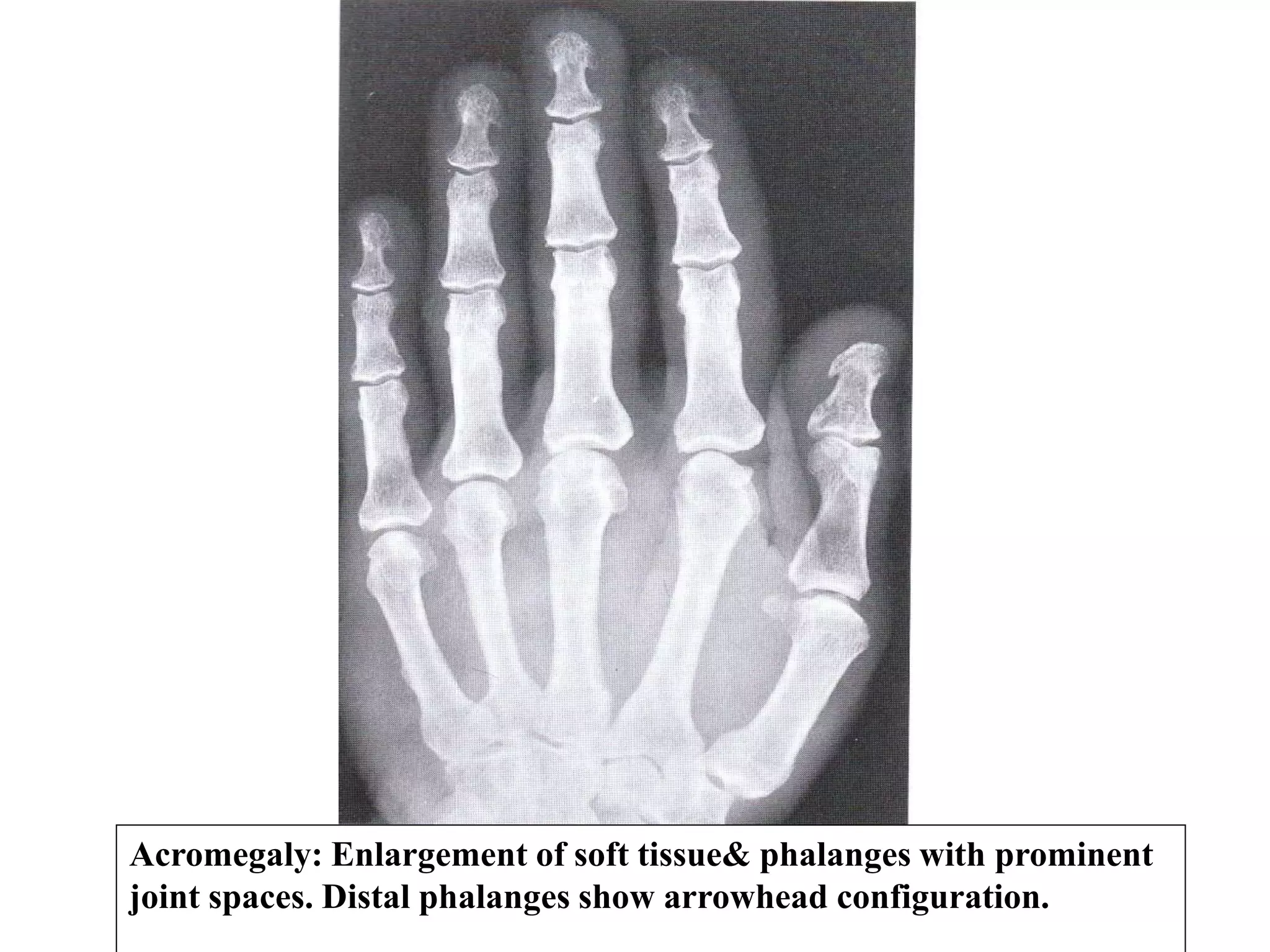
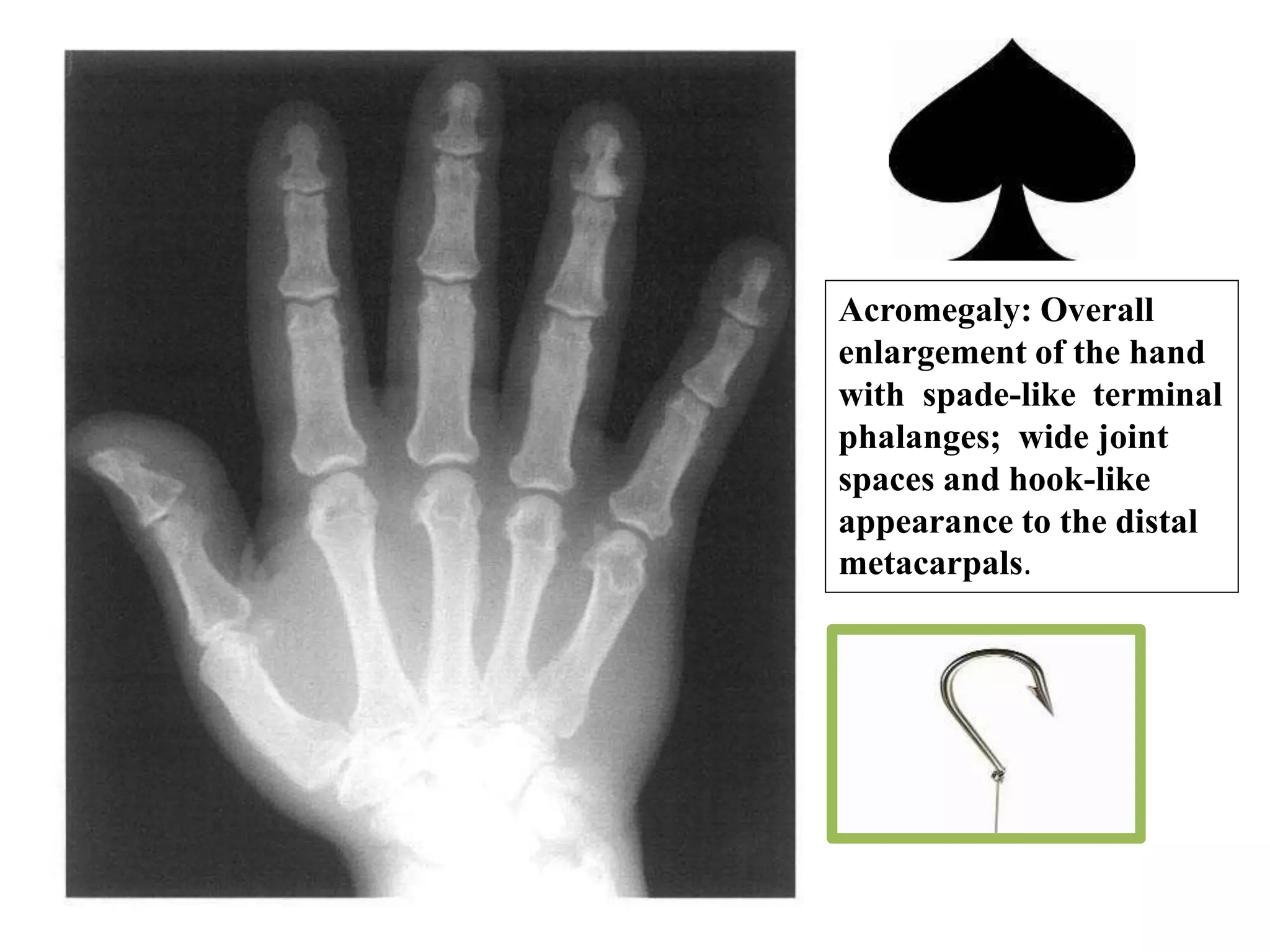
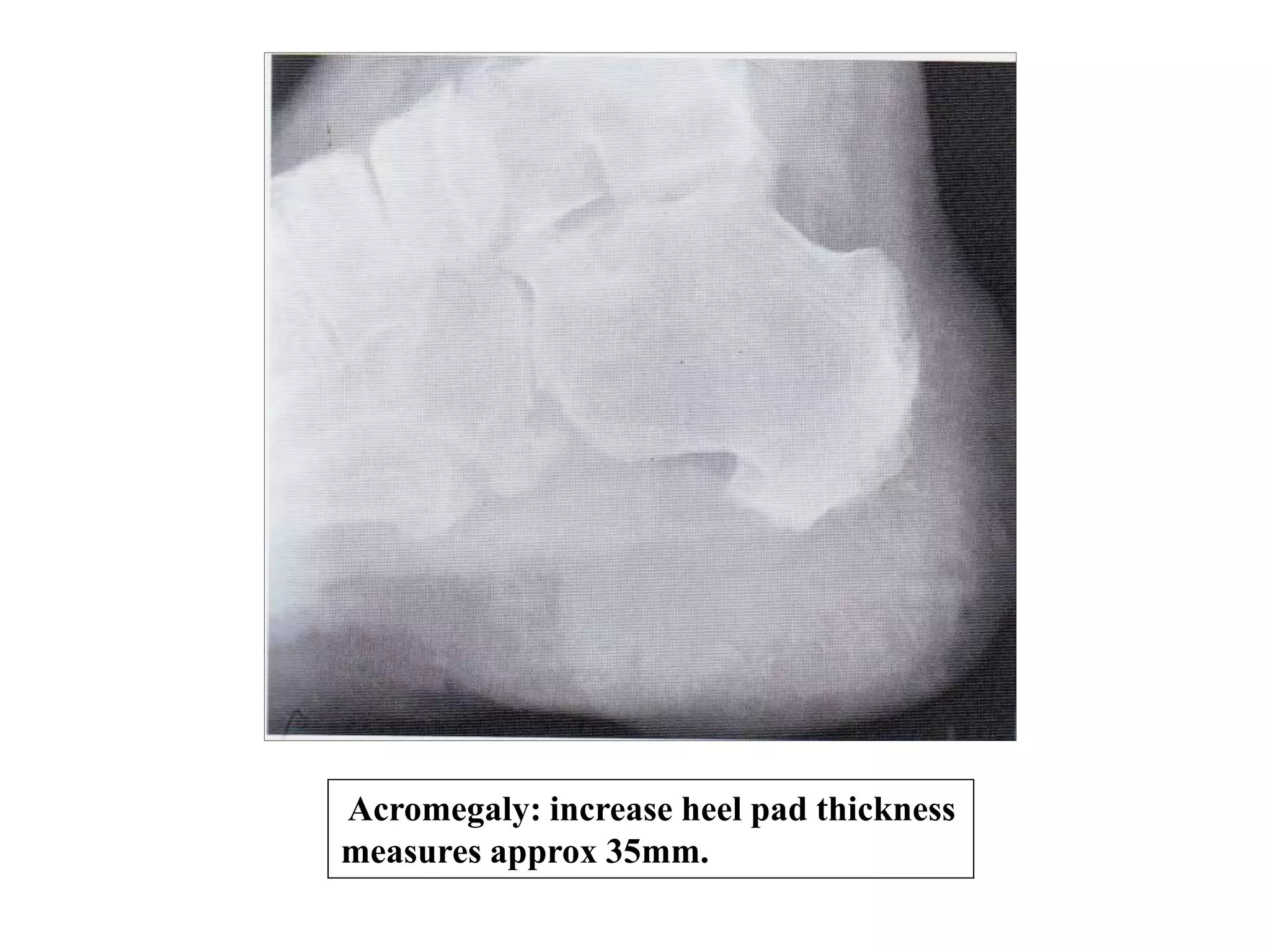
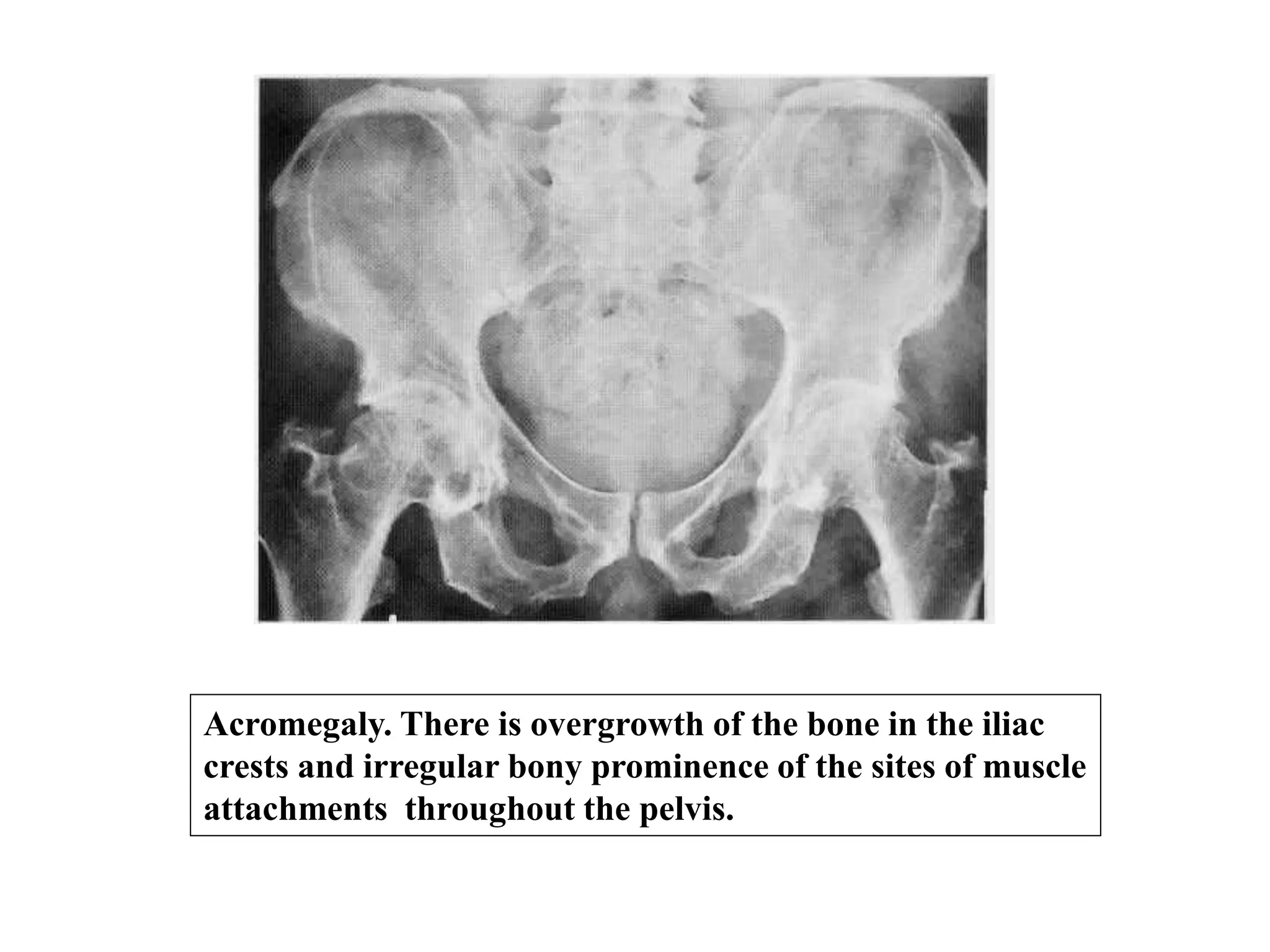
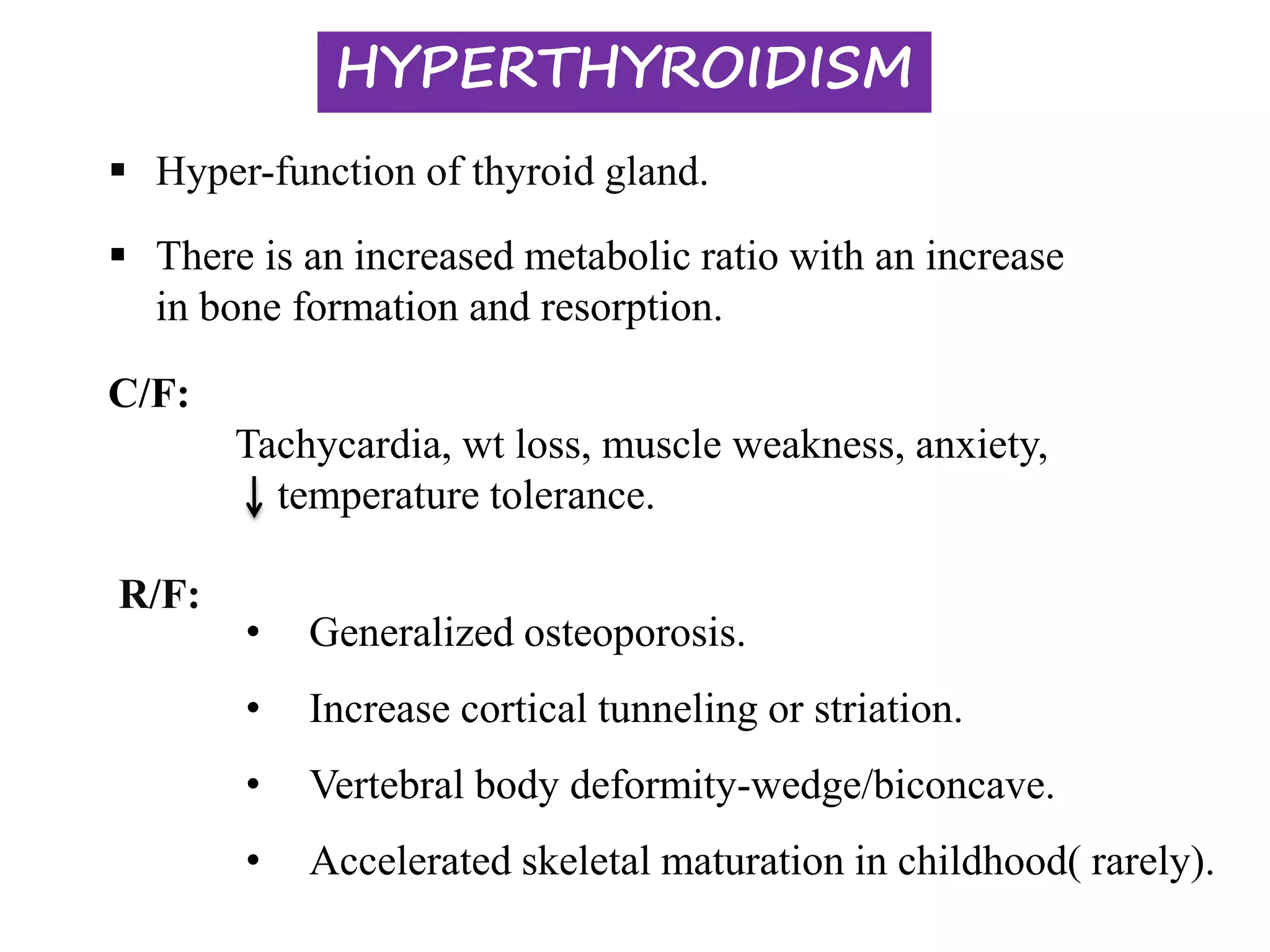
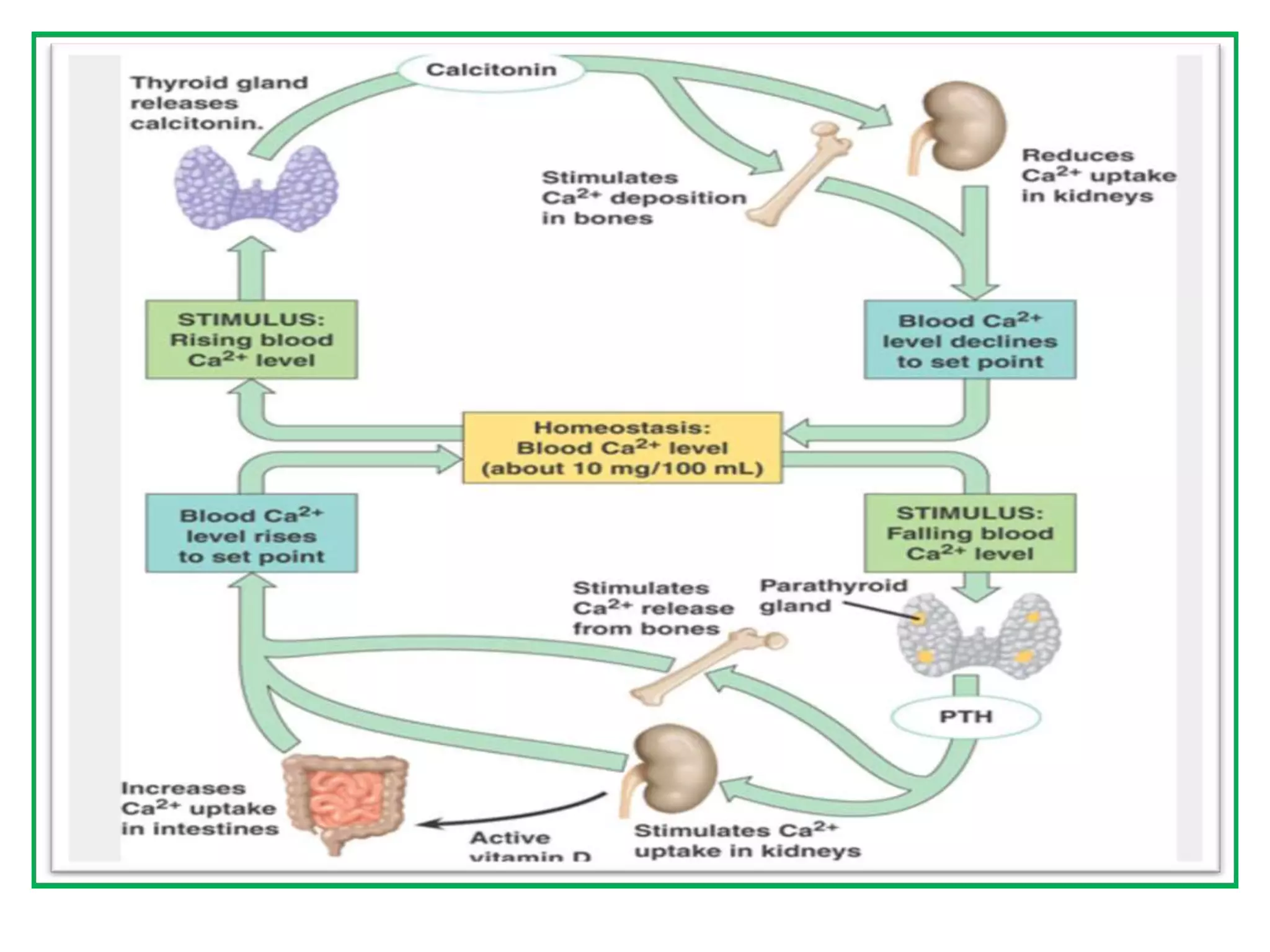
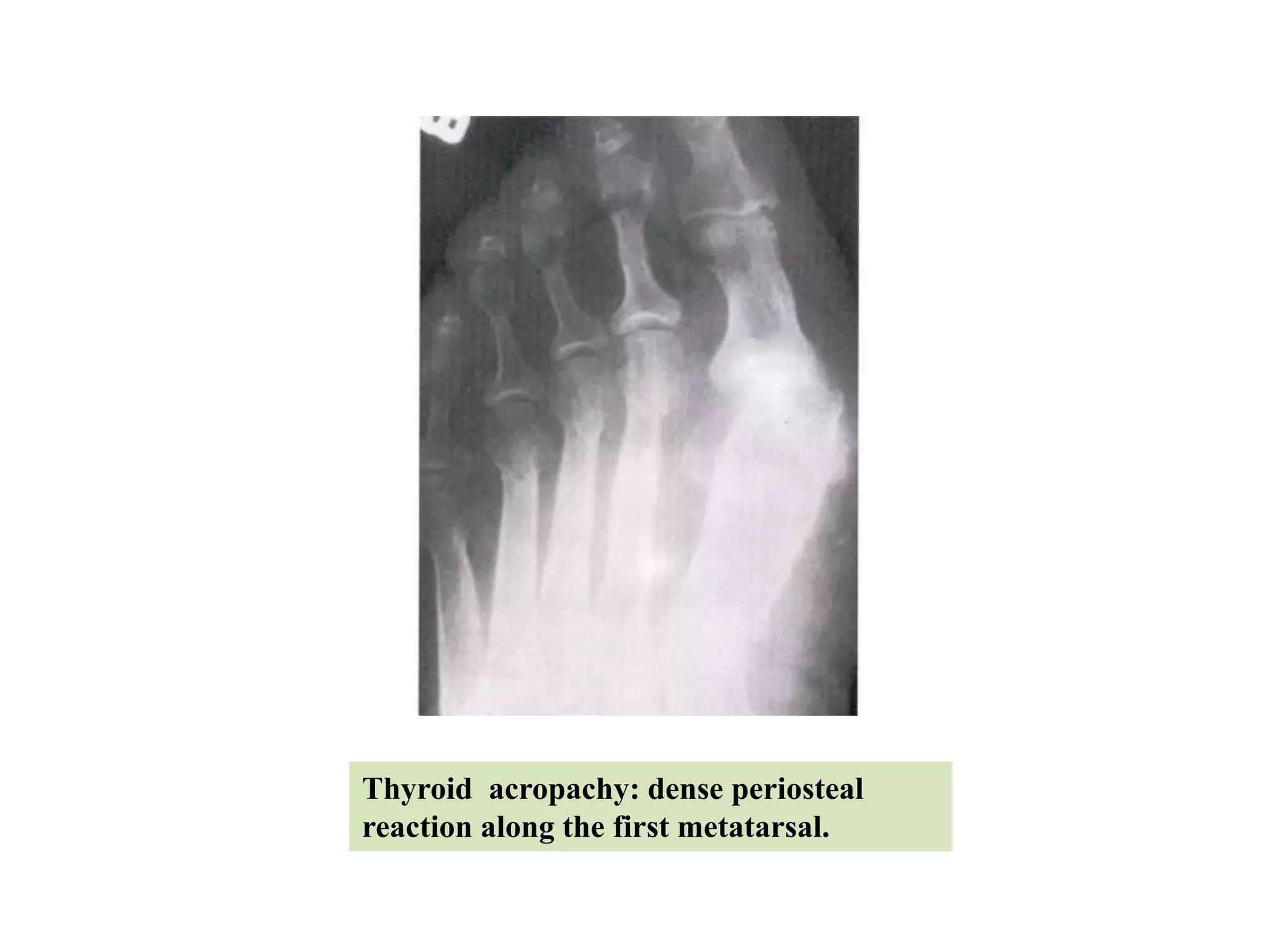
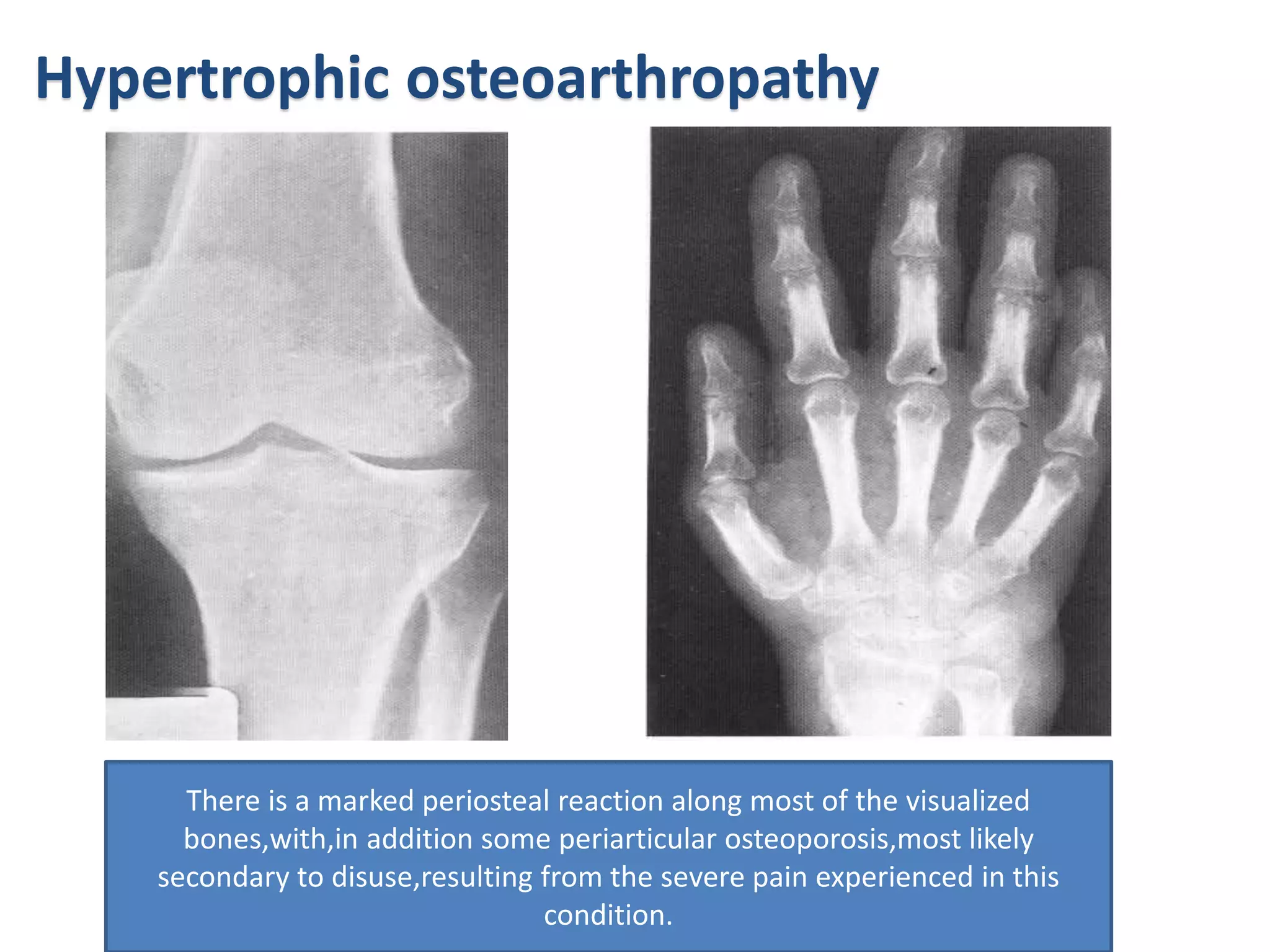
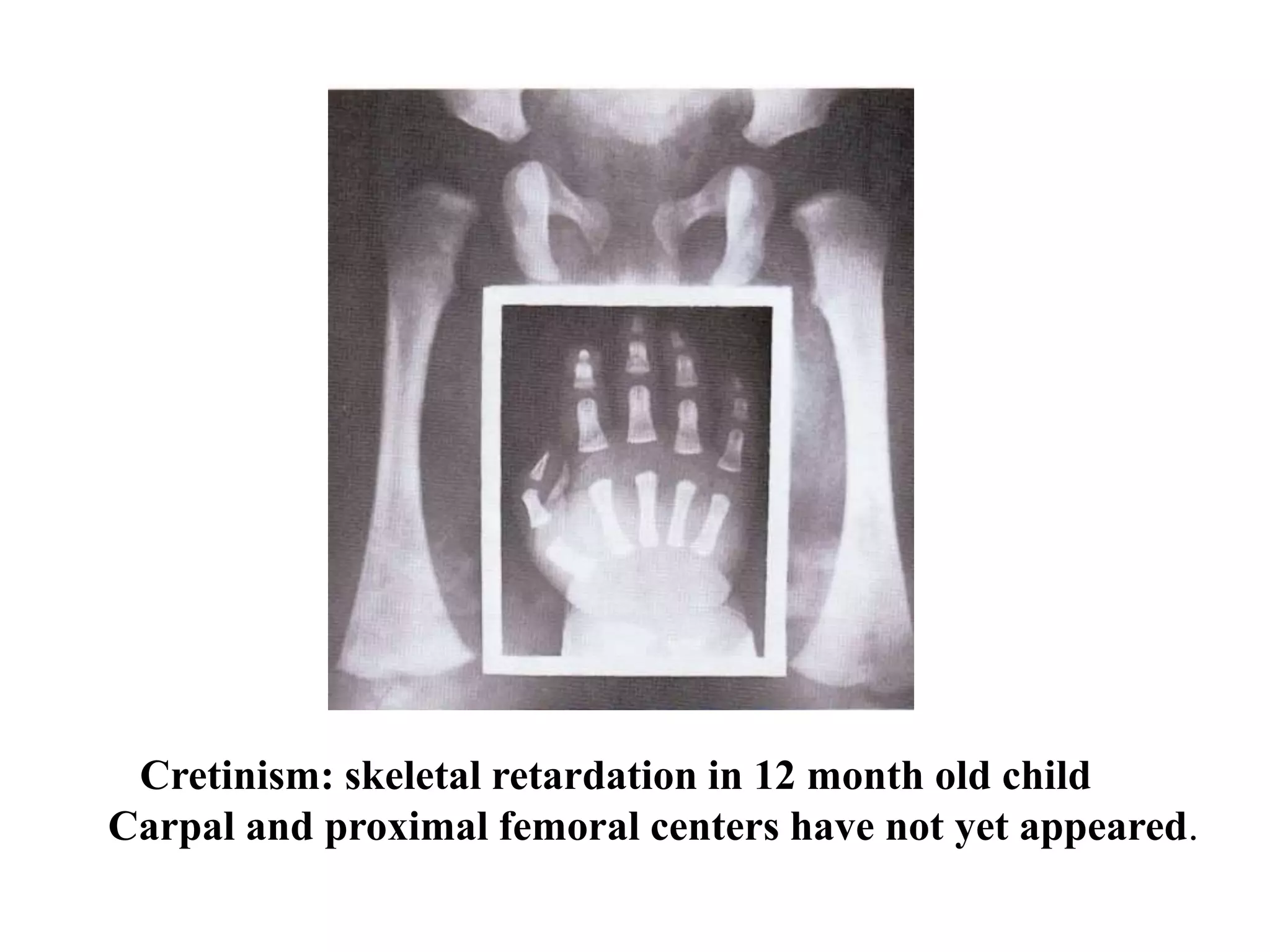
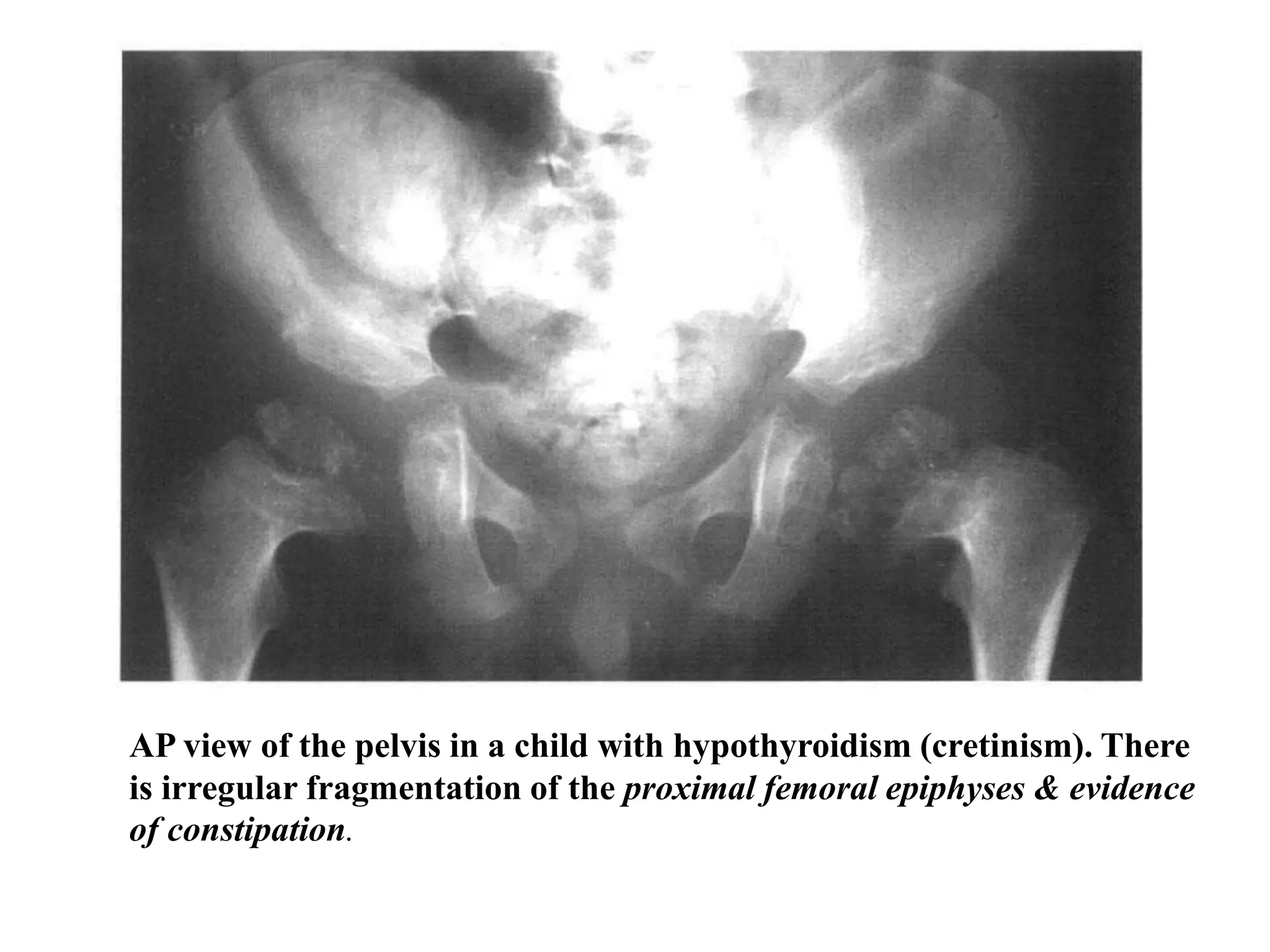
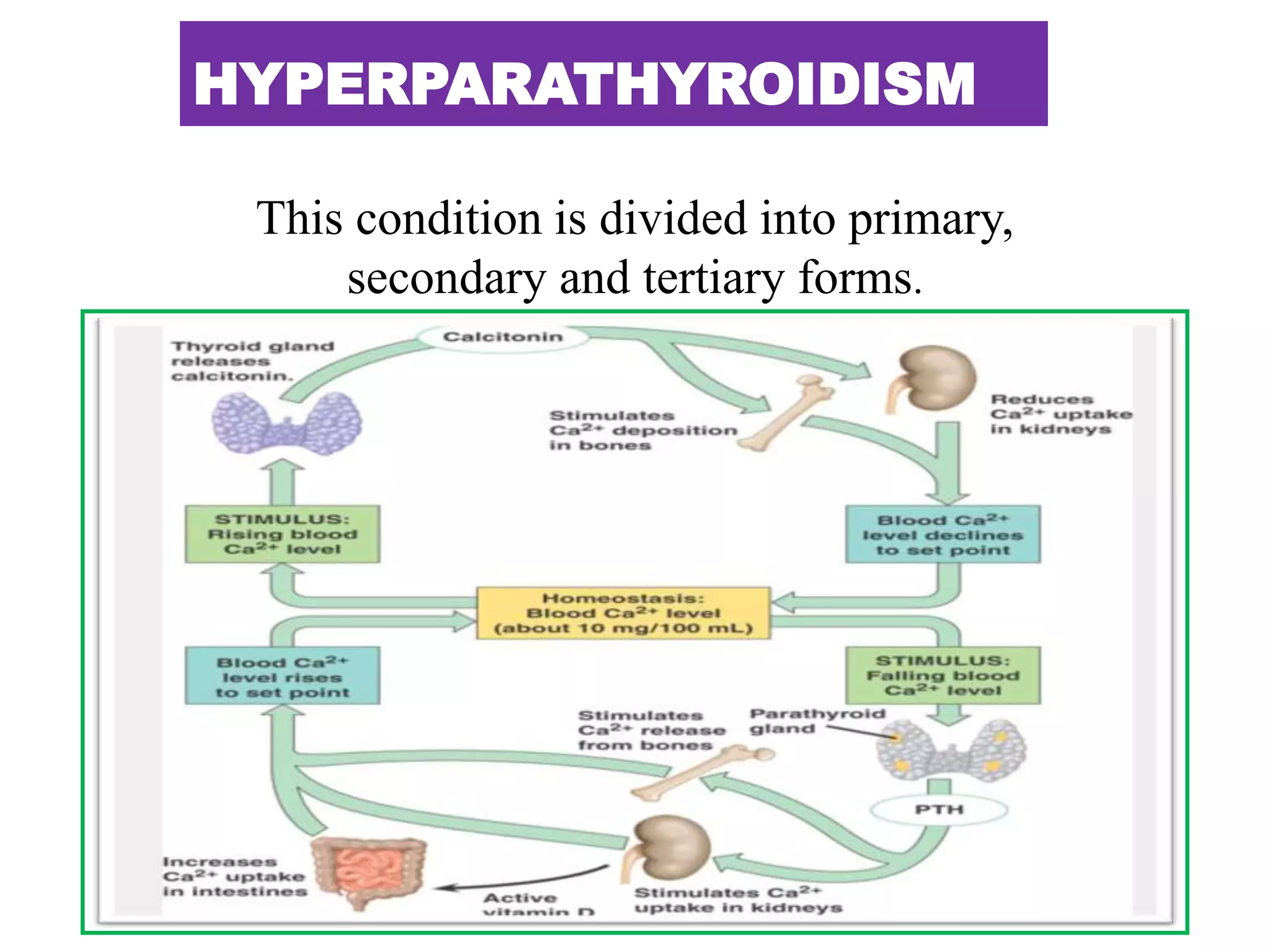
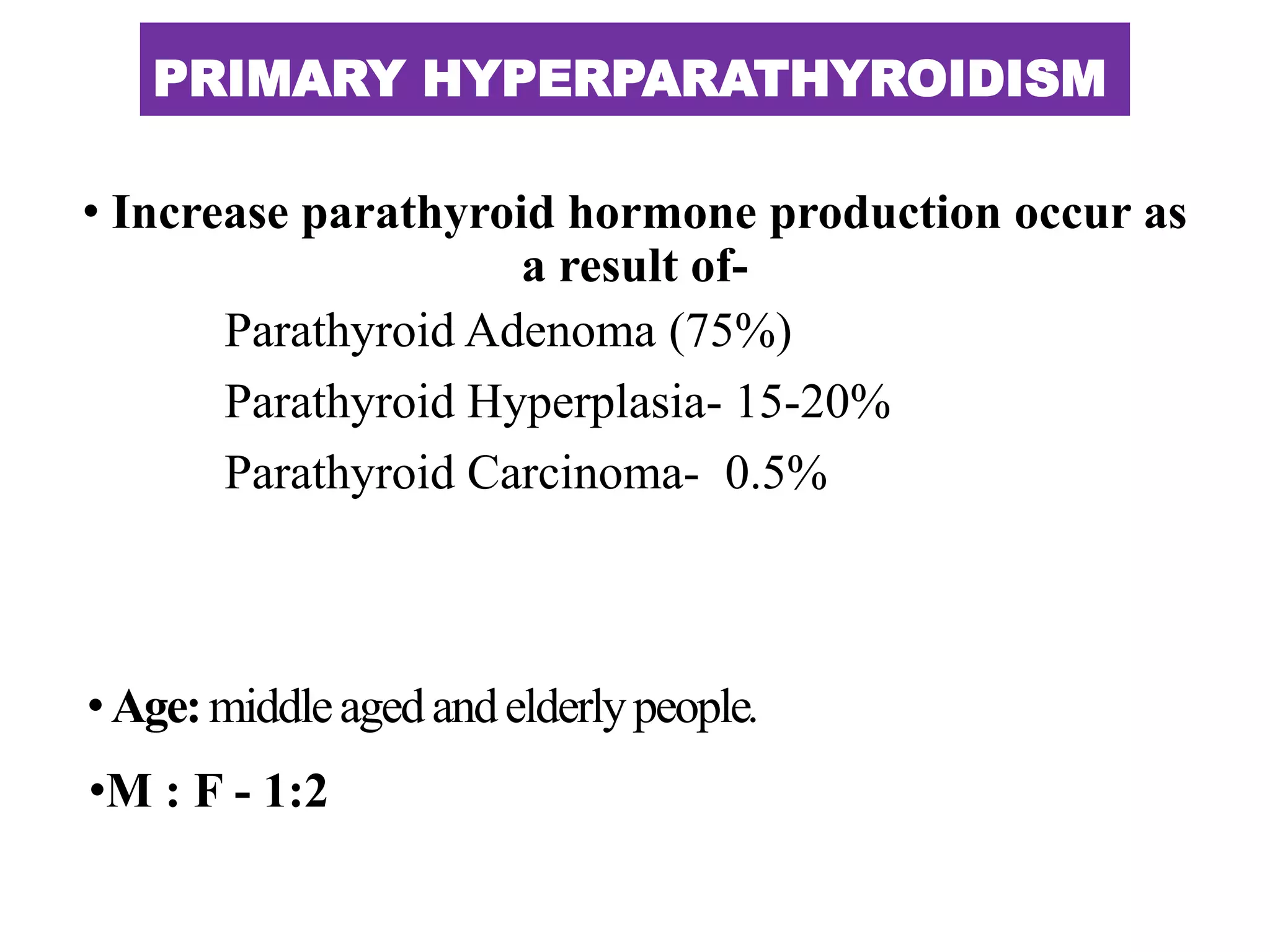
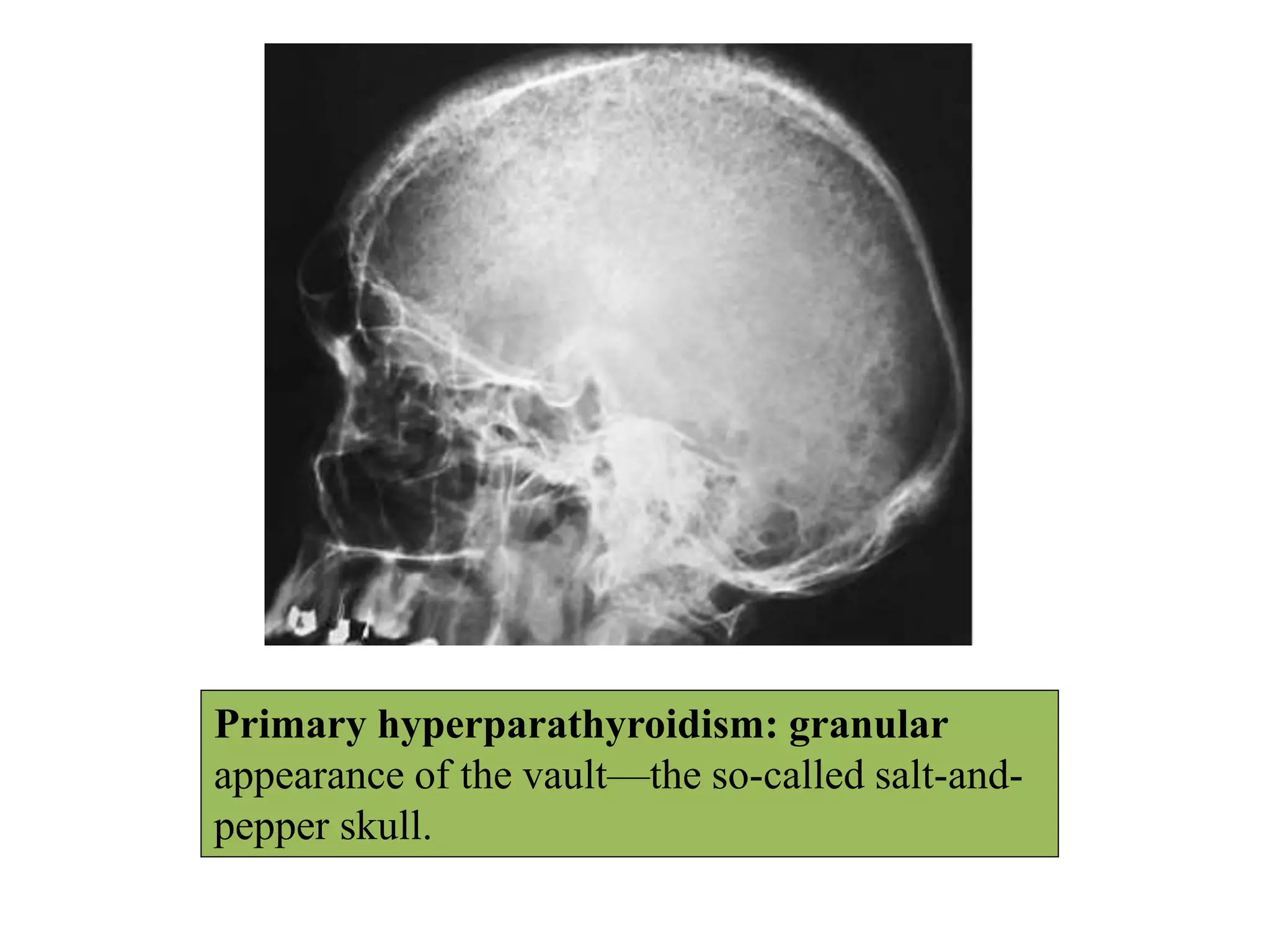
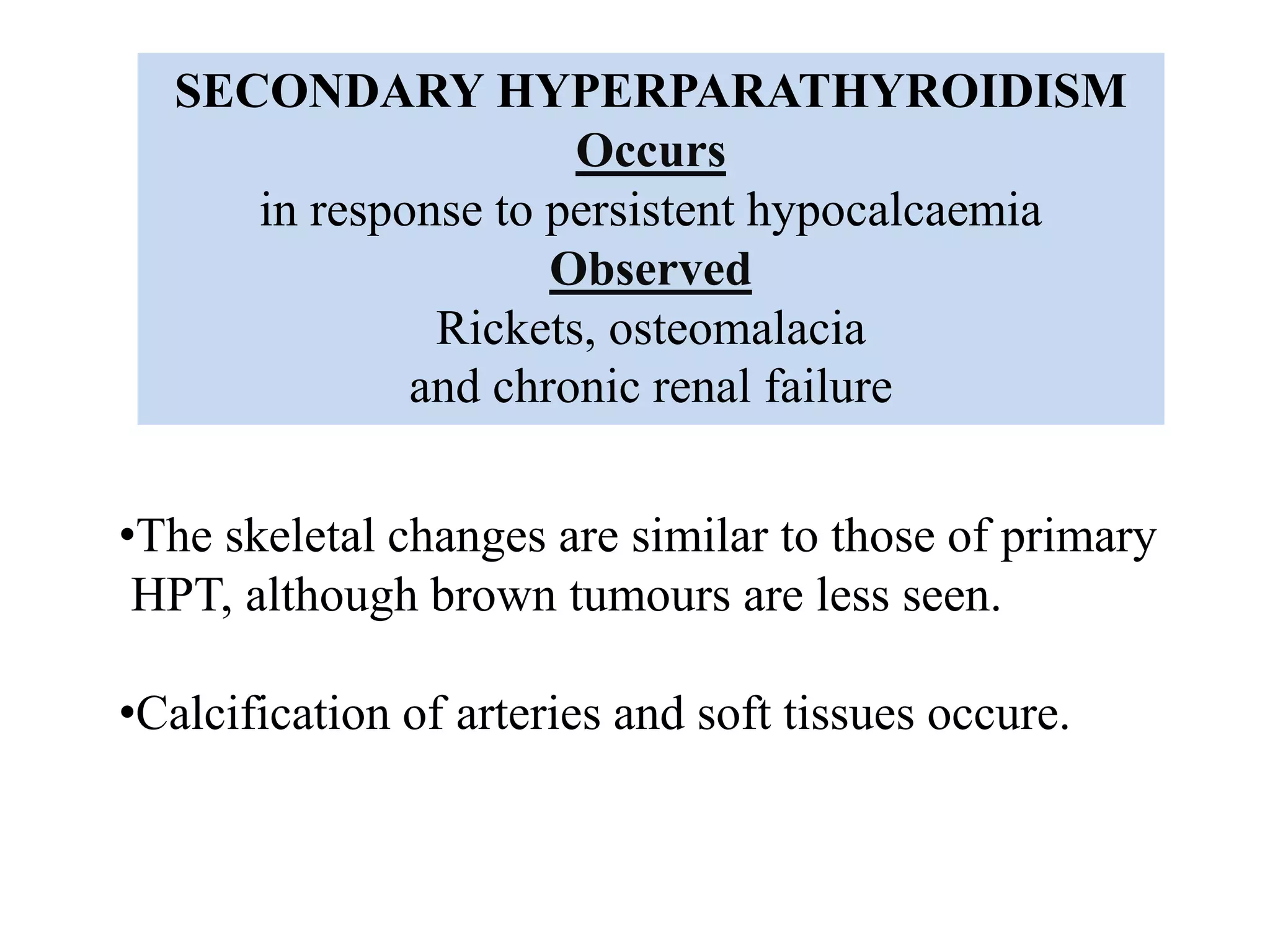
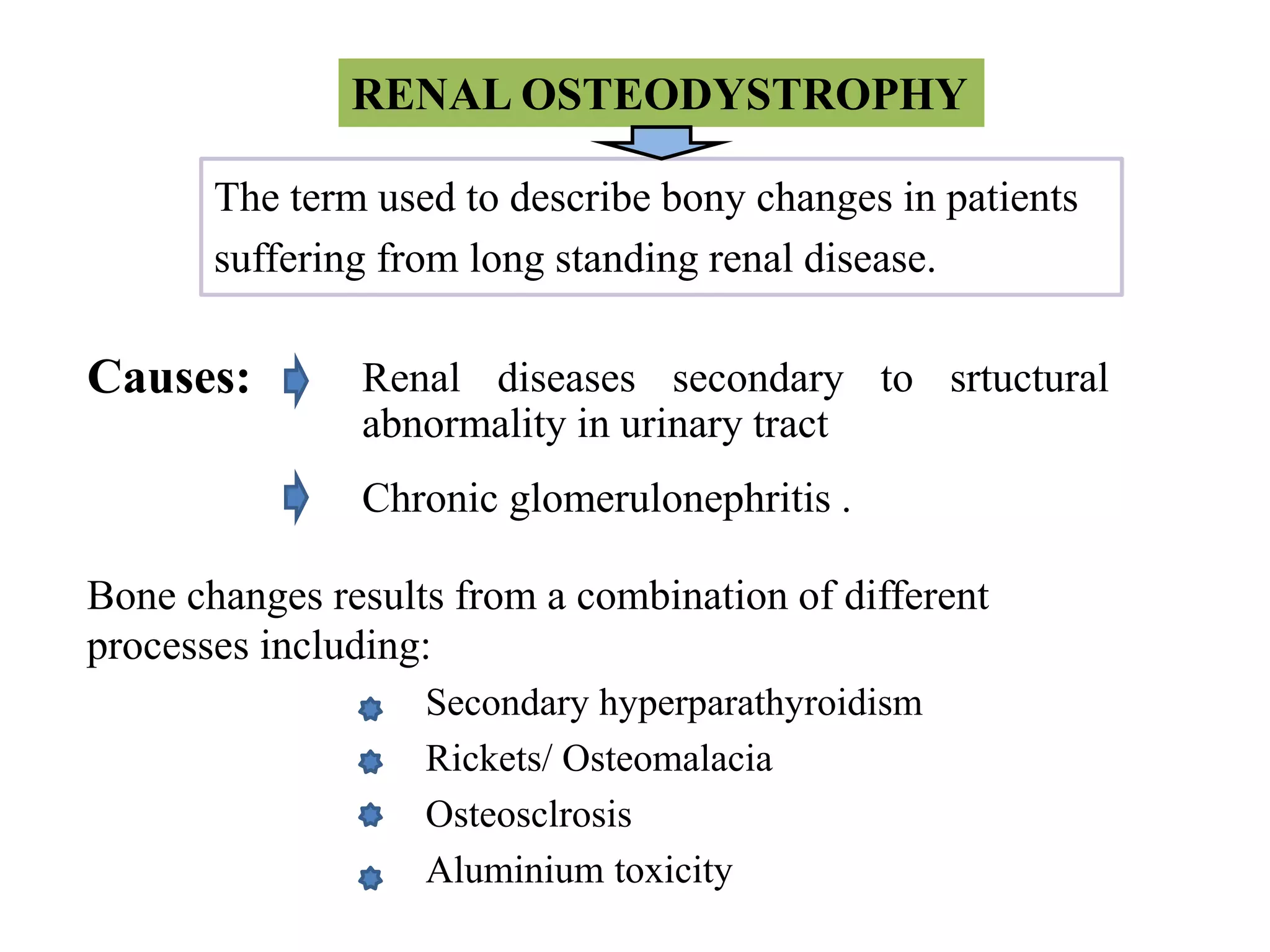
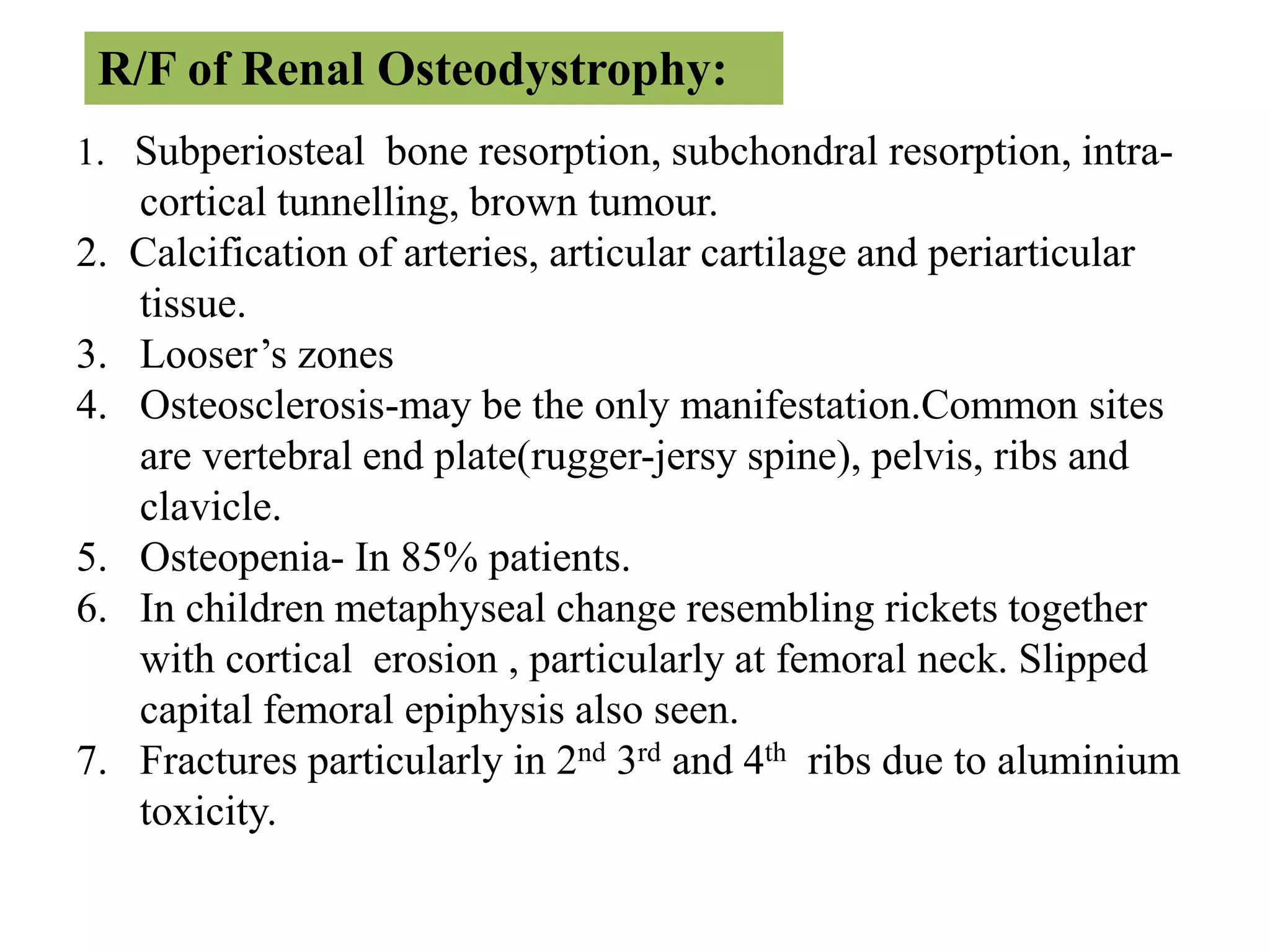
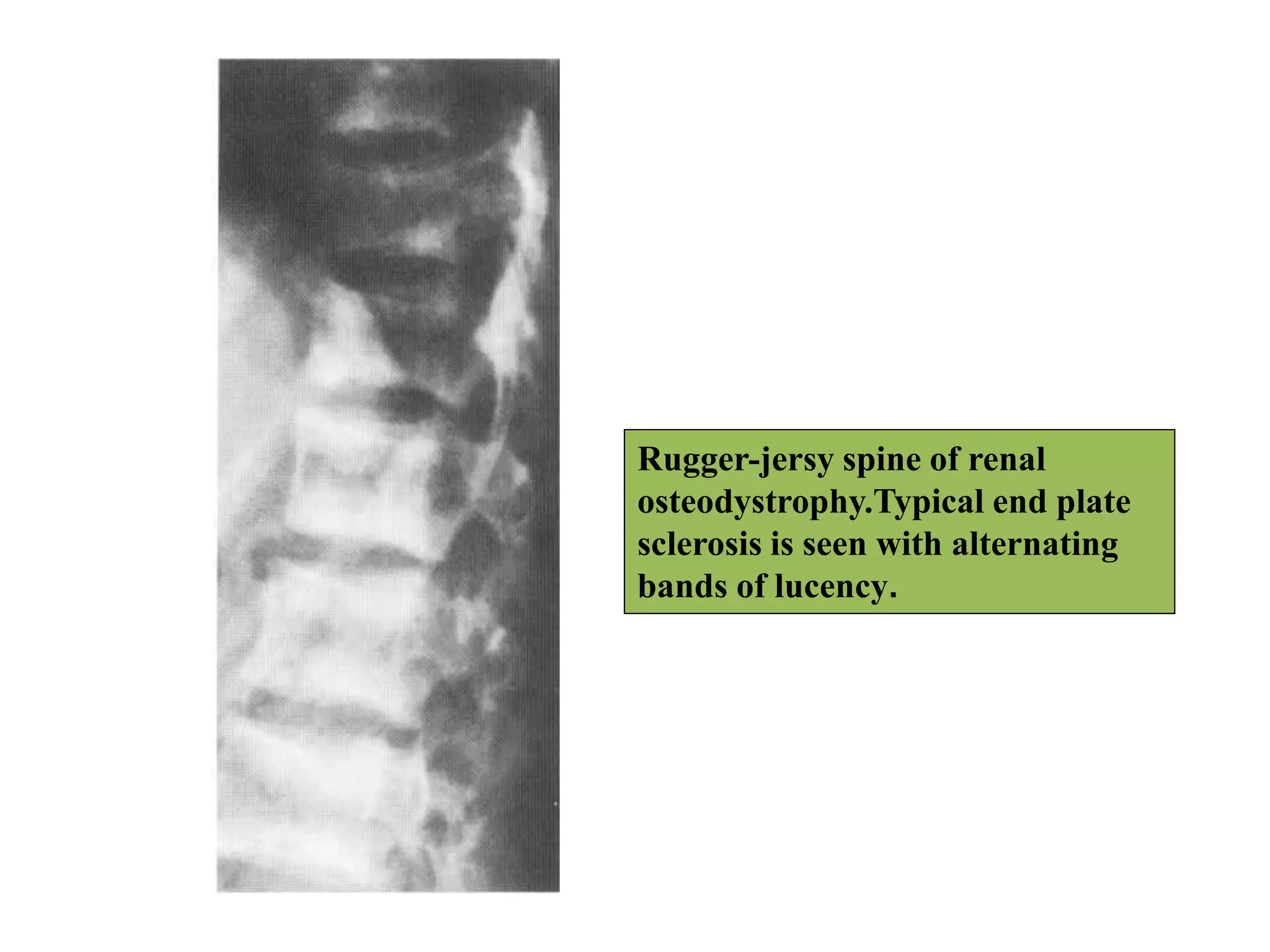
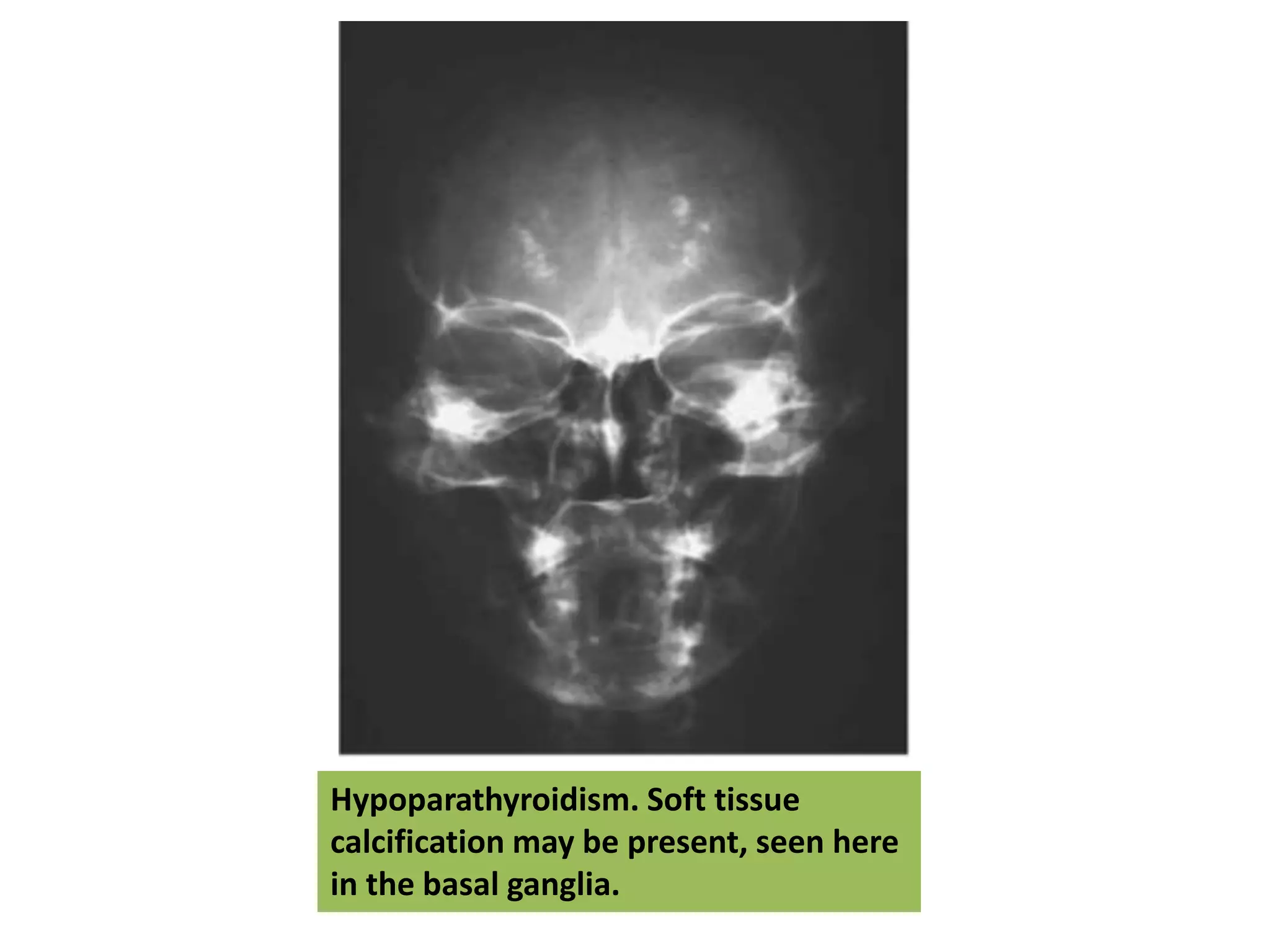
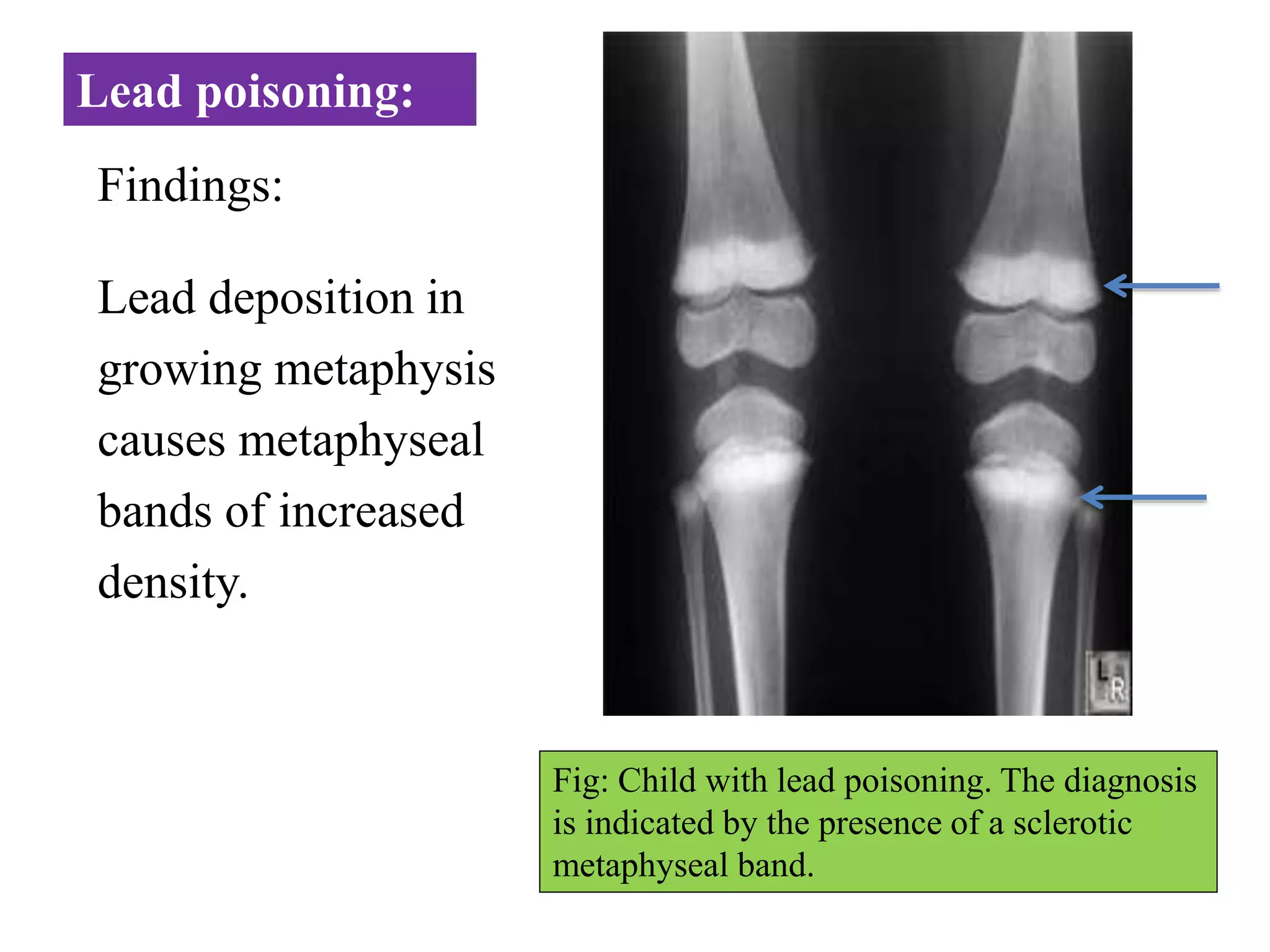
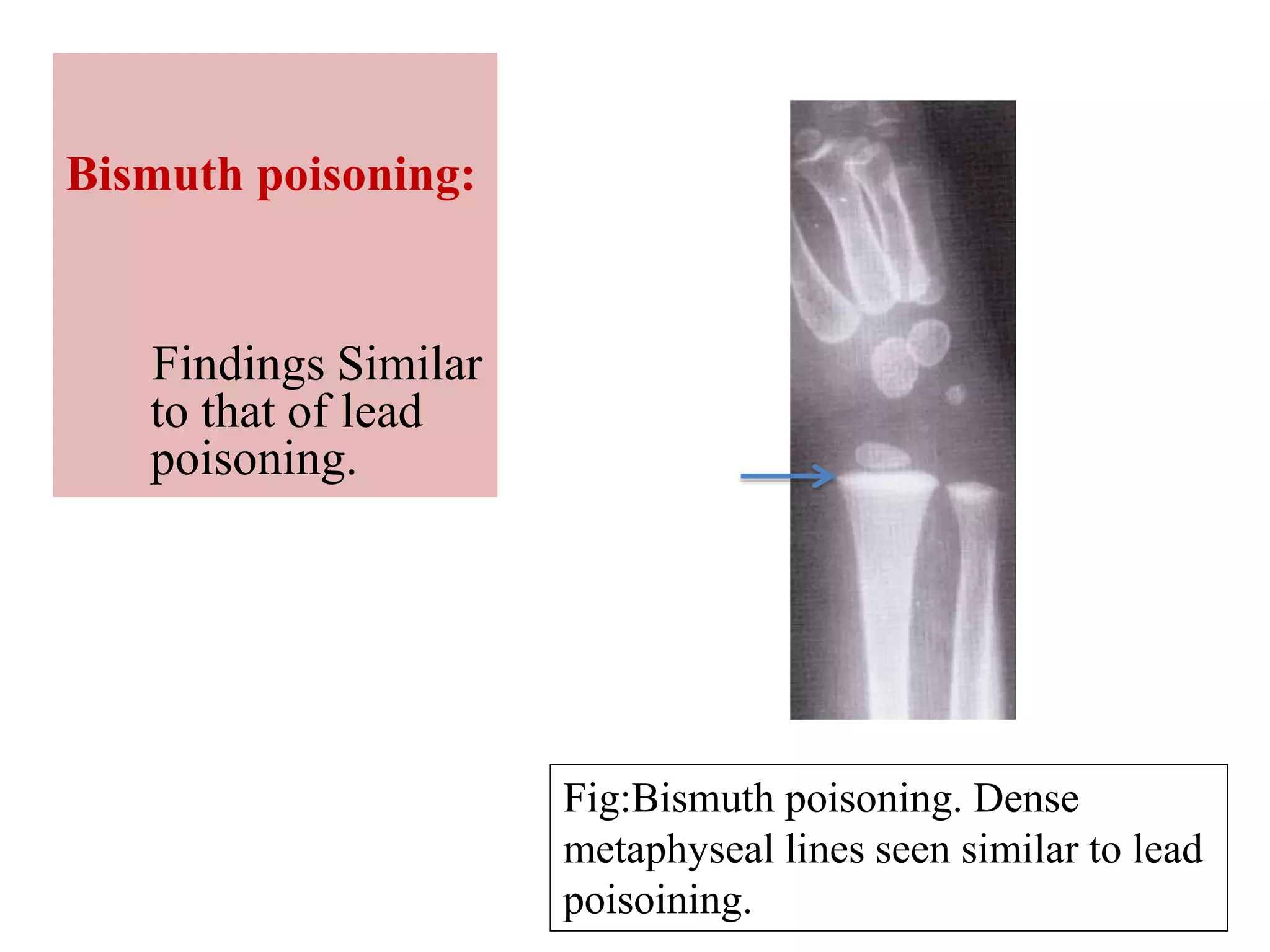
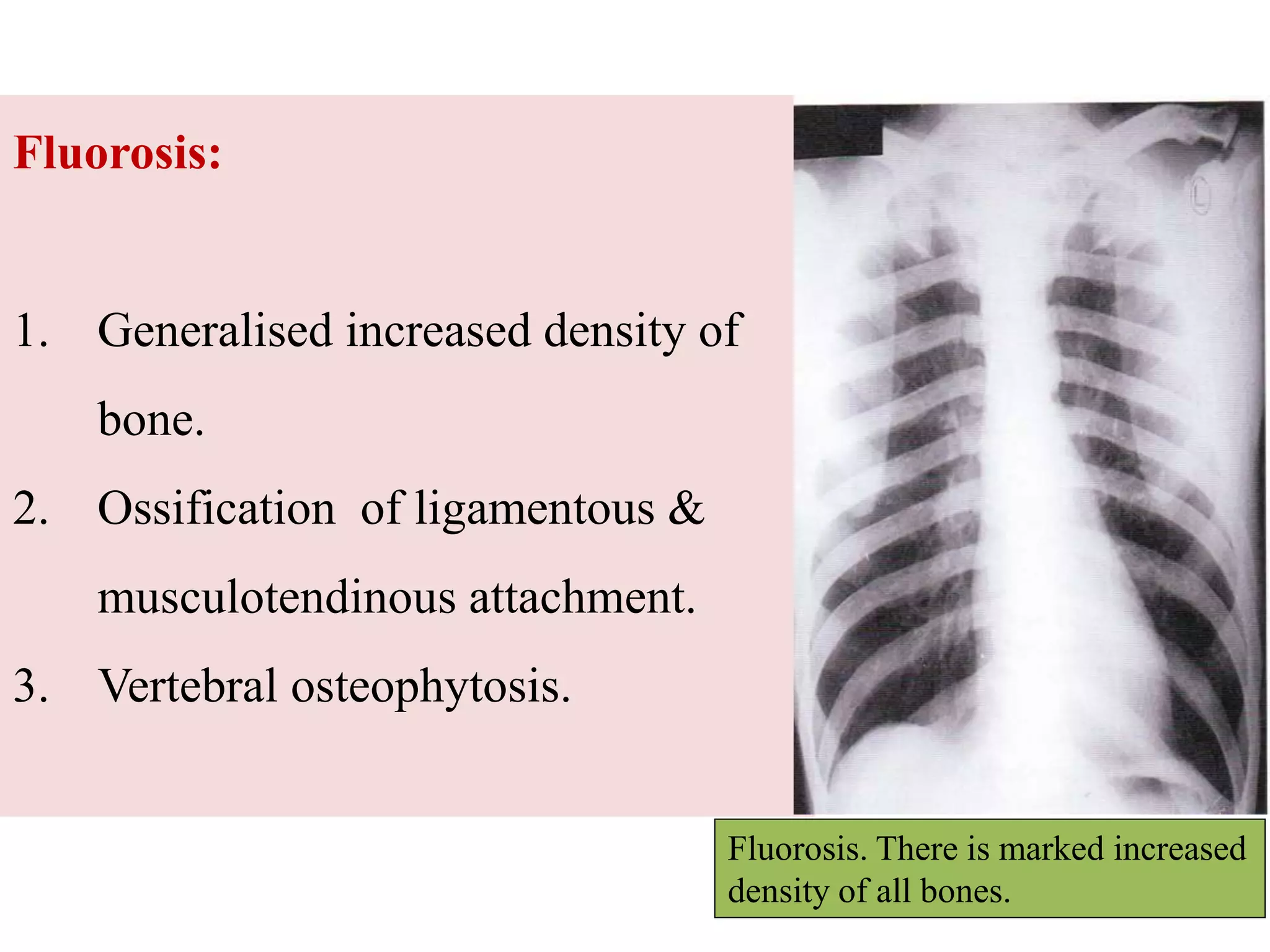
This document discusses various metabolic and endocrine disorders that can affect bone. It begins with an introduction and overview of topics to be covered, including diseases such as rickets, osteomalacia, scurvy, osteoporosis, and disorders of the pituitary, thyroid, and parathyroid glands. For each condition, the document discusses biochemical findings, clinical features, and radiographic manifestations and findings. It provides examples of radiographs demonstrating characteristic abnormalities seen in conditions like rickets, osteomalacia, scurvy, and acromegaly among others.