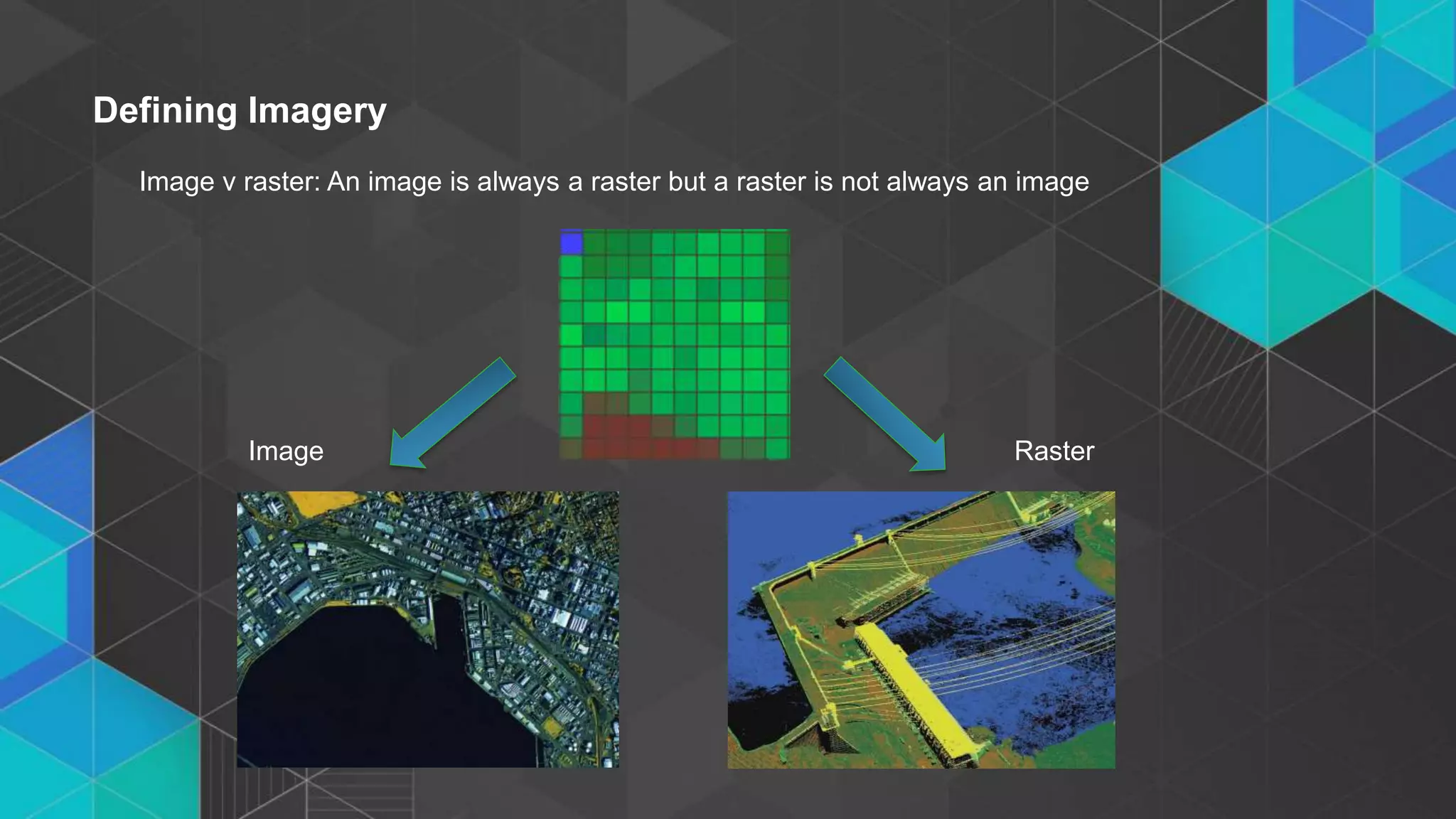
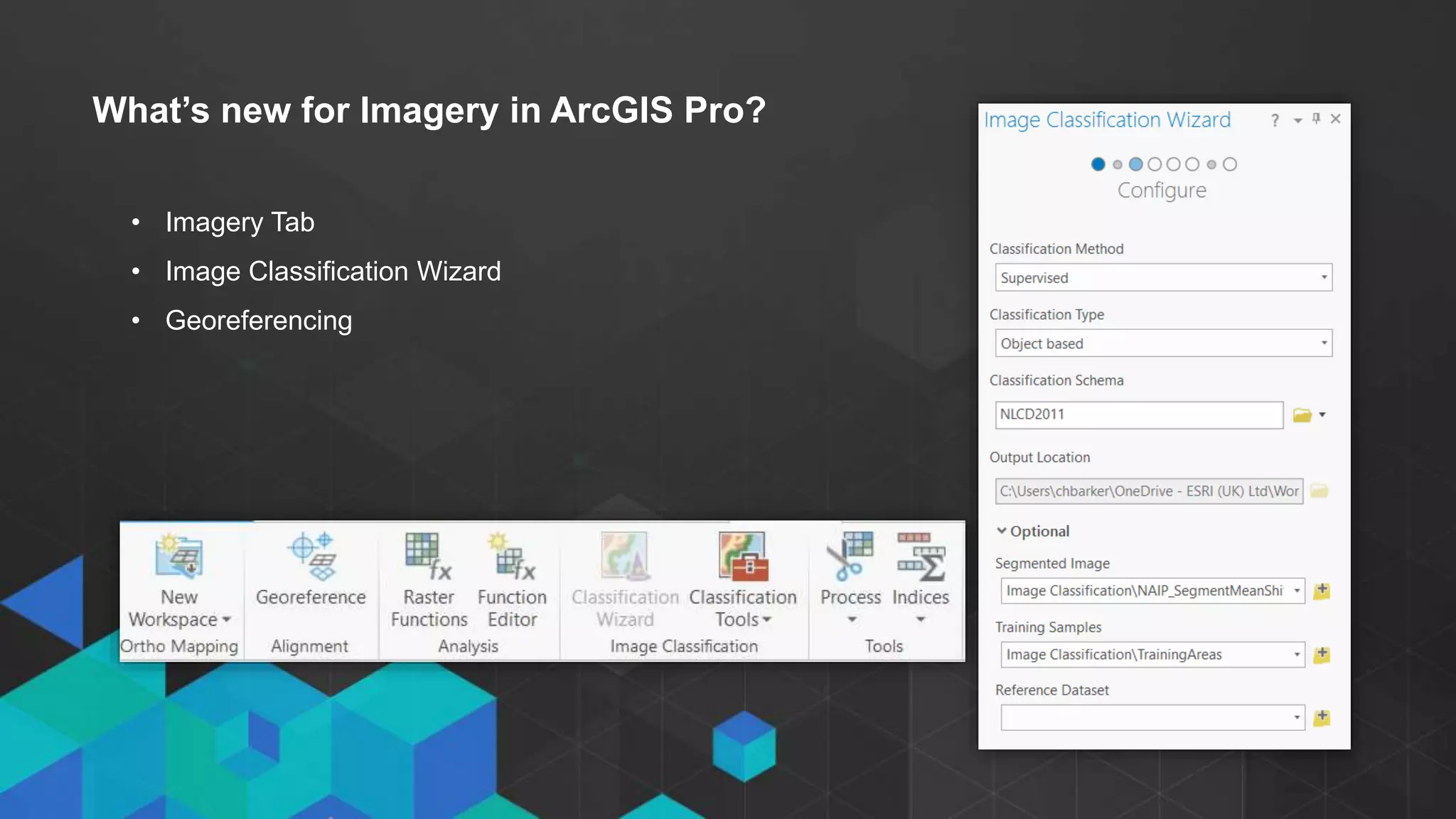
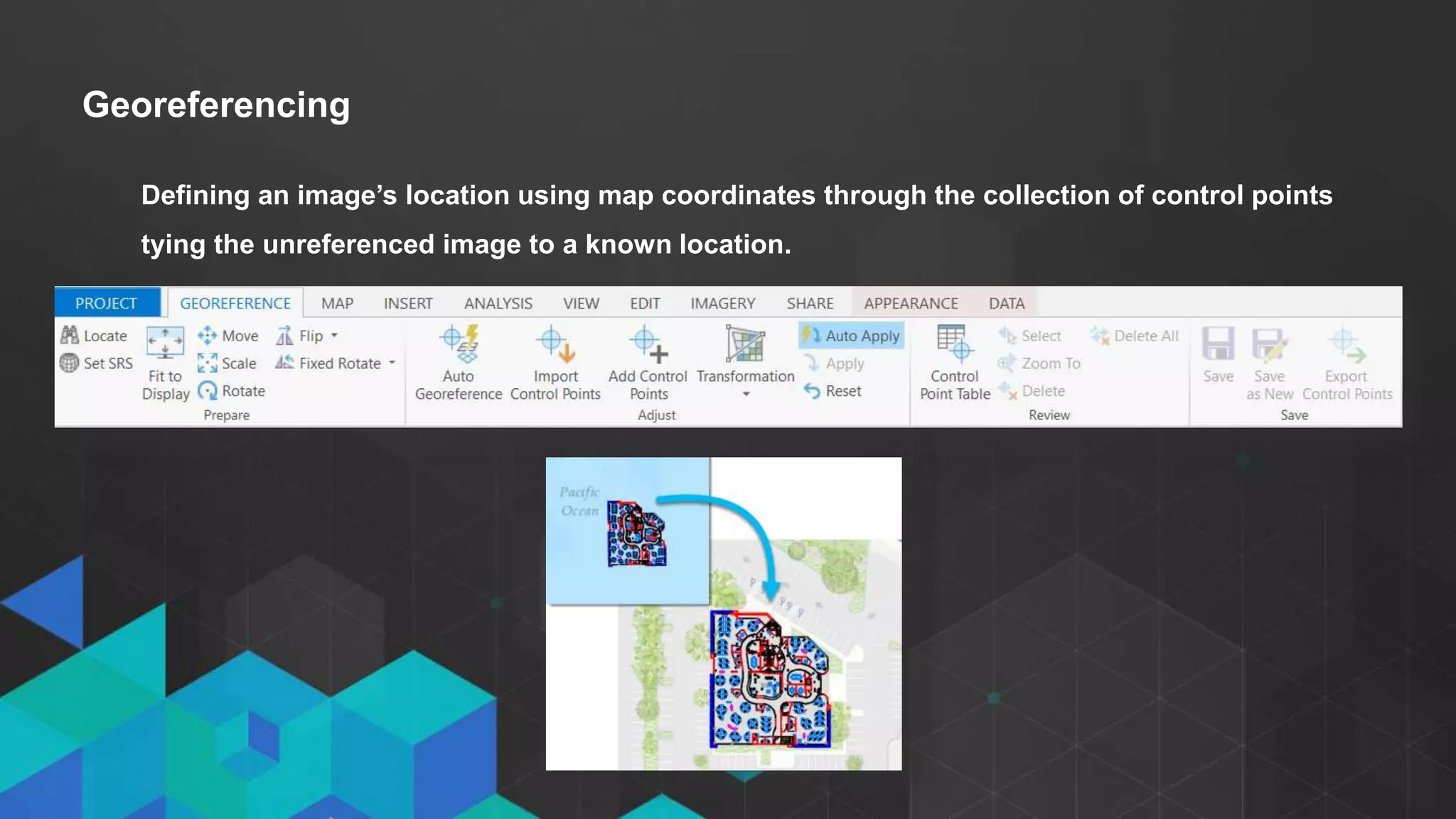
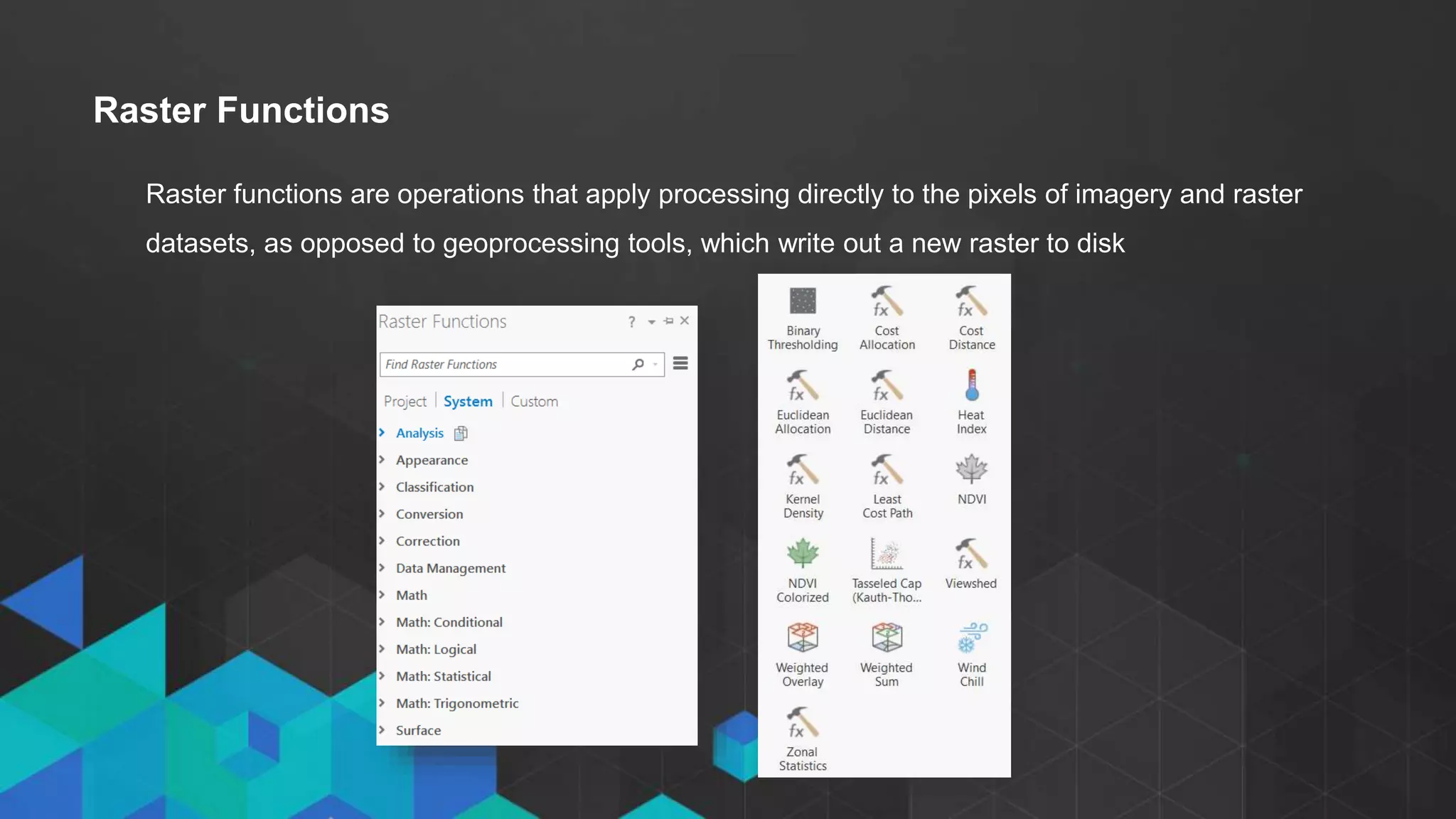
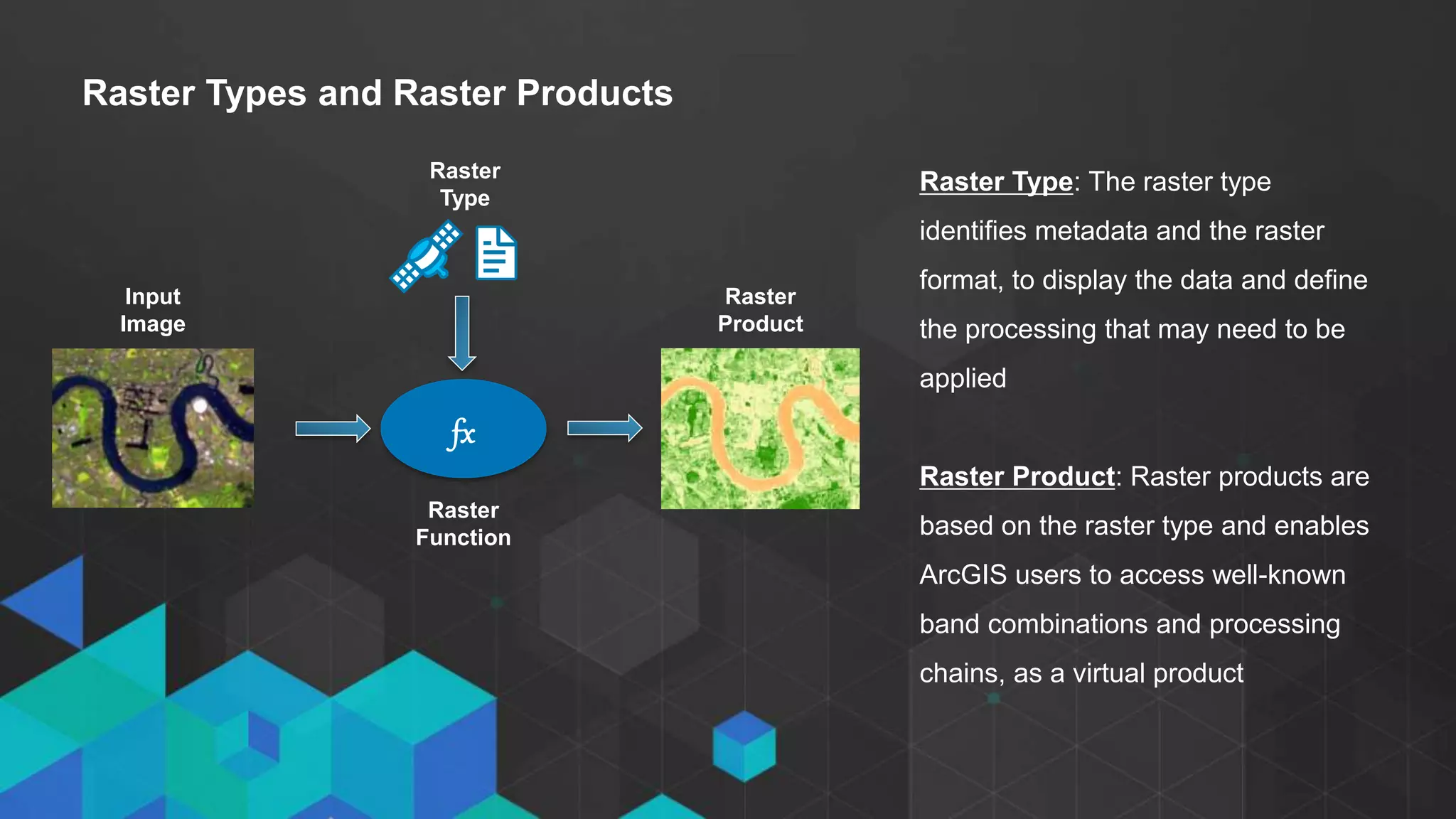
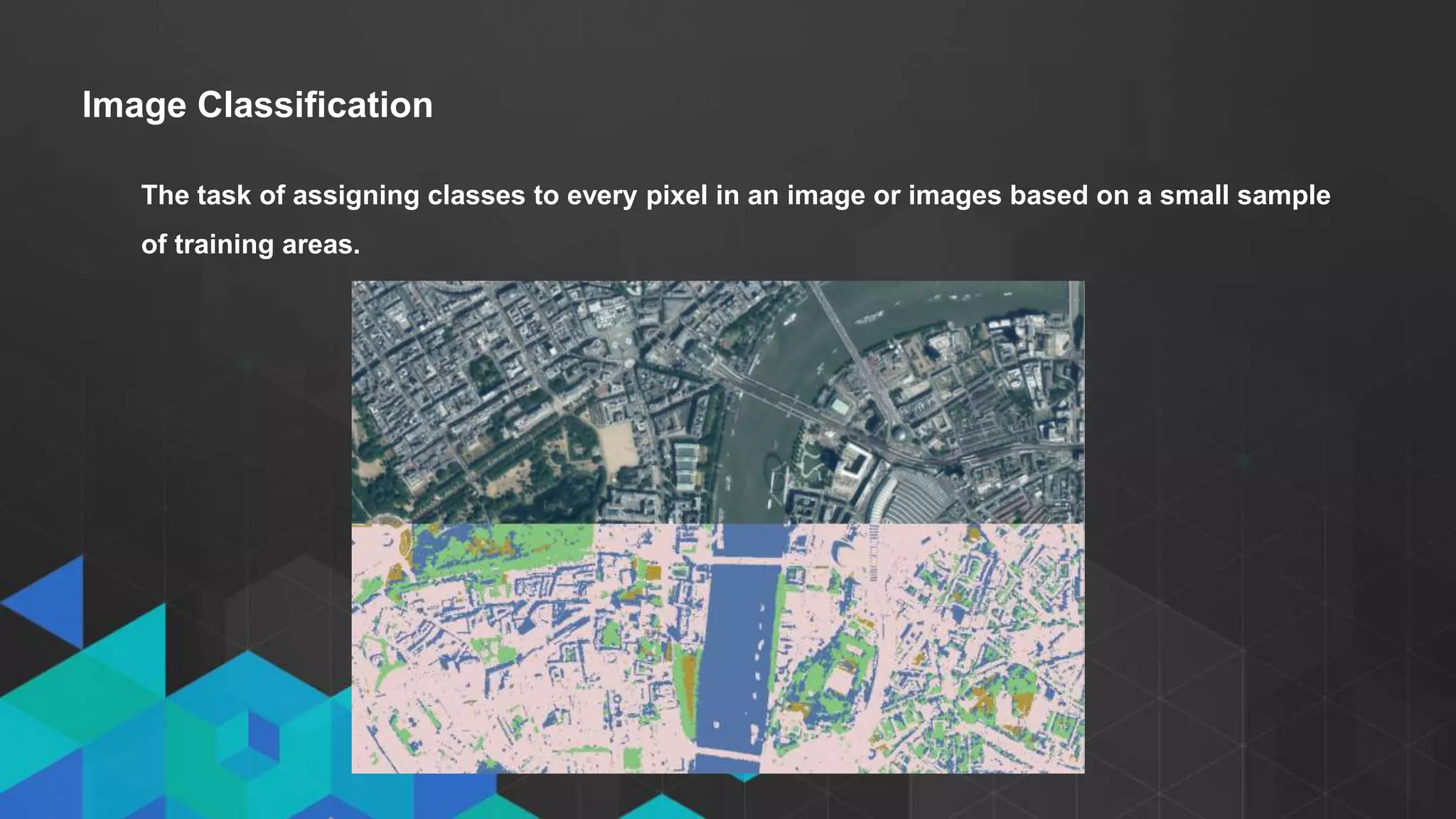
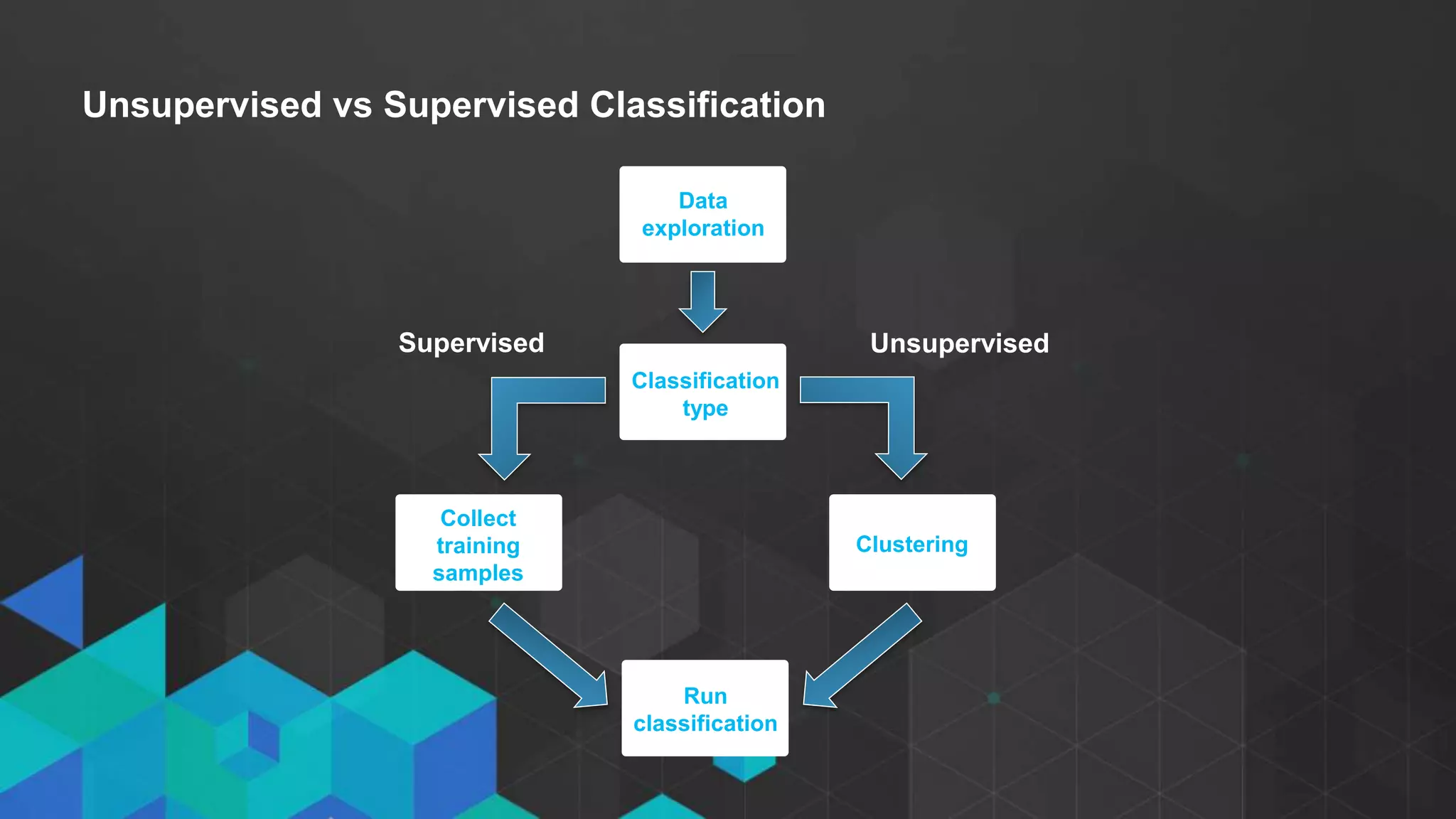
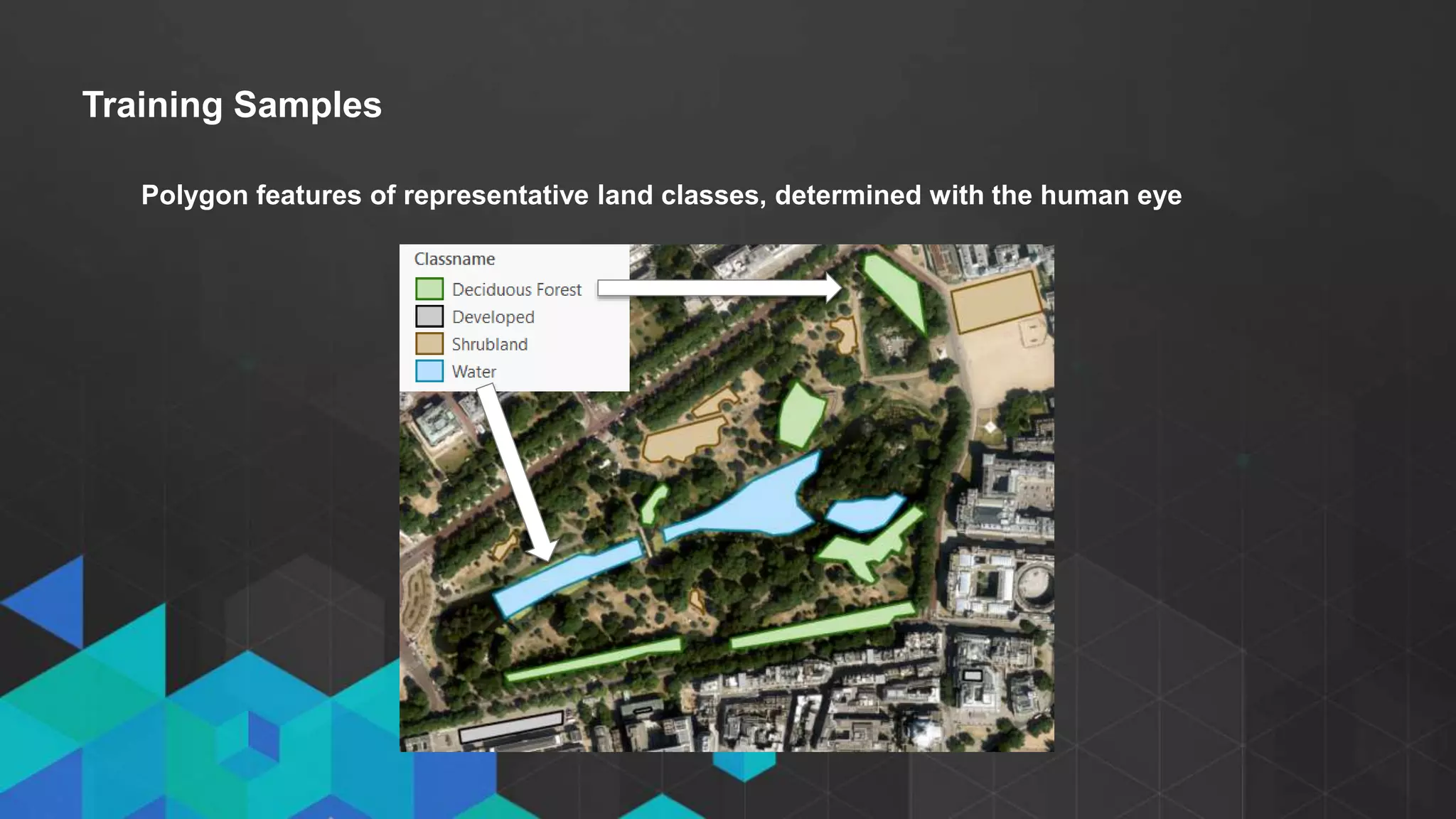
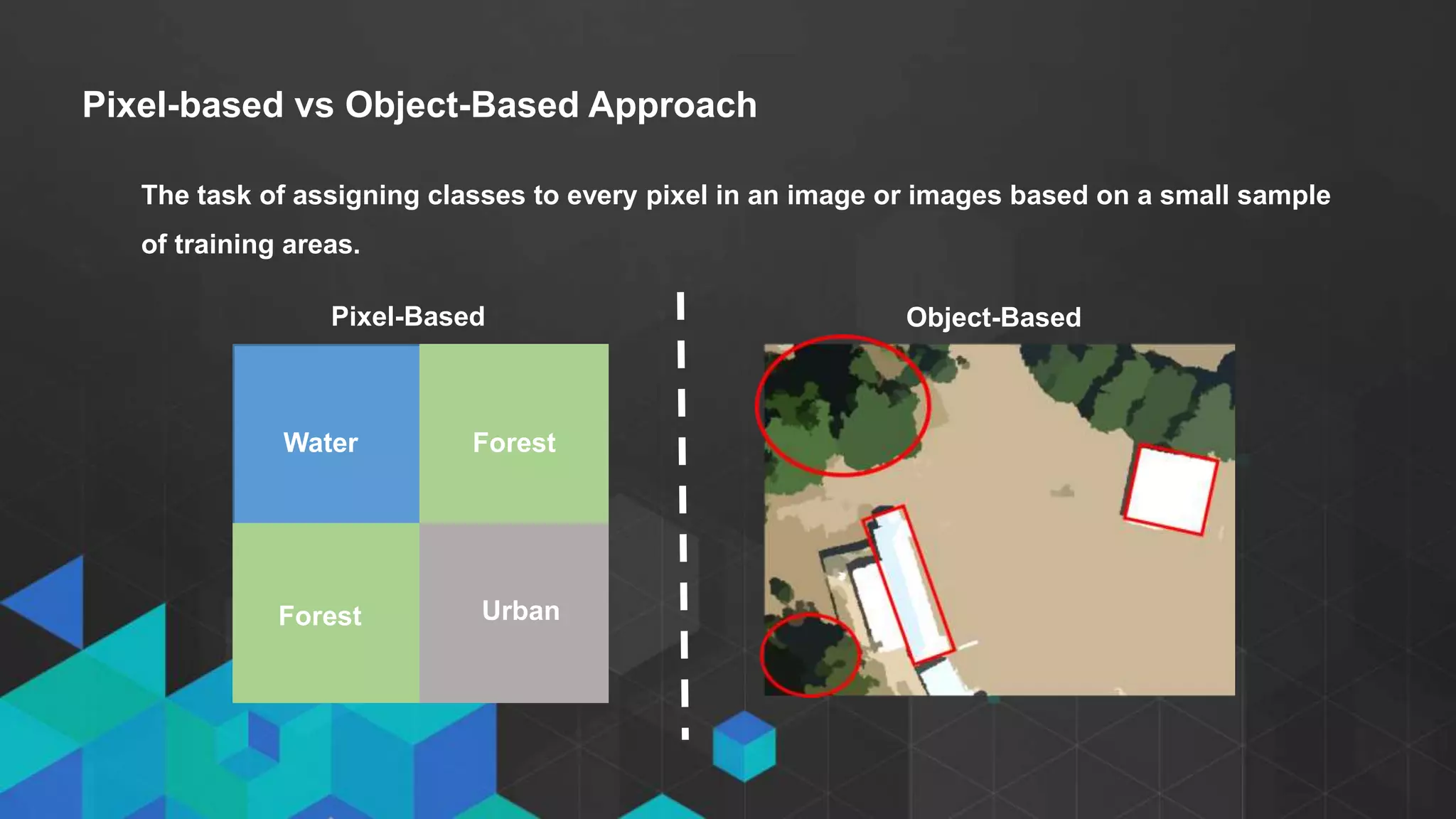
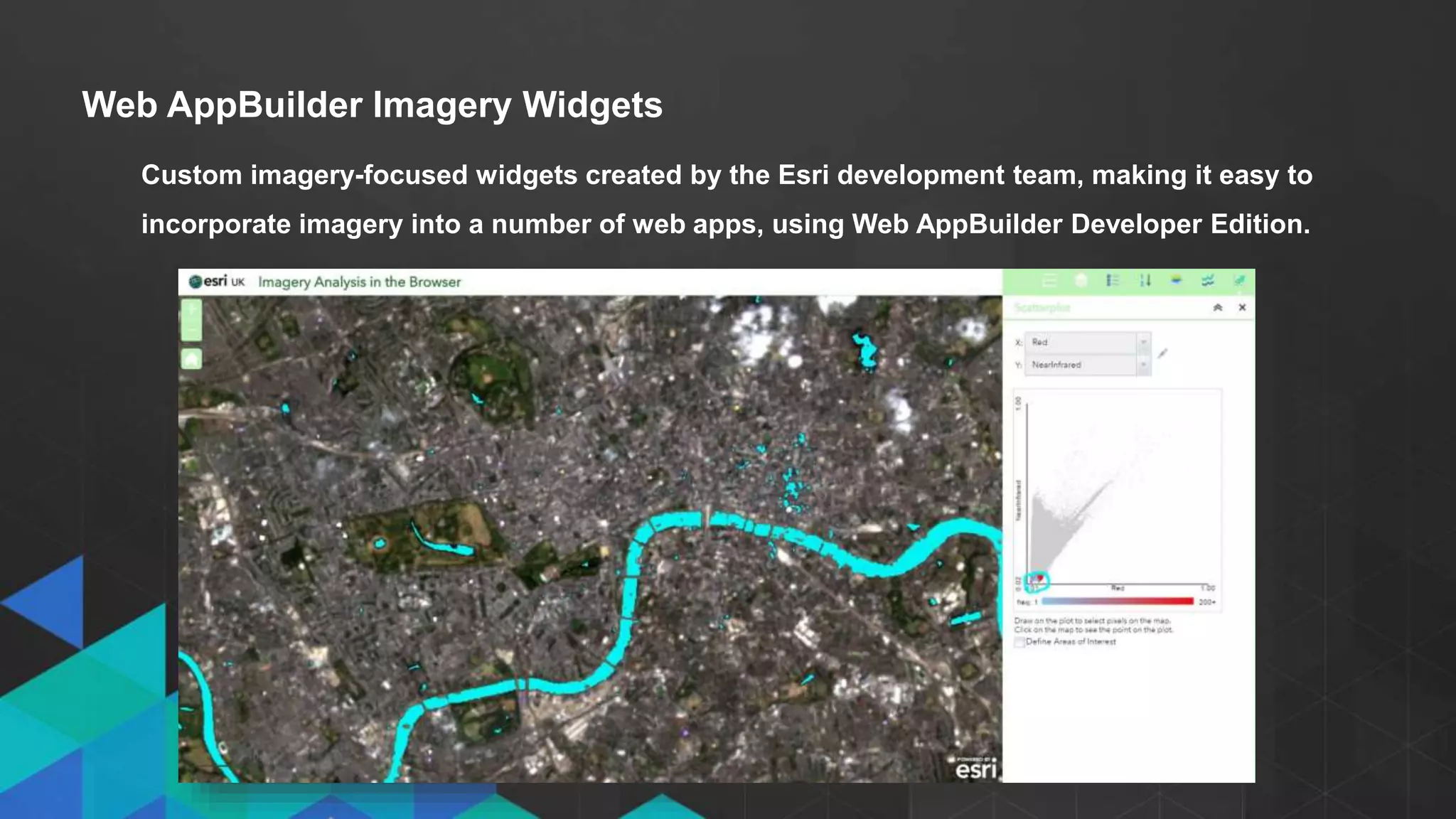
This document discusses imagery analysis in ArcGIS Pro. It covers what's new for imagery in ArcGIS Pro including the imagery tab and image classification wizard. It also discusses georeferencing raster functions for on-the-fly processing, raster products, the image classification wizard, and image analysis in the browser using Web AppBuilder imagery widgets. The document includes demos of georeferencing, using imagery from the living atlas and raster functions, raster products, the image classification wizard, and image analysis in the browser.