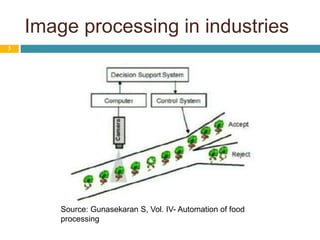
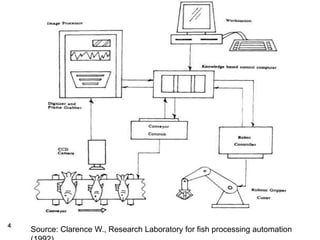
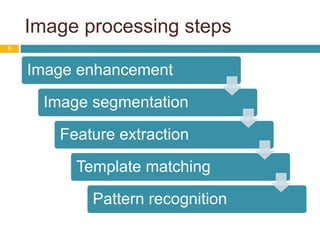
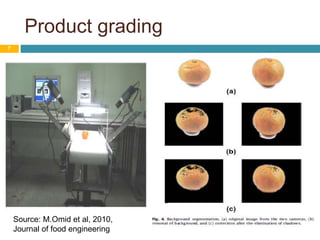
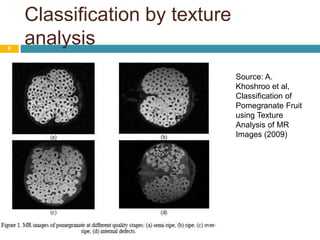
Image processing techniques are used in agro-based industries for quality control, product grading, and automation of tasks like packaging inspection and labeling. Key applications of image processing include examining visual features like color, texture, size, and shape to evaluate physical properties of food. While current systems are successful under constrained conditions, the field is still in its infancy. Future areas of focus include developing more robust 3D systems with color processing and artificial intelligence to handle biological variability and increase acceptability across multiple applications. Barriers to adoption include the need for specialized hardware and software as well as high system costs compared to benefits.