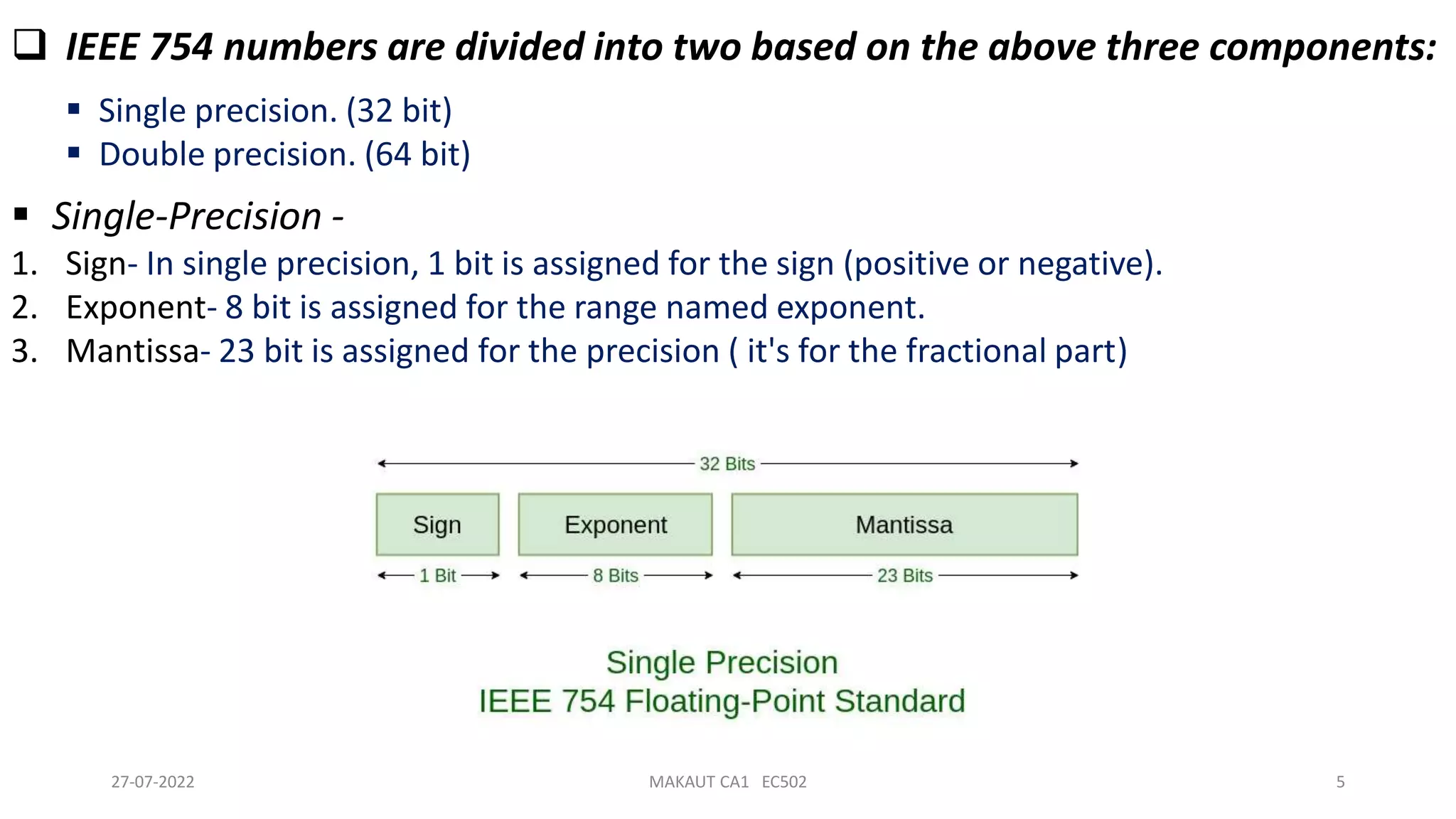
The IEEE 754 standard defines a common format for floating-point numbers that is used in computers and processors. It specifies the binary floating-point format including the sign, exponent and mantissa components. There are single and double precision formats that allocate 32 and 64 bits respectively. Single precision uses 1 bit for the sign, 8 bits for the exponent and 23 bits for the mantissa. Double precision uses 1 bit for the sign, 11 bits for the exponent and 52 bits for the mantissa. The standard helps to represent real numbers consistently in computers.