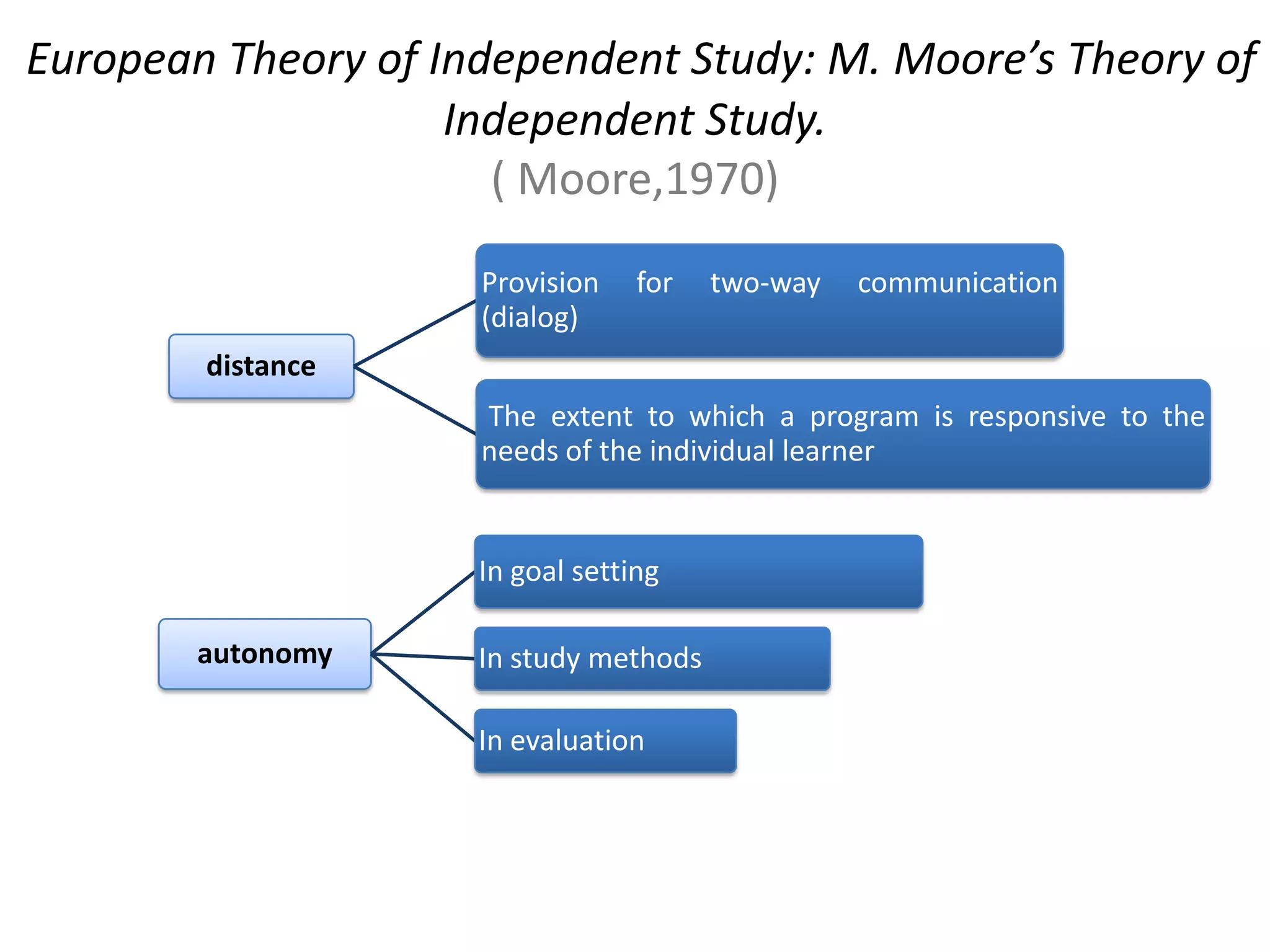
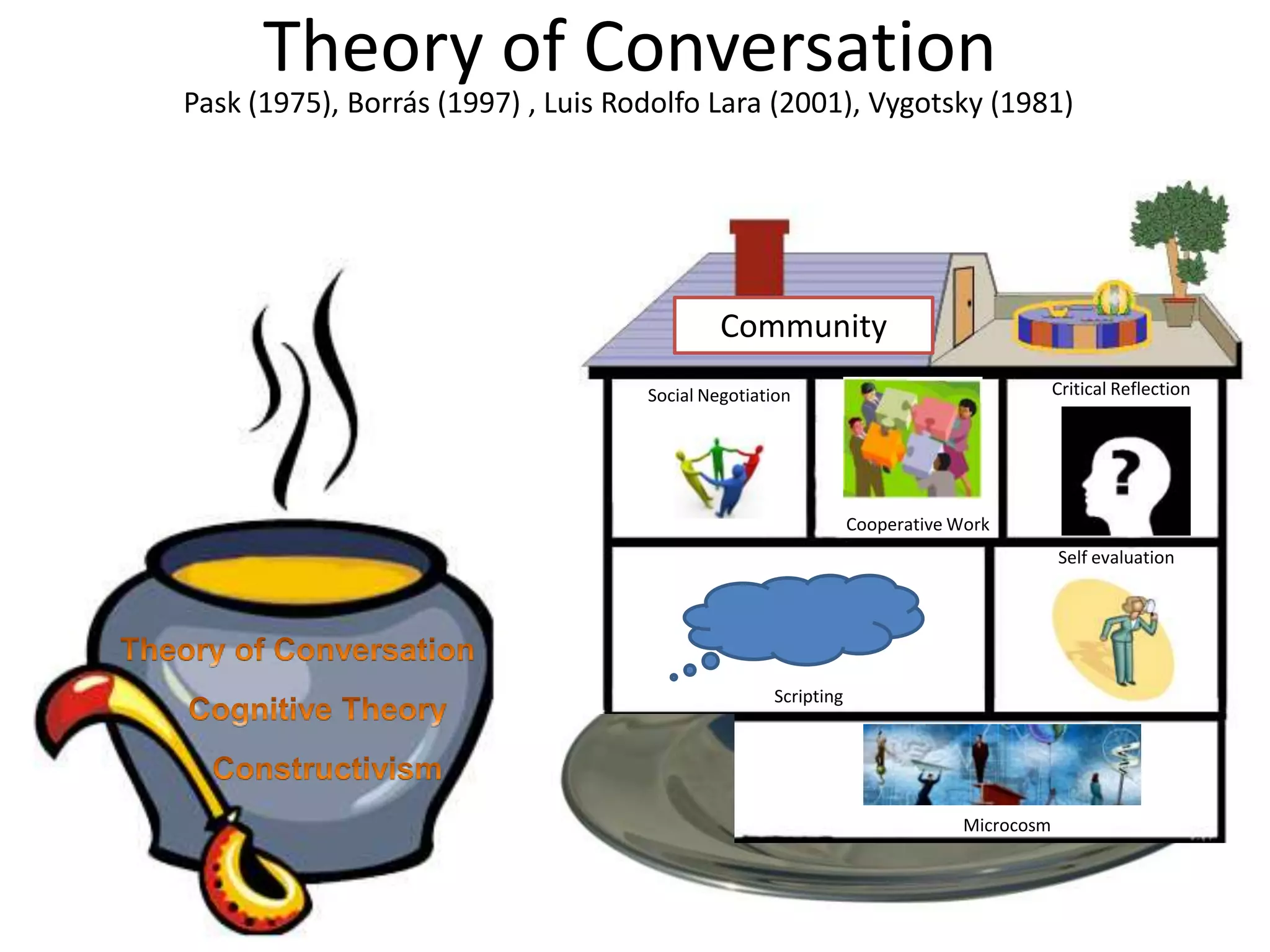
This document discusses various theoretical frameworks for distance education and ICT. It outlines three main categories of theories: independence and autonomy theories, theories of industrialization of teaching, and theories of interaction and communication. Specific theories discussed include the theories of independent study, Moore's theory of independent study, Peters' theory of industrialization of teaching, and theories emphasizing interaction and communication. The document also discusses applying these theories to designing distance learning environments using ICT and outlines pedagogical objectives for constructive learning environments.