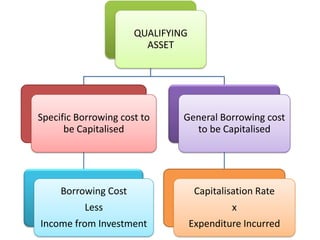
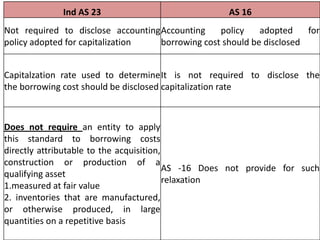
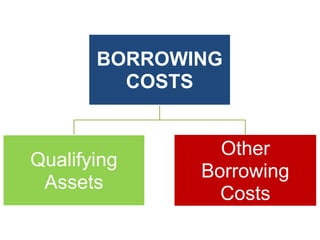
The document discusses the key aspects of accounting for borrowing costs as per Ind AS 23. It defines borrowing costs and qualifying assets. It covers the recognition, capitalization, suspension and cessation of capitalizing borrowing costs to qualifying assets. It also provides examples to illustrate the treatment of exchange differences and disclosures required.












![With regard to exchange difference required to be
treated as borrowing costs, the manner of arriving
at the adjustments stated therein shall be as follows
[Paragraph 6(e)]:
An amount which is equivalent to the extent to
which the exchange loss does not exceed the
difference between the cost of borrowing in
functional currency when compared to the cost of
borrowing in a foreign currency.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indas23-borrowingcost-130130092057-phpapp01/85/Ind-AS-23-borrowing-cost-14-320.jpg)