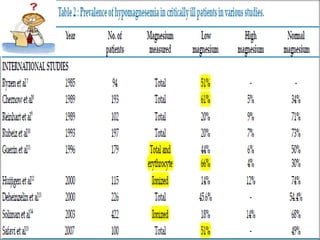
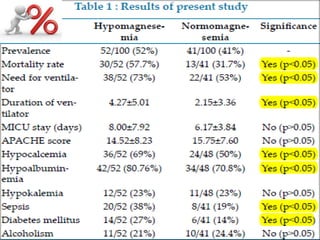
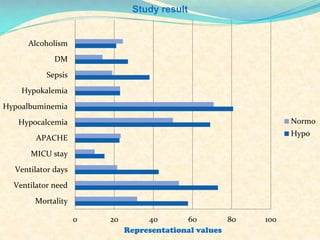
Hypomagnesaemia is a common electrolyte imbalance in critically ill patients that is associated with higher mortality and more frequent or prolonged need for ventilatory support. The study found hypomagnesaemia to be frequently associated with sepsis and diabetes mellitus in critically ill patients. While hypomagnesaemia's direct contribution to poor patient outcomes is unclear, correction of hypomagnesaemia through magnesium supplementation may have potential benefits for critically ill patients but requires further research.















![MAGNESIUM ESTIMATION
Specimen: non-hemolyzed serum or lithium heparin
plasma used. EDTA and citrate bind to the Mg.
24hr urine may be used and should be acidified to avoid
Ppt.
Colorimetric method/photometric[TITAN YELLOW]: Mg
binds to calmagite, formazen dye and methylthymol blue
to form a chromogen that is measure at 532- 600nm.
Ca2+ should be eliminated from the sample
AAS- absorbance at 285.2nm
ISE- free Mg with neutral carrier inonophores](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypomagnesemiaincriticallyillpatients-131125034908-phpapp01/85/Hypomagnesemia-in-critically-ill-patients-22-320.jpg)

