The document discusses various thyroid conditions including:
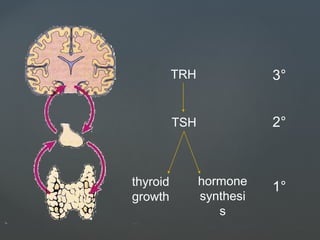
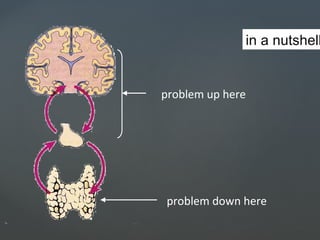
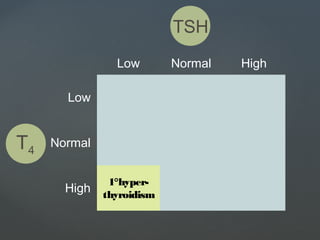
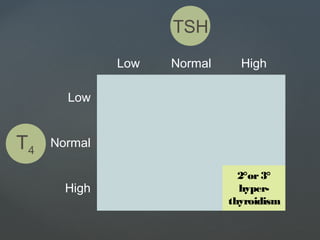
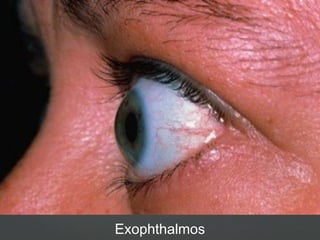
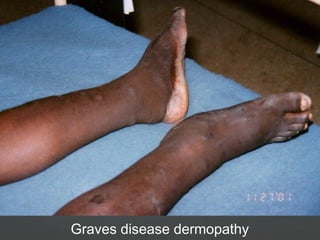
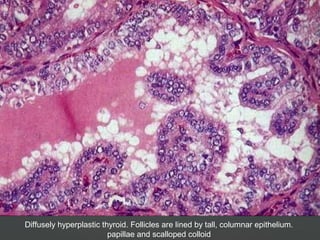
1) Hyperthyroidism which can be primary, secondary, or tertiary based on where the problem originates and causes signs of a hypermetabolic state. Graves disease is mentioned as the most common cause.
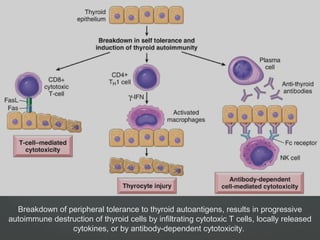
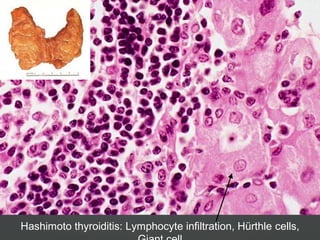
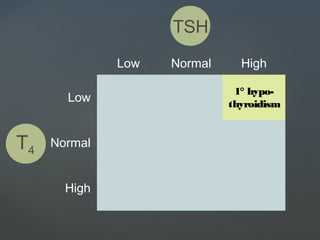
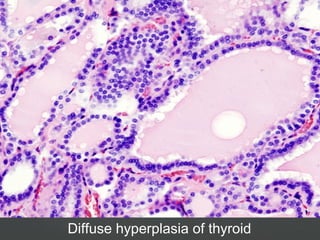
2) Hypothyroidism which also can be primary, secondary, or tertiary and causes a hypometabolic state. Causes mentioned include Hashimoto's thyroiditis which is the most common in the US.
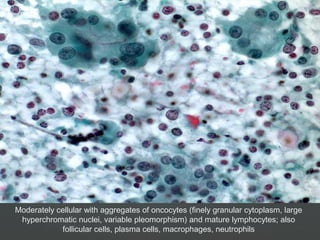
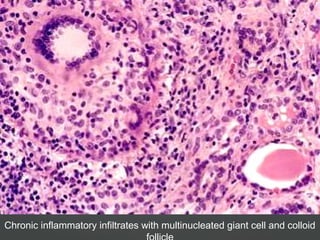
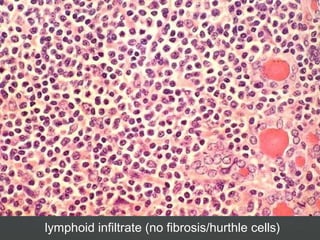
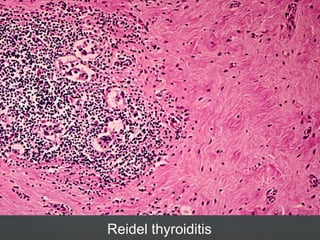
3) Specific thyroid conditions are described briefly including Hashimoto's thyroiditis, DeQuervain thyroiditis, subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis, and Riedel's thyroiditis.




![Diagnosis
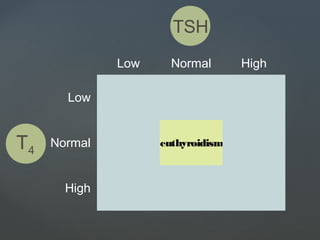
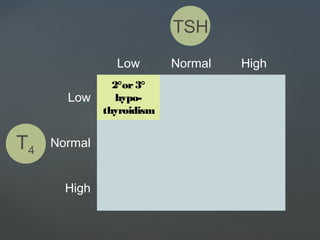
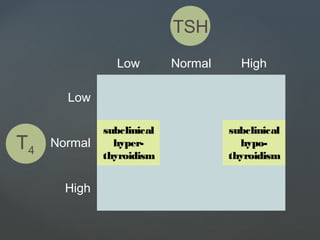
Lab Diagnosis :Lab Diagnosis : Low or suppressed TSH,
elevated free thyroxin
level (FT4)
[Normal value TSH – 0.46 – 5.68
mcIU/ml
FT4 – 10.0 – 28.2 pmol/L]
• 10% of patients have an increased total or free T3 level and
normal T4 level with suppressed TSH level, a condition
called "T3 toxicosis“ [Normal FT3 – 4.26 – 8.10 pmol/L]
• In Graves disease, elevated levels of antitopoisomerase
antibodies and antithyroglobulin antibodies are found in 80%
and 50% of cases, respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypo-hyperthyroidism-180710160349/85/Hypo-and-Hyper-Thyroidism-13-320.jpg)



![• Causes:
• endemic iodine deficiency,
• genetic problems (inborn error of thyroid metabolism
[dyshormonogenetic goiter])
• Thyroid agenesis [PAX8, FOXE1, TSH receptor mutations]
• Thyroid hypoplasia
• Symptoms are mild to severe
• Treatment: thyroid hormone replacement
• Prevention better
Congenital Hypothyroidism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypo-hyperthyroidism-180710160349/85/Hypo-and-Hyper-Thyroidism-21-320.jpg)