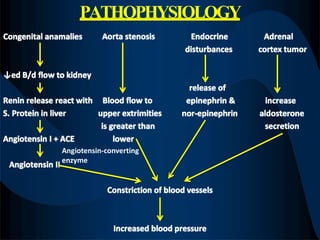
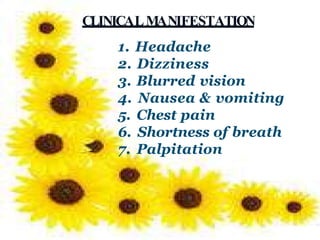
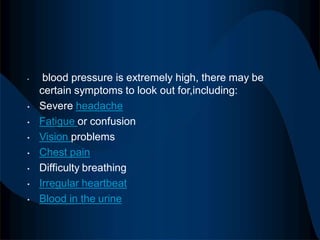
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, is when blood pressure is consistently higher than normal levels. There are two main types of hypertension - primary/essential hypertension which has no identifiable cause and occurs in 95% of hypertensive patients, and secondary hypertension which is caused by an underlying condition and occurs in 5% of patients. Risk factors for developing hypertension include increasing age, family history, being overweight, lack of exercise, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain chronic conditions. Symptoms of severe hypertension can include headaches, confusion, vision issues, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like diet changes and exercise as well as medications to lower blood pressure. Uncontrolled hypertension can increase the risk of heart attack, stroke