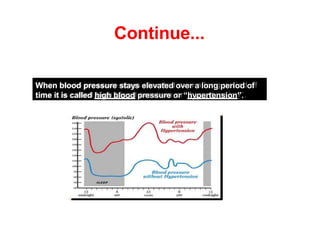
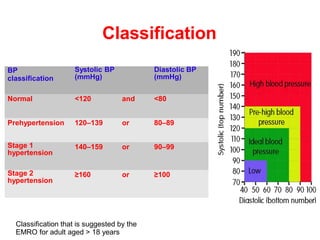
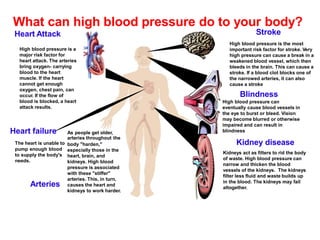
The document provides an overview of hypertension, including its definition, classification, and predisposing factors. It highlights the risks associated with high blood pressure, such as heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease, while also suggesting preventive measures to maintain healthy blood pressure levels. Key recommendations include managing weight, increasing physical activity, and adopting a low-sodium diet.