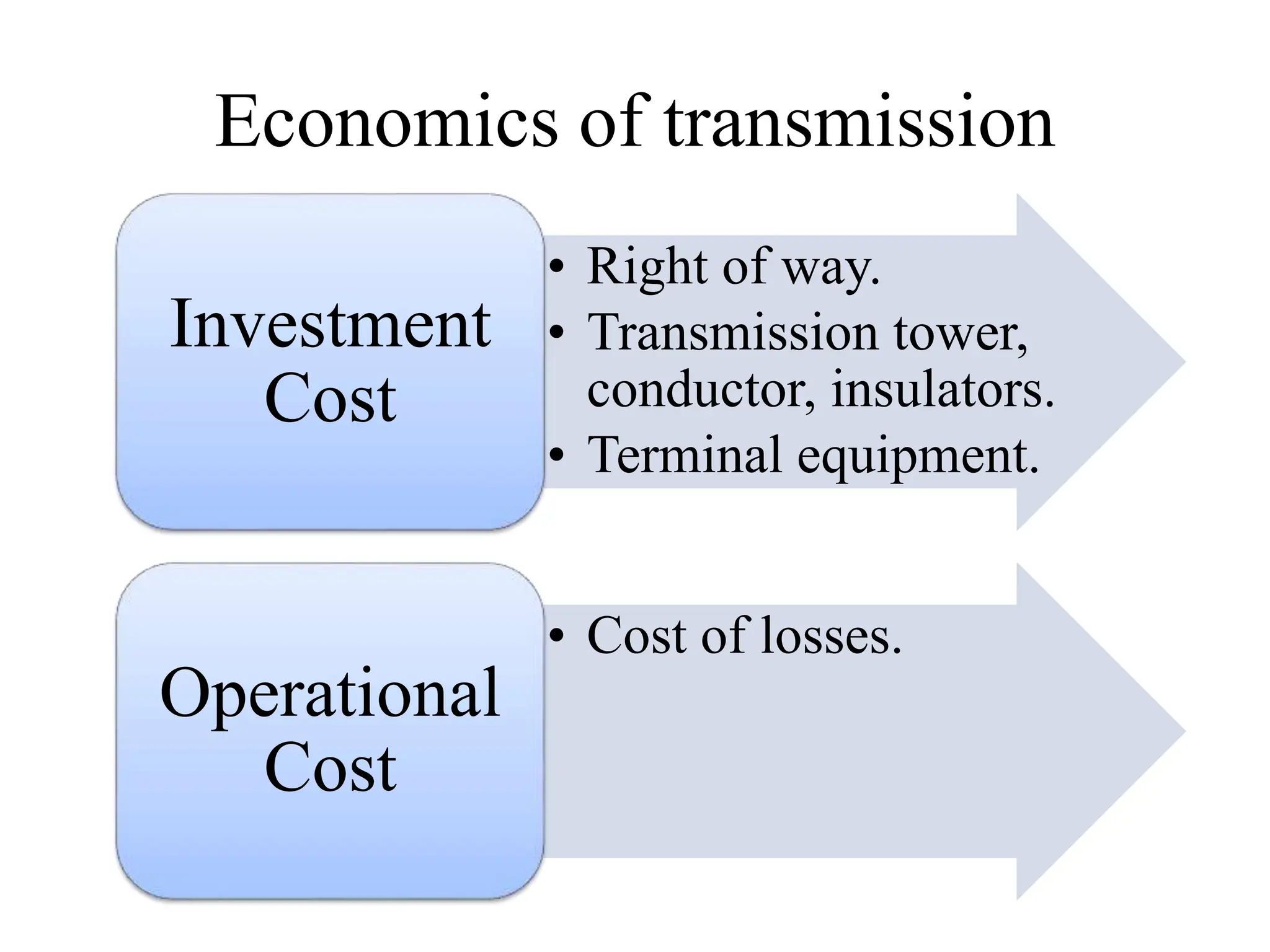
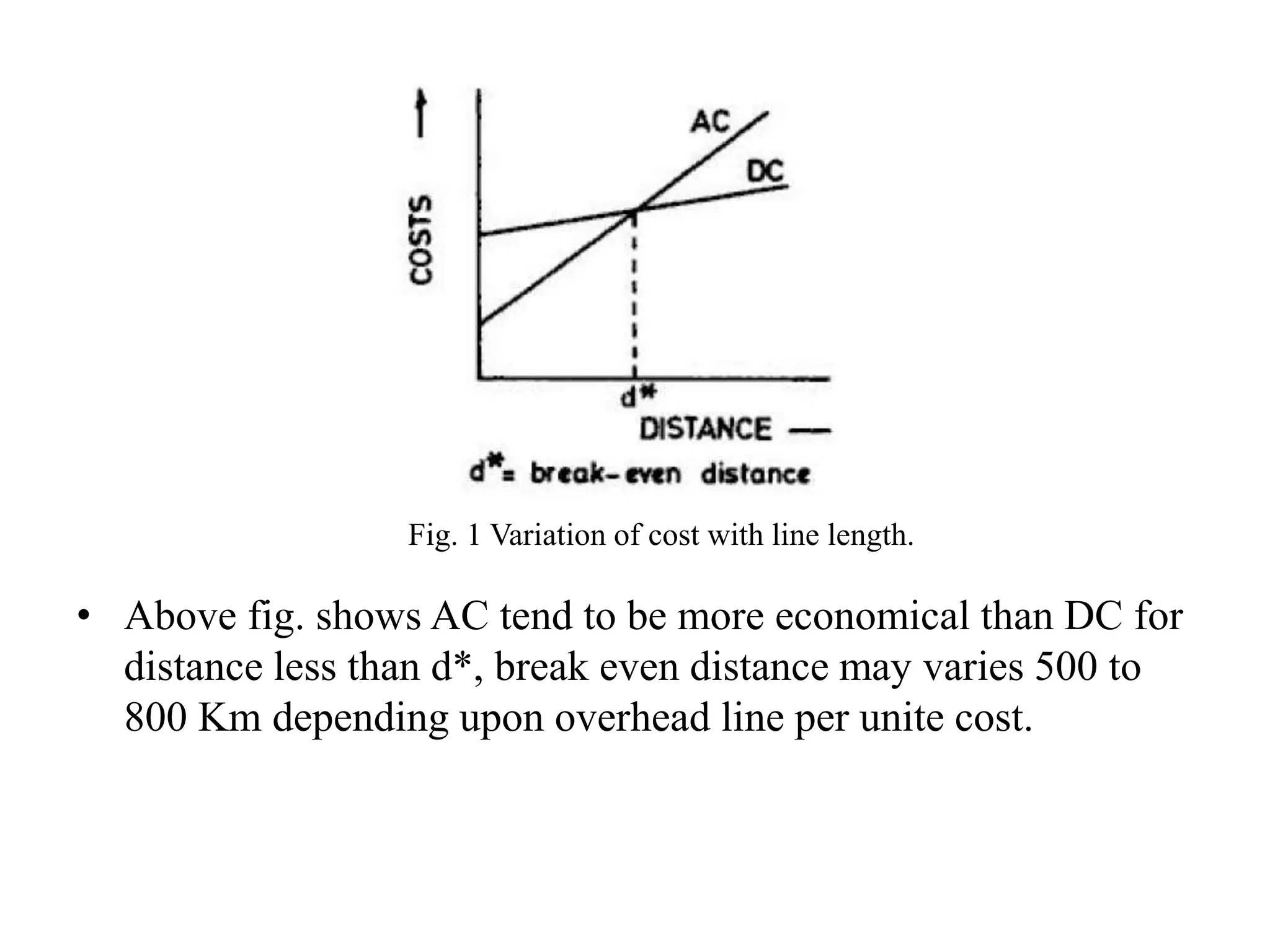
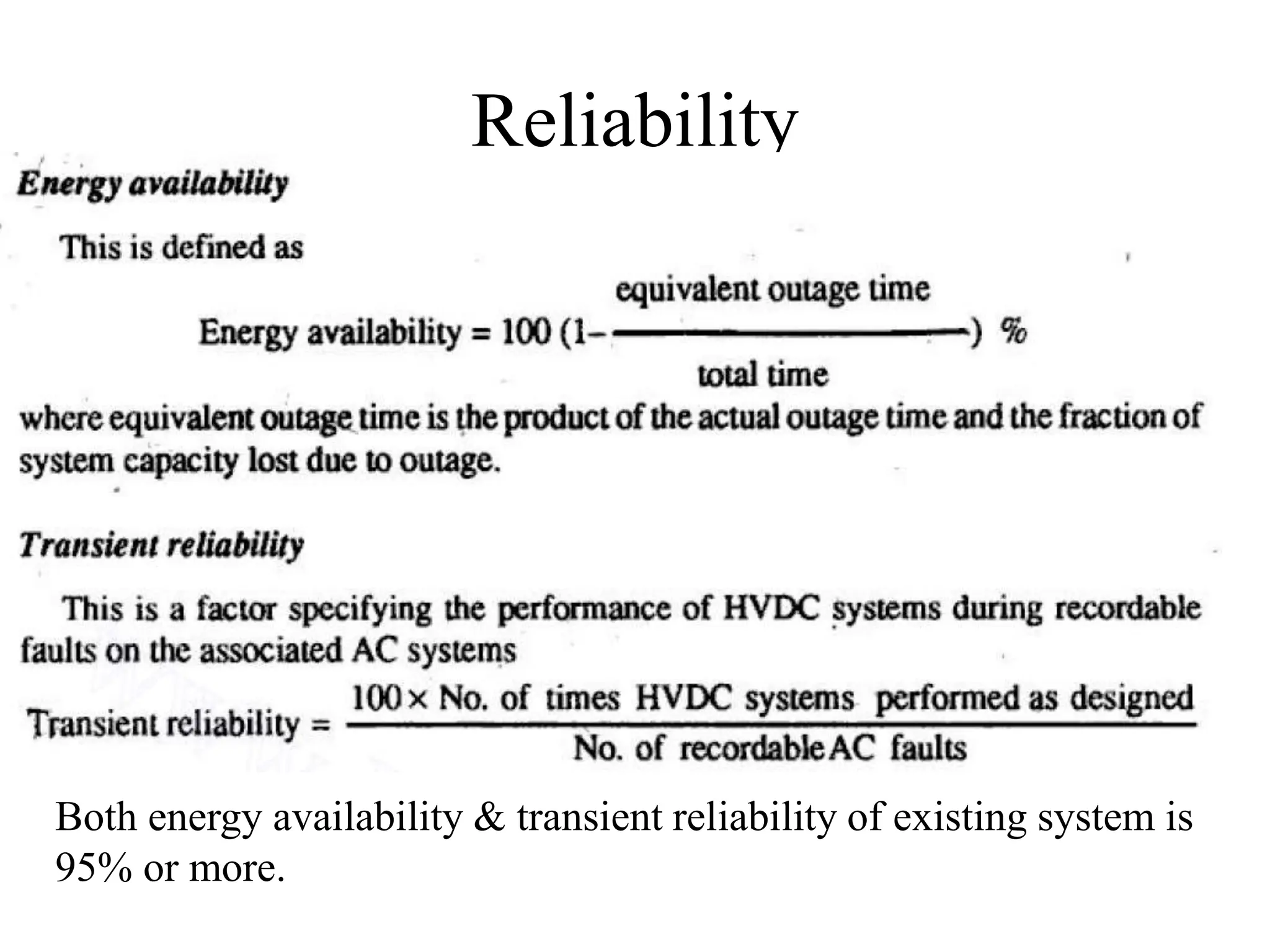
AC transmission is typically more economical than DC for distances less than 500-800 km. DC transmission has technical advantages like full control of transmitted power, improved stability, and fast fault current limiting. While DC requires less land, simpler towers and conductors, it has higher costs for conversion equipment and lacks transformers for voltage changes. Both AC and DC systems can achieve 95% or more reliability when considering energy availability and transient performance.