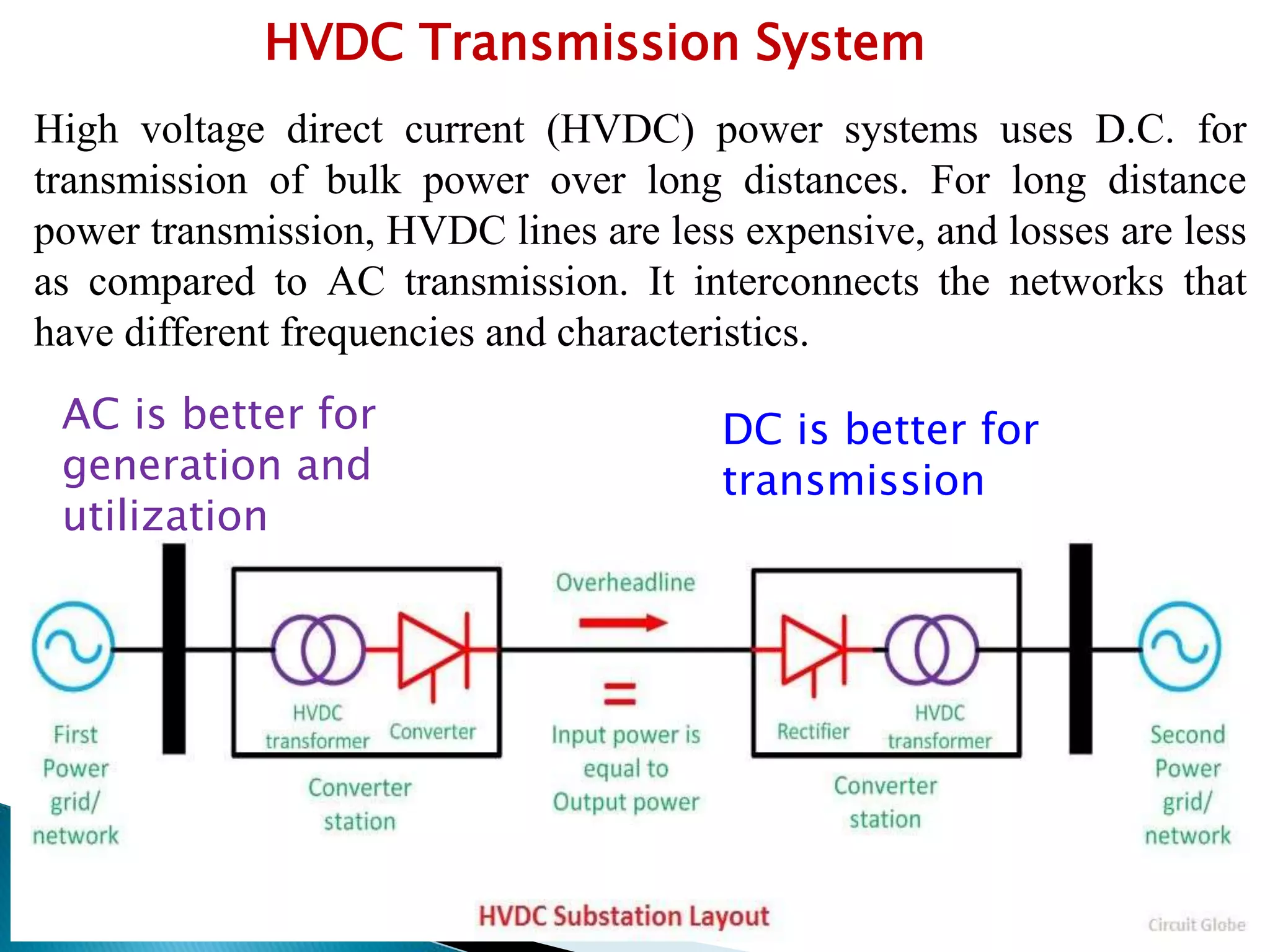
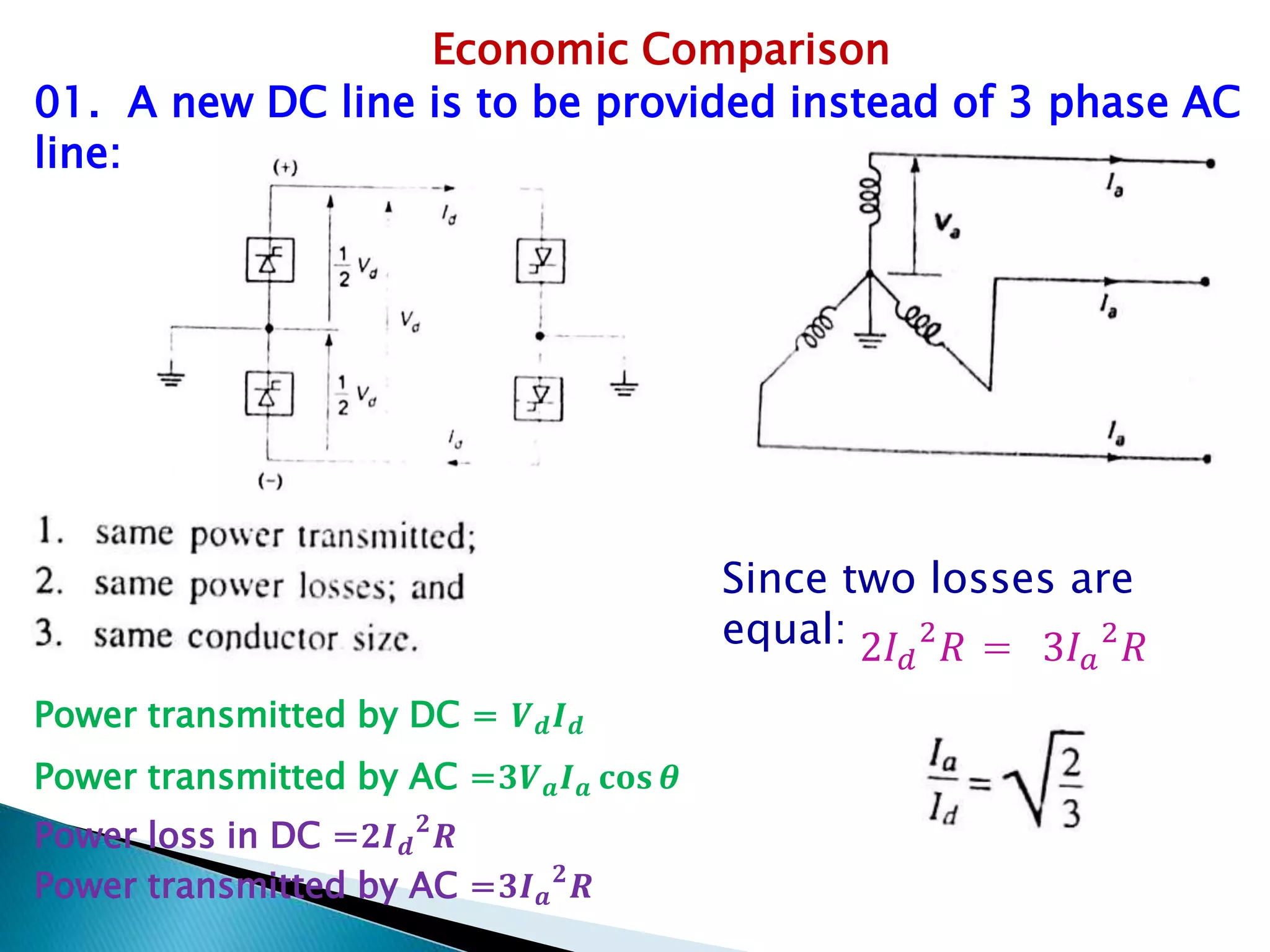
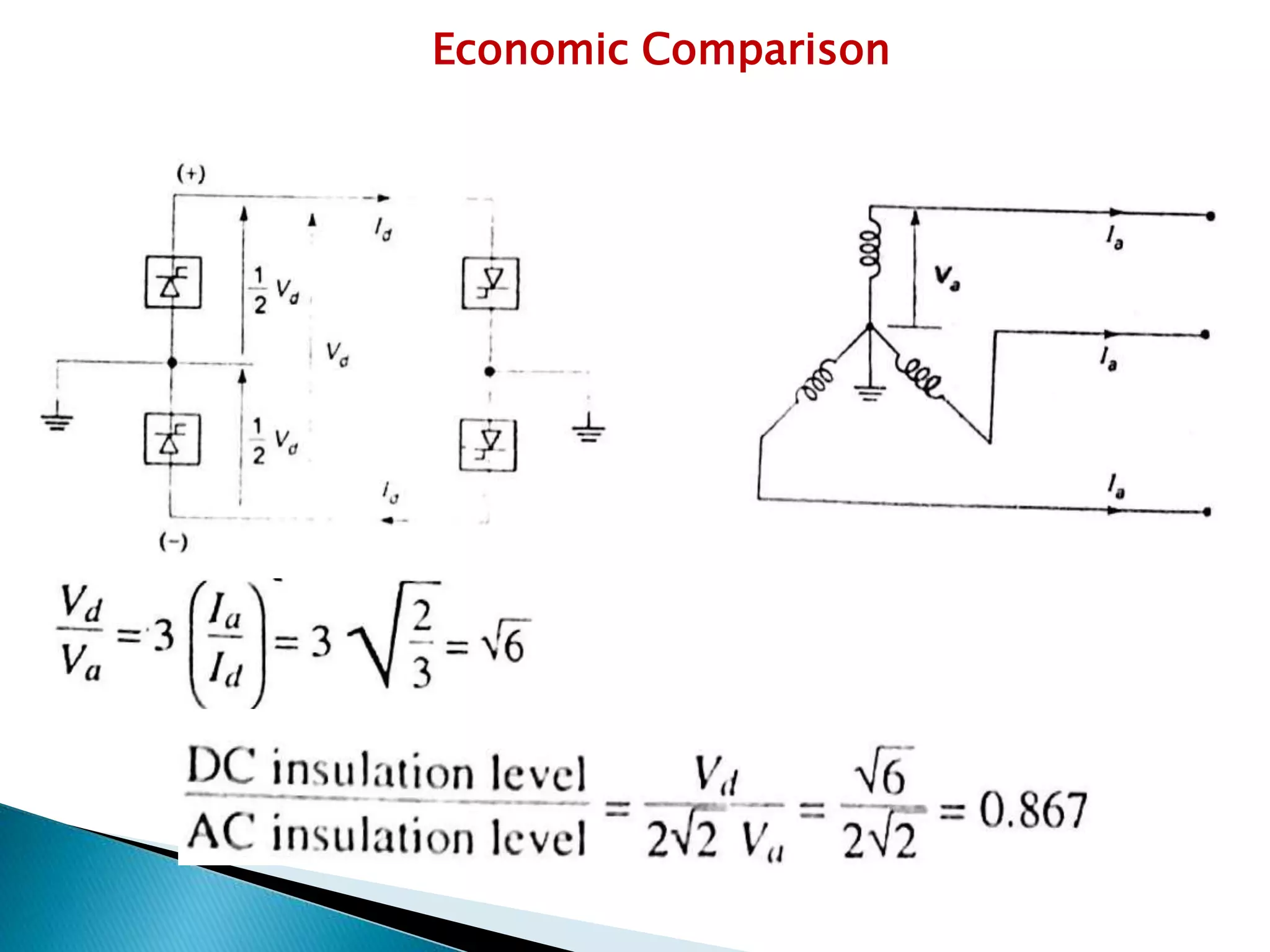
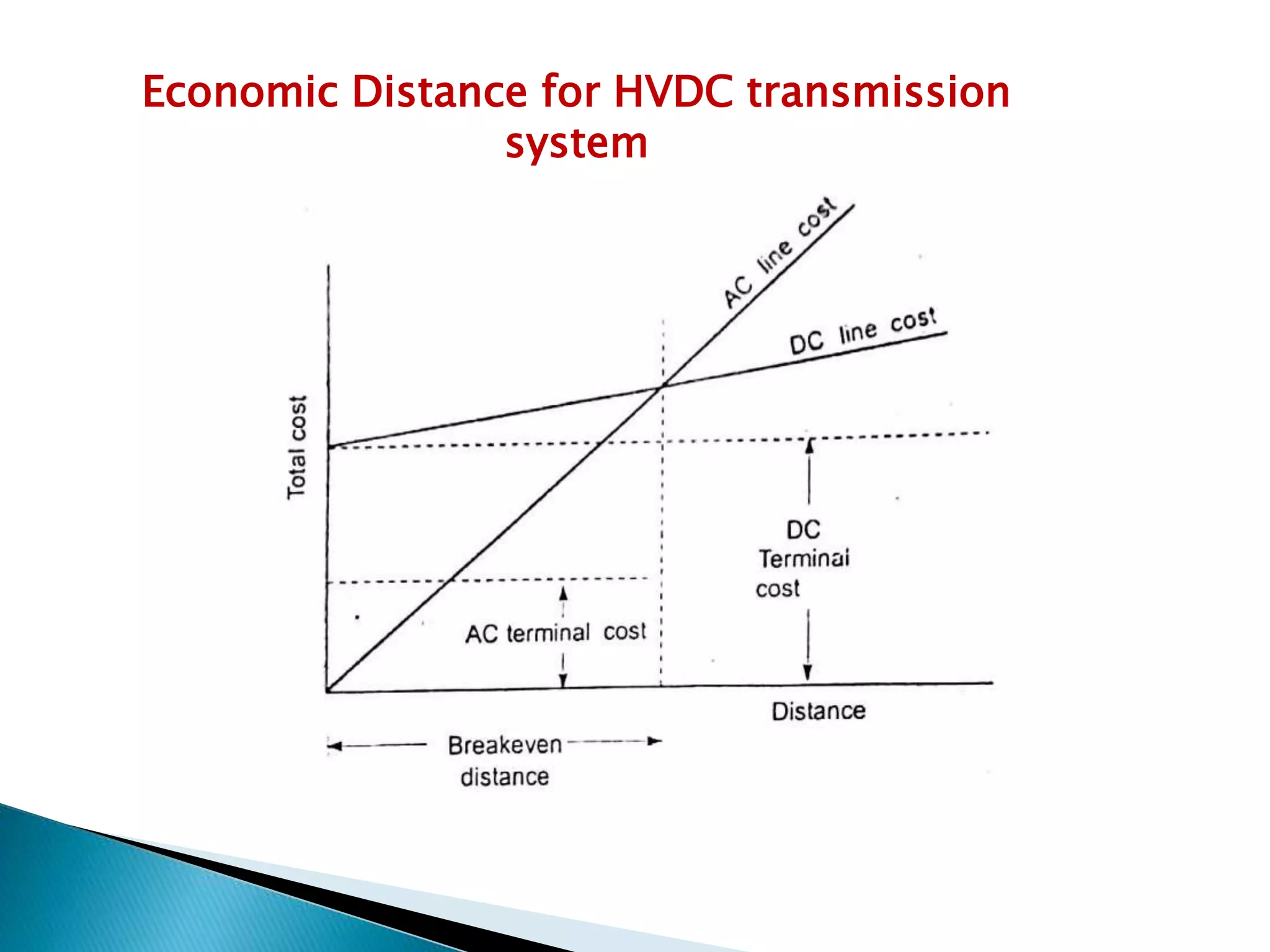
1. HVDC transmission uses direct current for the bulk transmission of power over long distances, as it is less expensive and has lower losses compared to AC transmission.
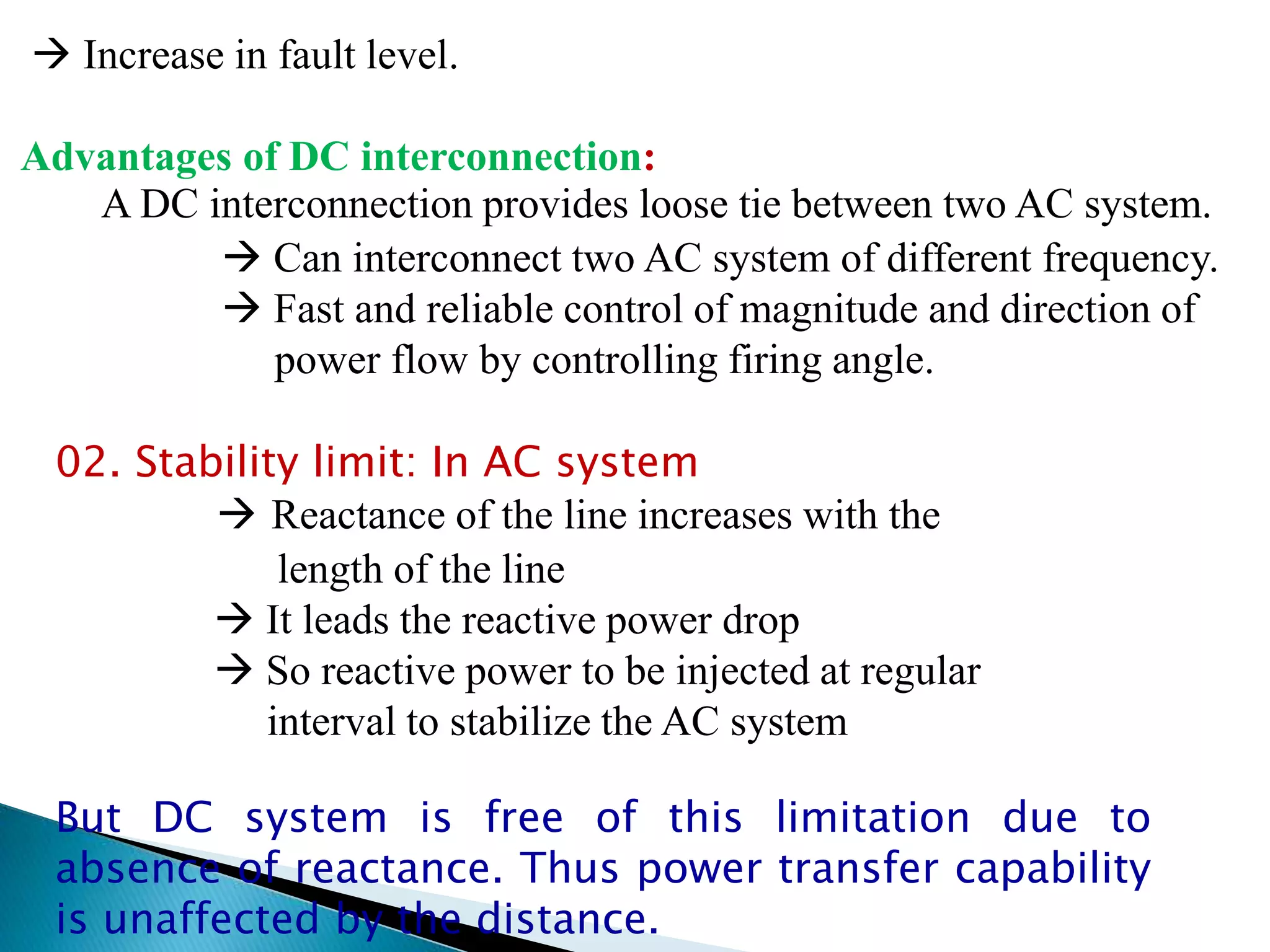
2. HVDC transmission can interconnect power networks with different frequencies and characteristics.
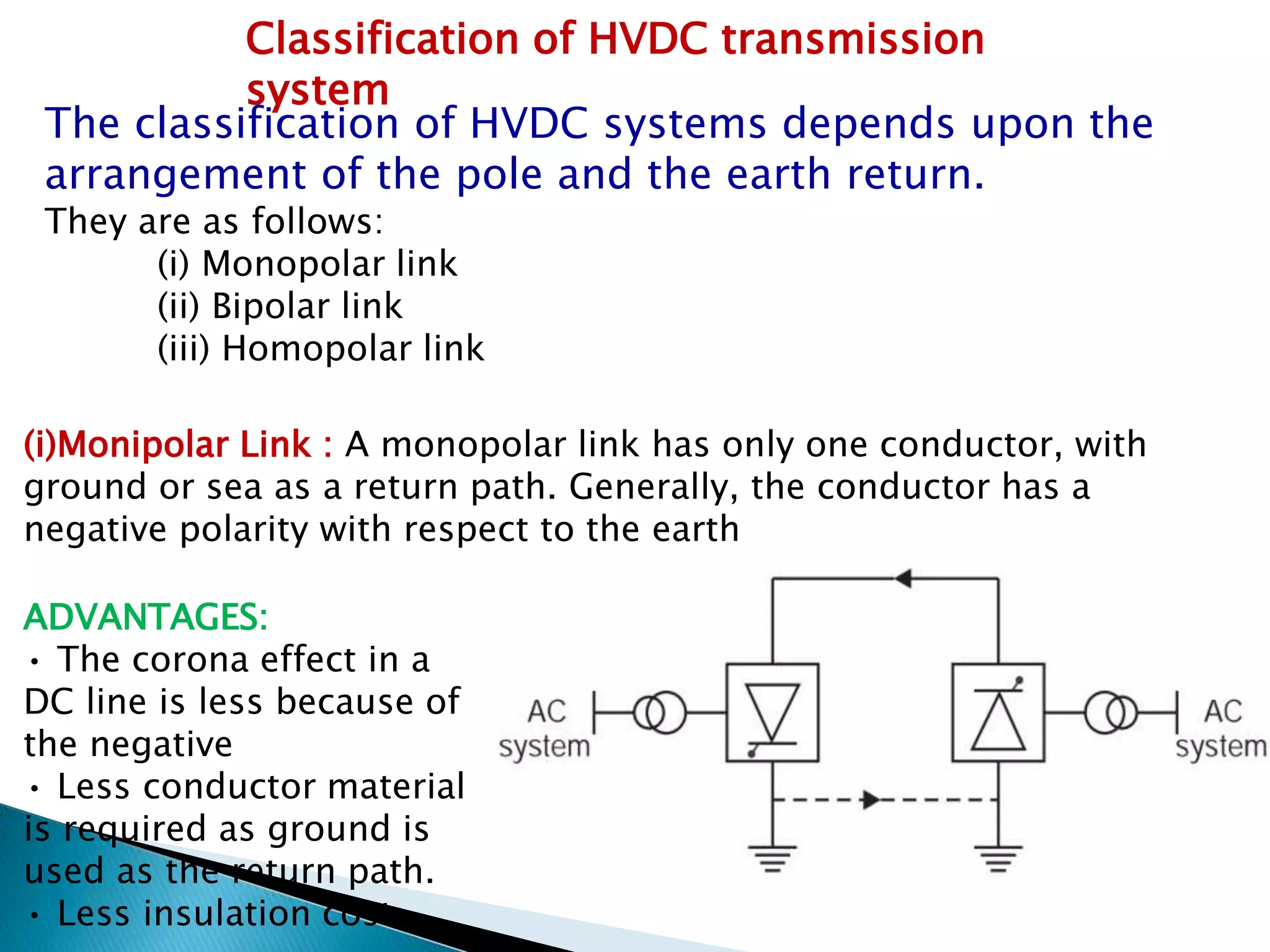
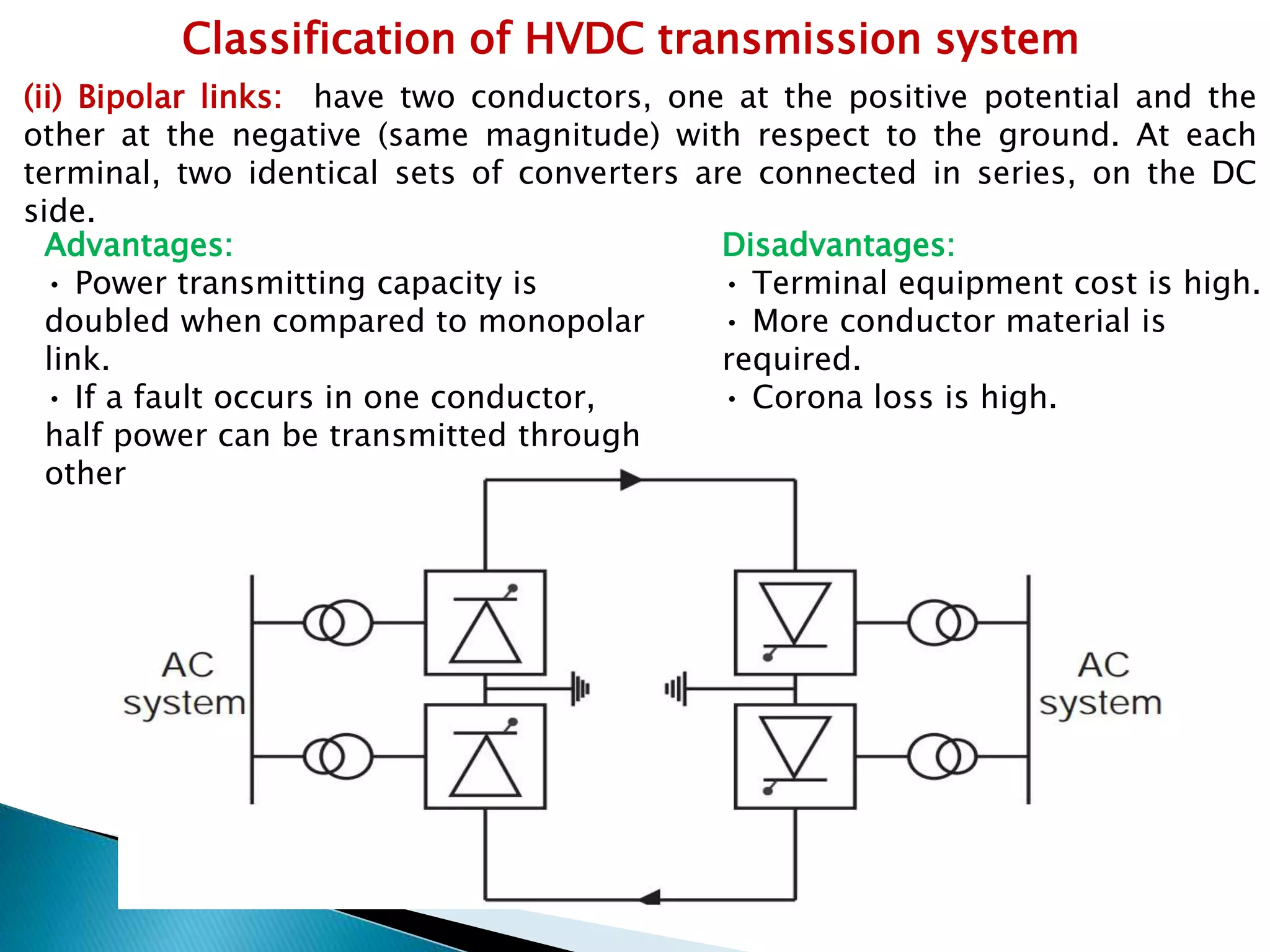
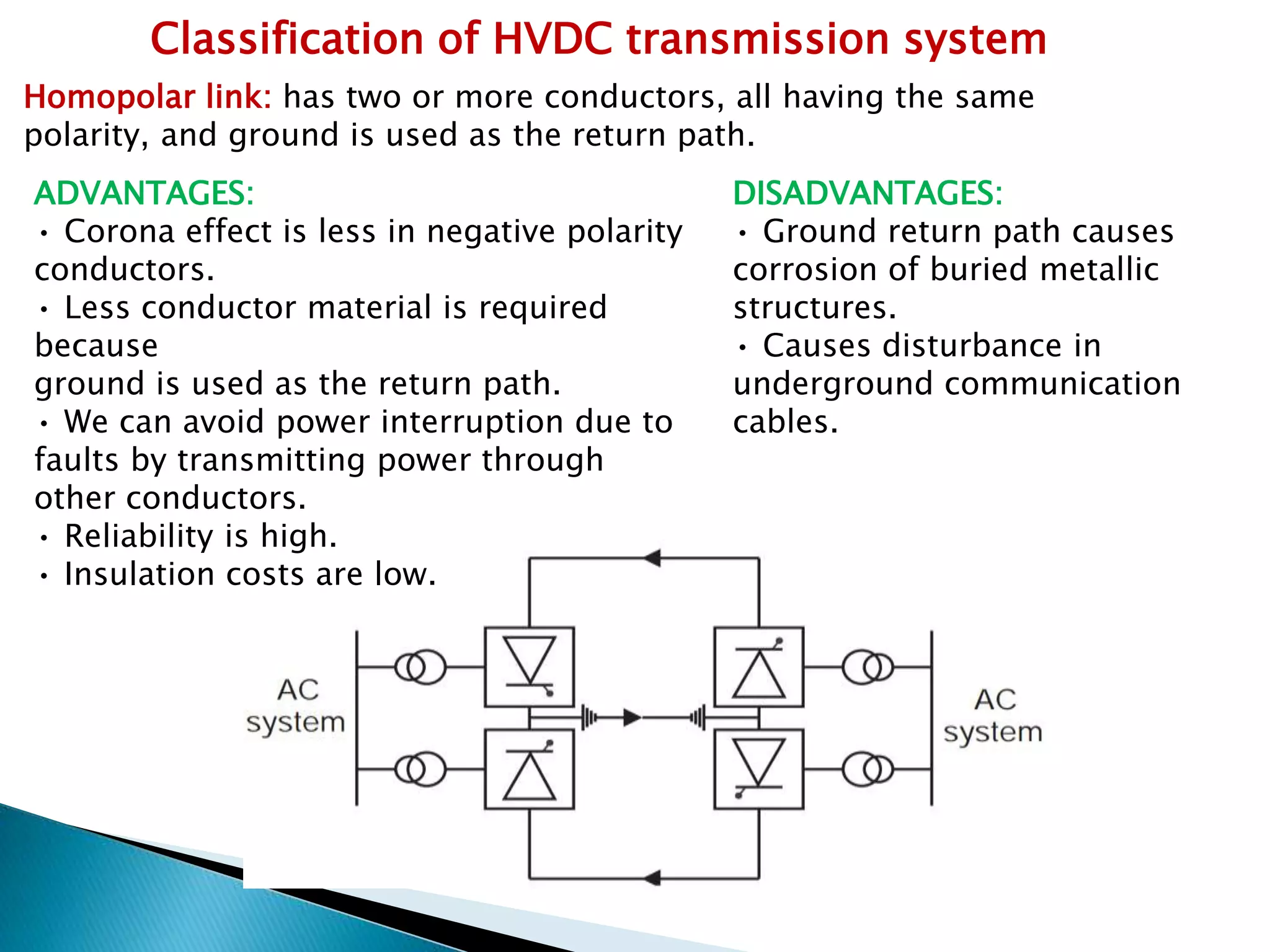
3. HVDC transmission systems are classified as monopolar, bipolar, or homopolar depending on the arrangement of poles and the use of earth return. Bipolar links transmit twice the power of monopolar but have higher costs.