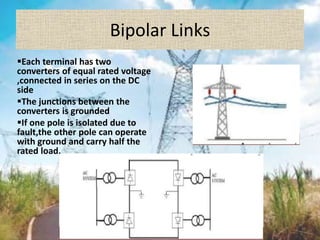
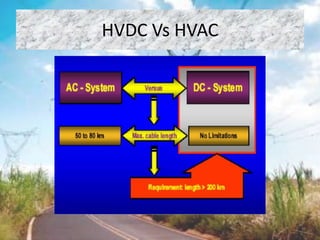
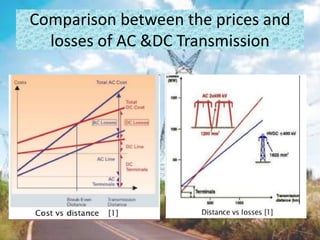
This document discusses HVDC (high voltage direct current) transmission technology. It begins with an introduction that defines HVDC and explains its use for long distance and submarine cable power transmission. It then categorizes different types of HVDC systems and configurations, including monopolar, bipolar, and homopolar links. Key components of HVDC systems like converters, smoothing reactors, and reactive power supplies are also outlined. The document compares HVDC to HVAC transmission and lists advantages like lower transmission losses over long distances. It concludes by noting that while HVDC has high initial costs, the overall costs are lower than HVAC transmission due to reduced line losses and maintenance needs.