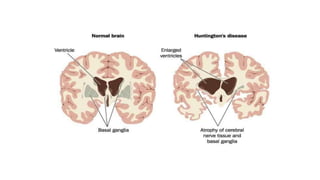
Huntington's disease is a hereditary, progressive neurological disorder characterized by the degeneration of brain cells, leading to chorea and cognitive decline. Common symptoms include involuntary movements, mood changes, and difficulties with coordination and speech, progressing through early, middle, and late stages of severity. Diagnosis involves medical history and imaging tests, while management includes medication, therapy, and psychological support.