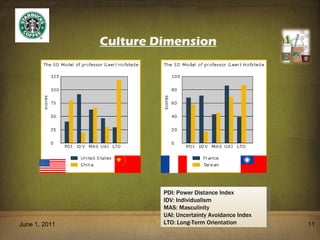
The document provides an overview of Starbucks' history, culture, operations, and employee programs. It discusses how Starbucks was founded in 1971 and has since expanded globally. It also summarizes Starbucks' focus on cultural diversity and inclusion, talent staffing and development, and community involvement through philanthropic initiatives. Starbucks aims to create an empowering work environment for employees while respecting local cultures as it continues to grow internationally.