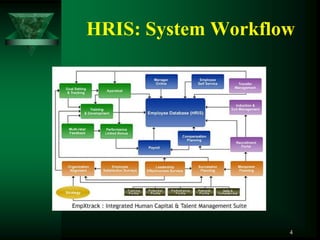
The document discusses auditing the human resources (HR) function of an organization. It covers dimensions of HR auditing including legal compliance, functional effectiveness, and strategic alignment.
Key aspects of the HR audit process include defining the audit scope and statements, accessing current HR policies, practices, and data through documentation reviews and interviews, and analyzing the results to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement. The audit aims to evaluate if HR supports business objectives and strategies, complies with employment laws, and delivers services efficiently. Ratios on costs, productivity, and turnover are also examined.