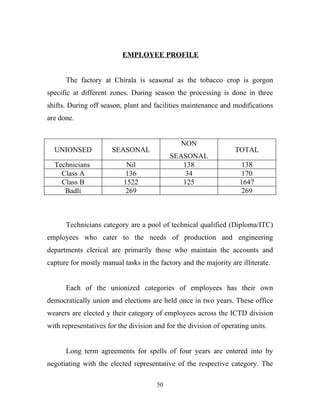
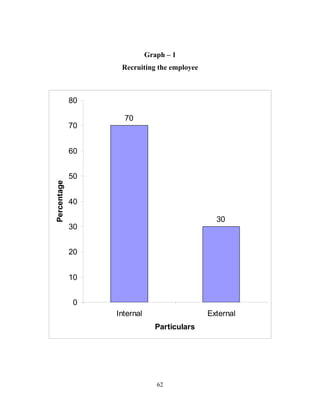
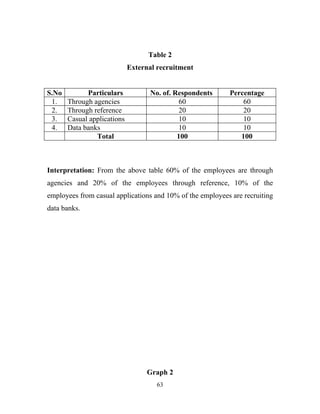
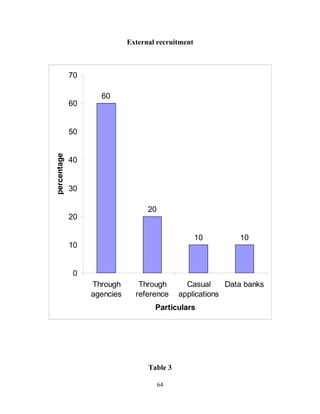
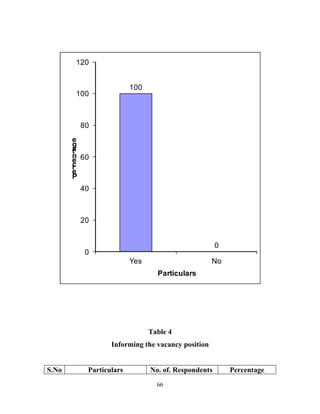
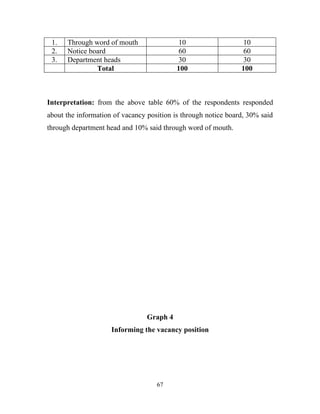
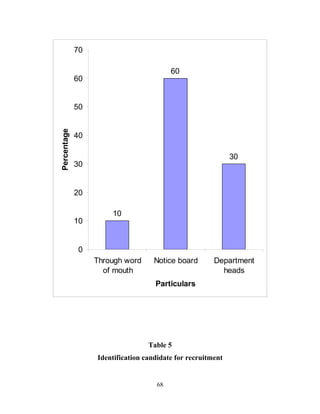
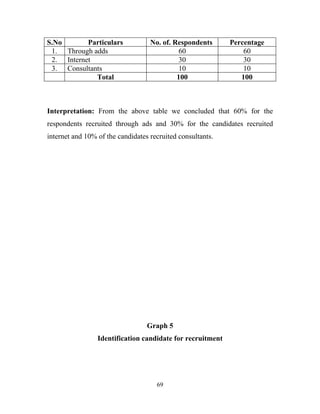
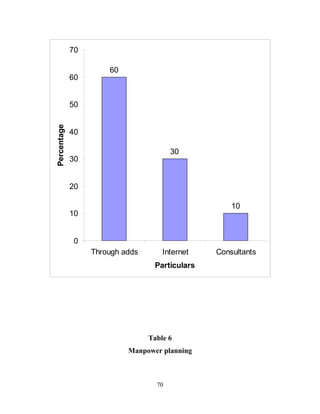
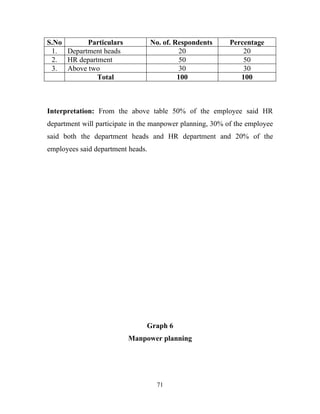
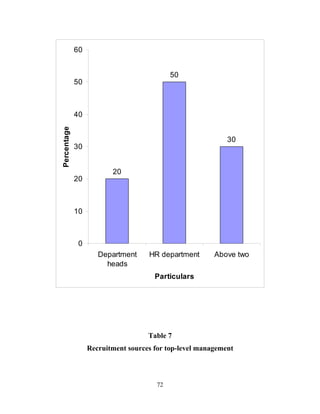
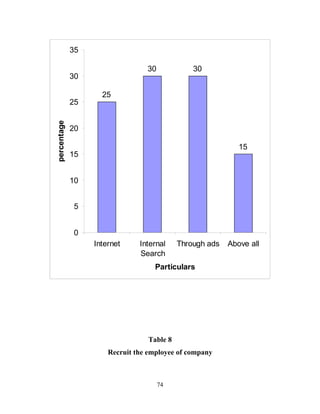
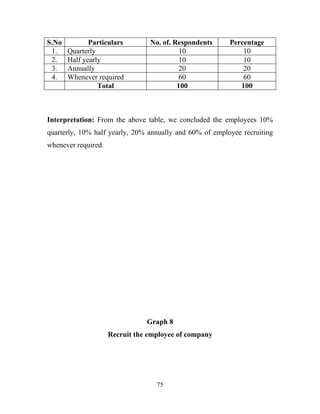
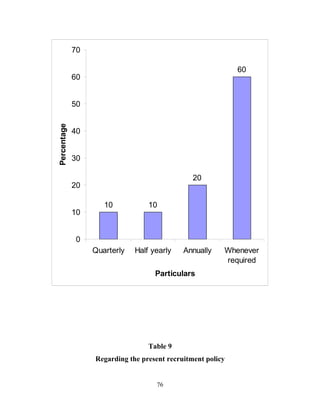
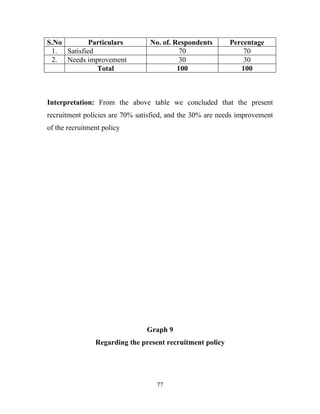
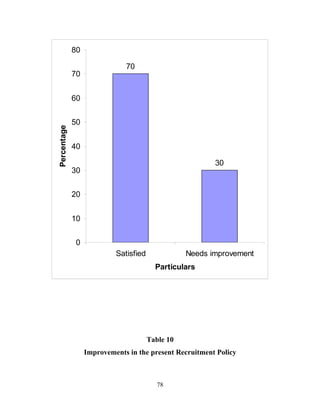
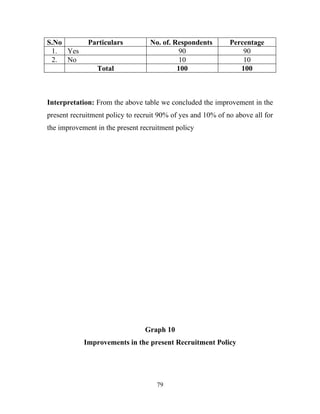
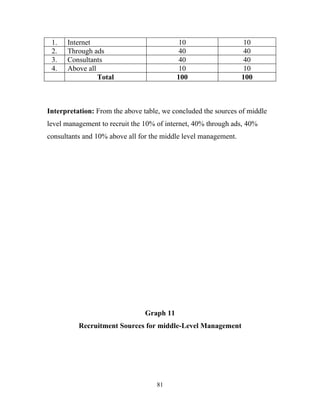
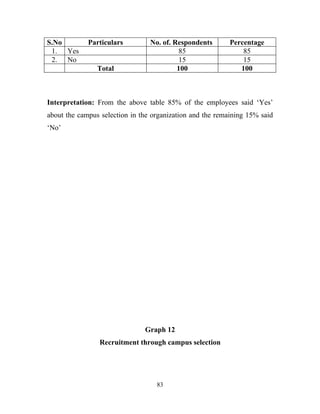
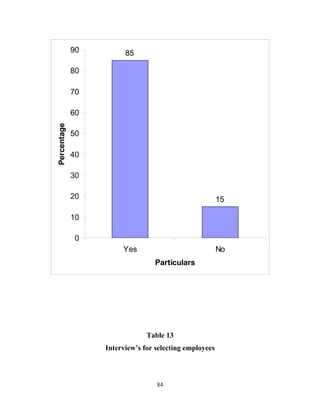
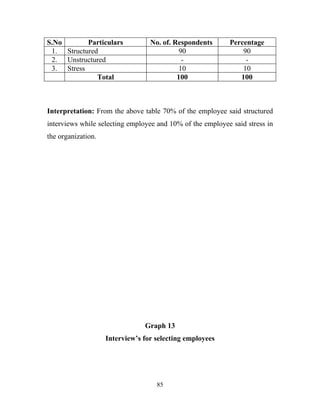
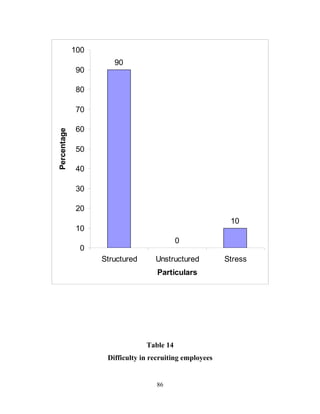
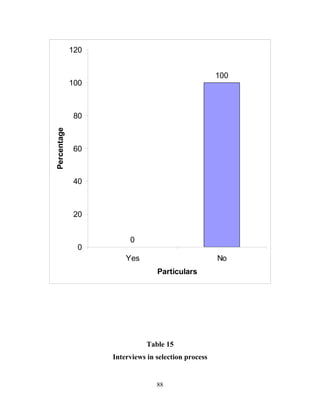
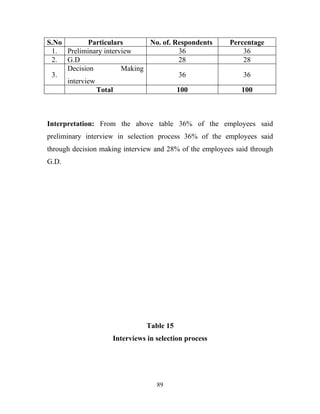
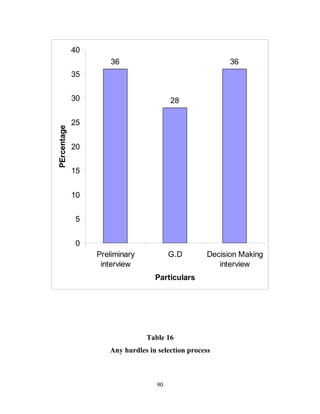
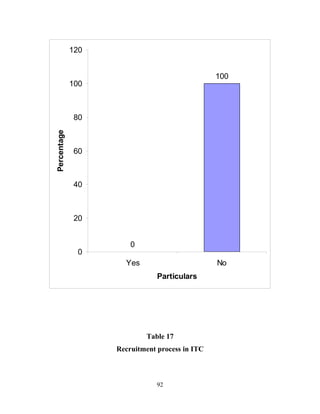
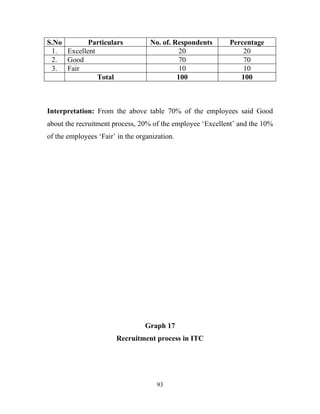
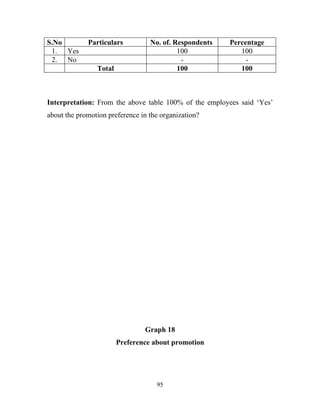
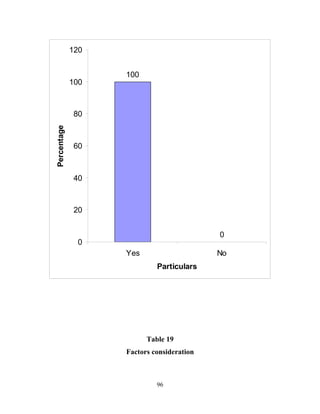
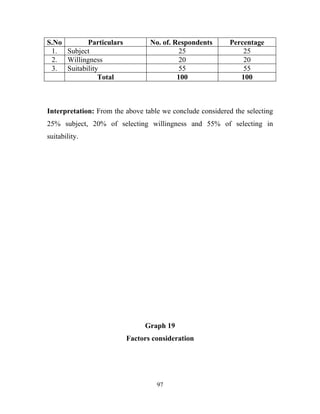
The document discusses the recruitment and selection process within organizations. It begins by explaining the importance of human resource planning and management for organizational success. It then describes the key objectives and functions of human resource departments, including recruitment and selection. The next sections provide details on the recruitment process, including sources of recruitment both internal and external. It also discusses some common constraints on recruitment. Finally, it outlines the typical steps in a selection process, including application screening, testing, interviews and making a final job offer. The overall summary is that effective recruitment and selection processes are important for organizations to identify and hire the right employees.