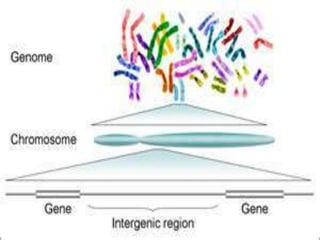
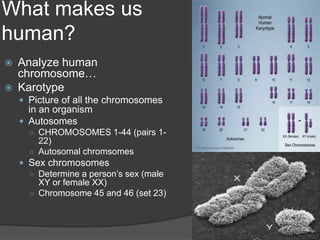
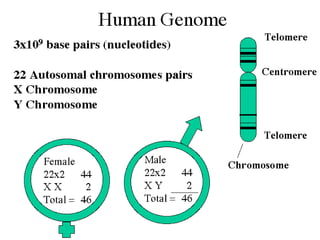
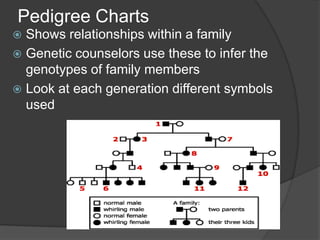
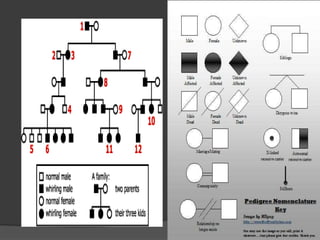
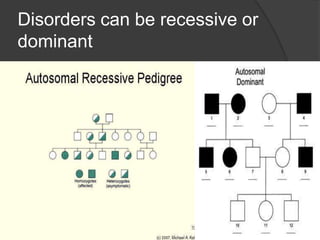
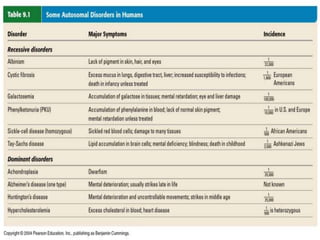
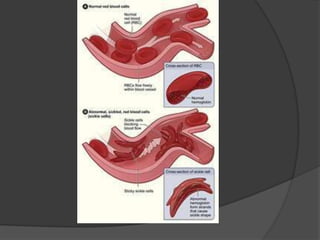
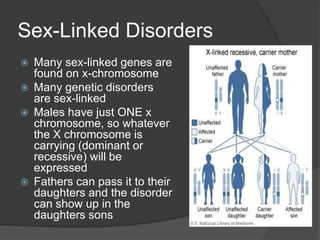
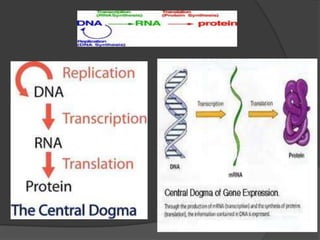
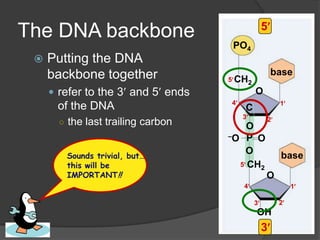
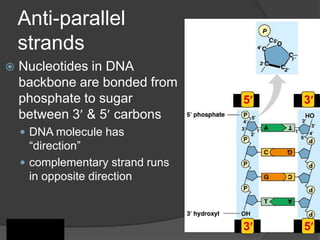
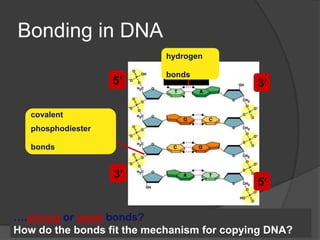
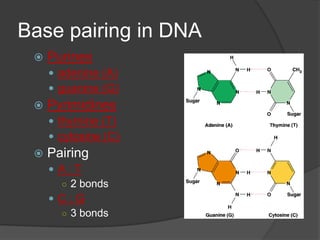
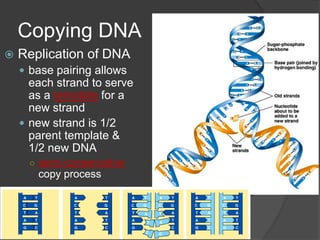
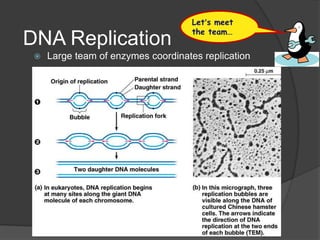
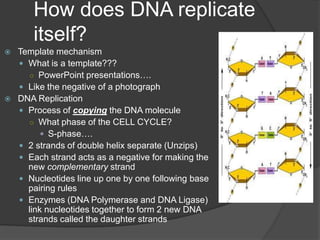
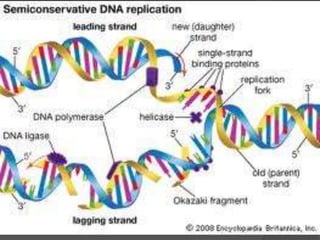
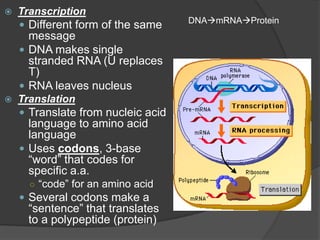
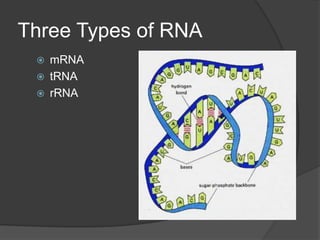
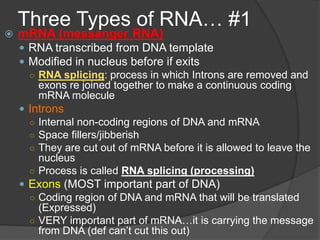
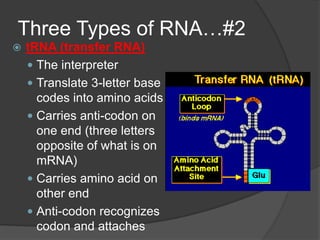
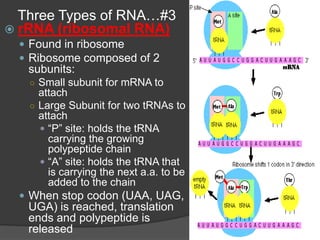
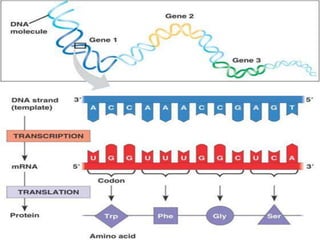
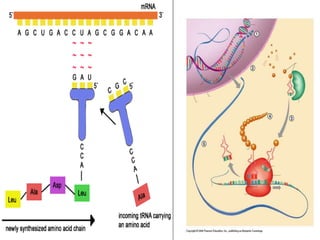
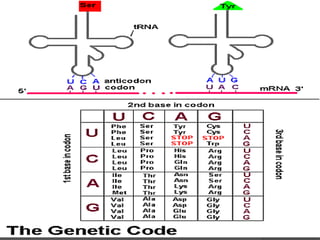
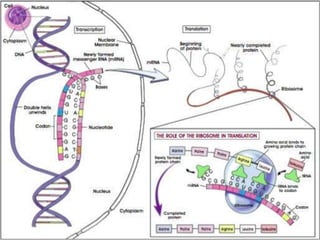
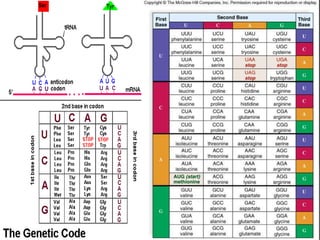
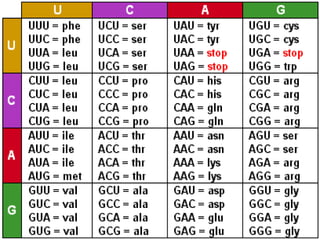
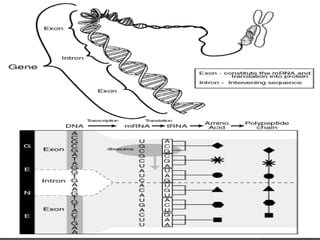
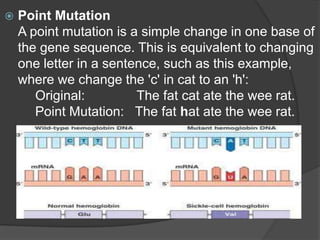
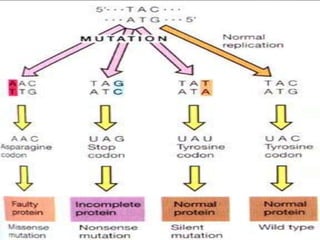
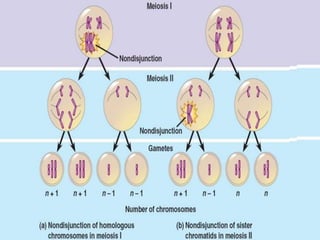
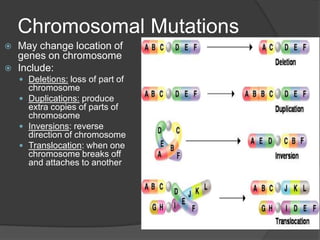
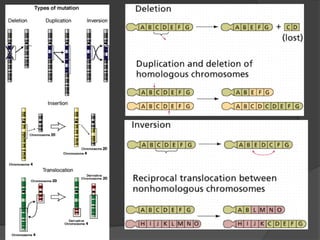
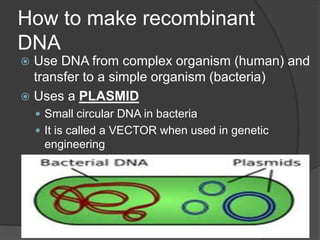
Here are the key types of point mutations:
- Base substitution: Replacement of one base or nucleotide with another. This can sometimes cause a change in the protein made.
- Silent mutation: A base substitution that does not cause a change in the protein expressed by a gene, such as when different codons code for the same amino acid.
- Missense mutation: A base substitution that results in a different amino acid being incorporated into the protein. This often impairs the protein's function.
- Nonsense mutation: A base substitution that creates a stop codon, causing premature termination of protein synthesis. This usually results in a nonfunctional protein.
So in summary, point mutations are single base changes that