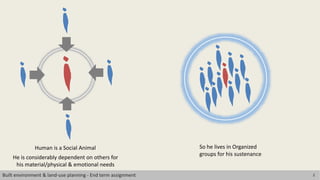
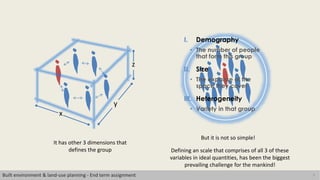
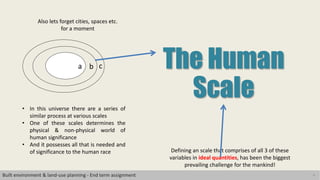
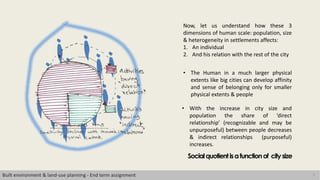
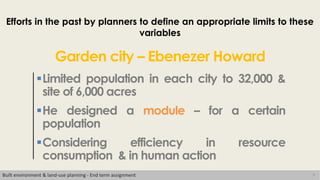
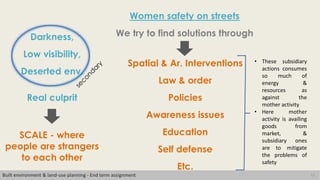
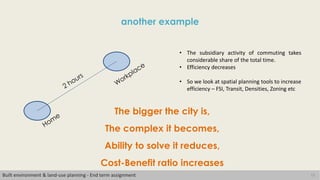
This document discusses the concept of human scale in urban planning. It defines human scale as comprising three dimensions: population size, physical size of the space, and heterogeneity. Maintaining an ideal balance across these three dimensions has been a challenge for planners. The document argues that as city size and population increase, social relationships decrease and become more indirect. It examines how human scale affects individuals and their relationships within cities. Historical examples of efforts to define limits on city size and population are provided. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of considering scale in planning approaches to identify an appropriate human scale.