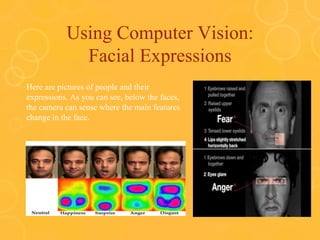
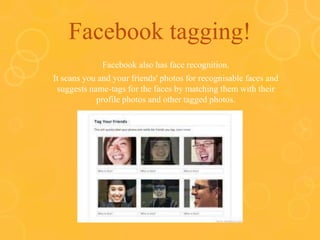
Computer vision can be used for many applications like facial expression detection, camera mice that move the cursor based on head movements, detecting text and defects. It allows those with limited mobility to interact with computers. Computer vision tasks include image processing, feature extraction, object detection and more. Major applications include manufacturing defect detection, barcode and text reading, and computer vision is a key technology enabling self-driving cars.