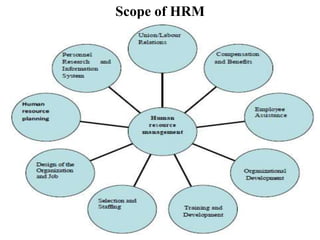
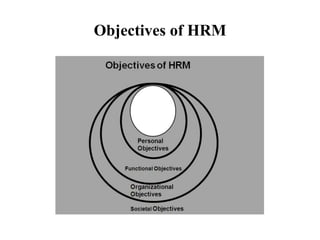
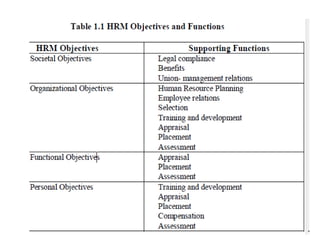
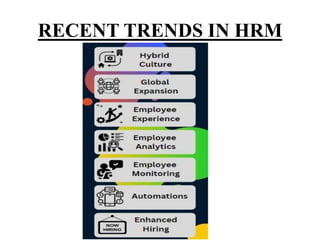
The document discusses several key aspects of human resource management including:
1. The management process and functions of HRM like planning, organizing, staffing, leading, and controlling.
2. The objectives of HRM which include developing human capital, organizational climate, performance standards, and employer-employee relationships.
3. The roles and responsibilities of HR managers in facilitating development, communication, and achieving organizational objectives.