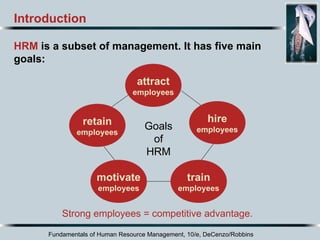
This document discusses the key roles and goals of human resource management (HRM) in a changing global environment. It outlines how HRM must adapt to technological advances, workforce diversity, and continuous changes. The roles of HRM include attracting, retaining, and training employees while ensuring ethical compliance and monitoring the labor supply and economic conditions.