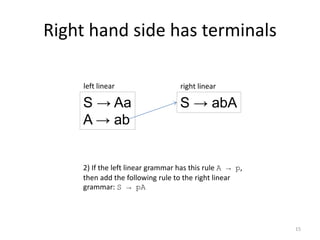
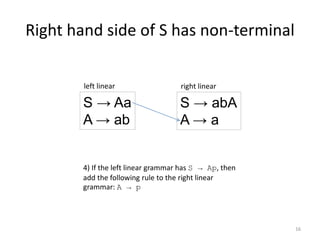
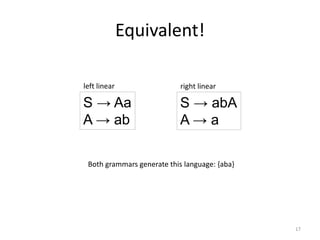
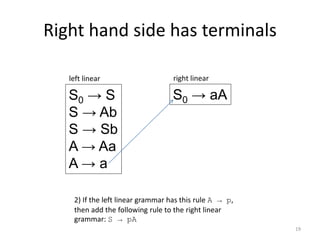
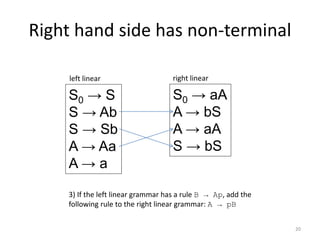
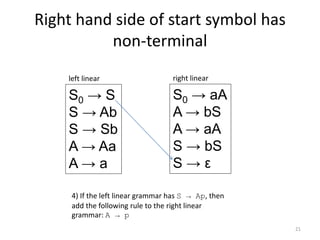
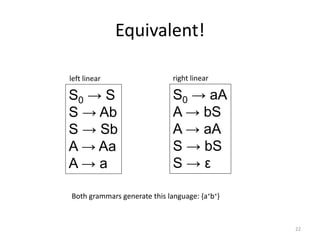
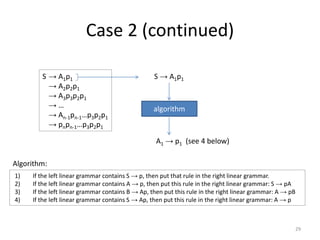
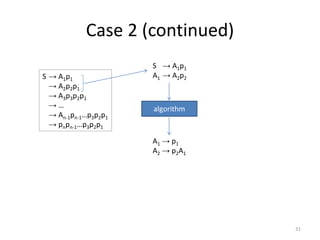
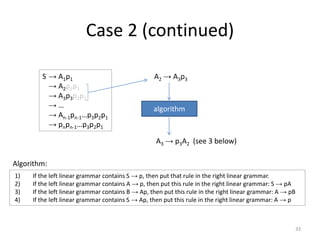
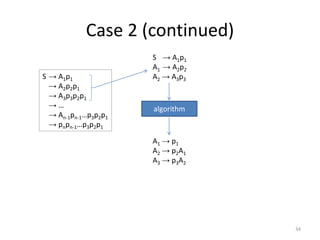
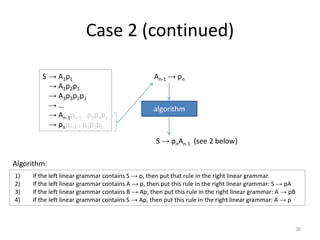
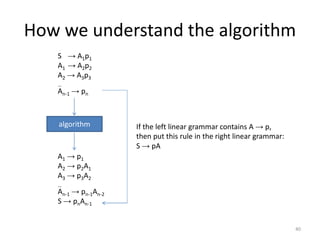
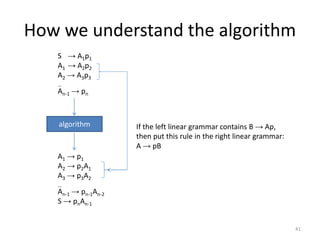
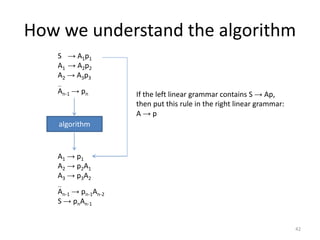
The document describes an algorithm for converting a left linear grammar to an equivalent right linear grammar in 4 steps:
1. If the left grammar has a rule with terminals on the right-hand side, add it to the right grammar.
2. If a rule has a non-terminal followed by terminals, make the non-terminal the start and add the terminals.
3. If a rule has a non-terminal preceding another non-terminal and terminals, make the first non-terminal produce the second and terminals.
4. If the start rule has a non-terminal and terminals, make the non-terminal produce the terminals.
The algorithm is guaranteed to produce an equivalent right linear grammar