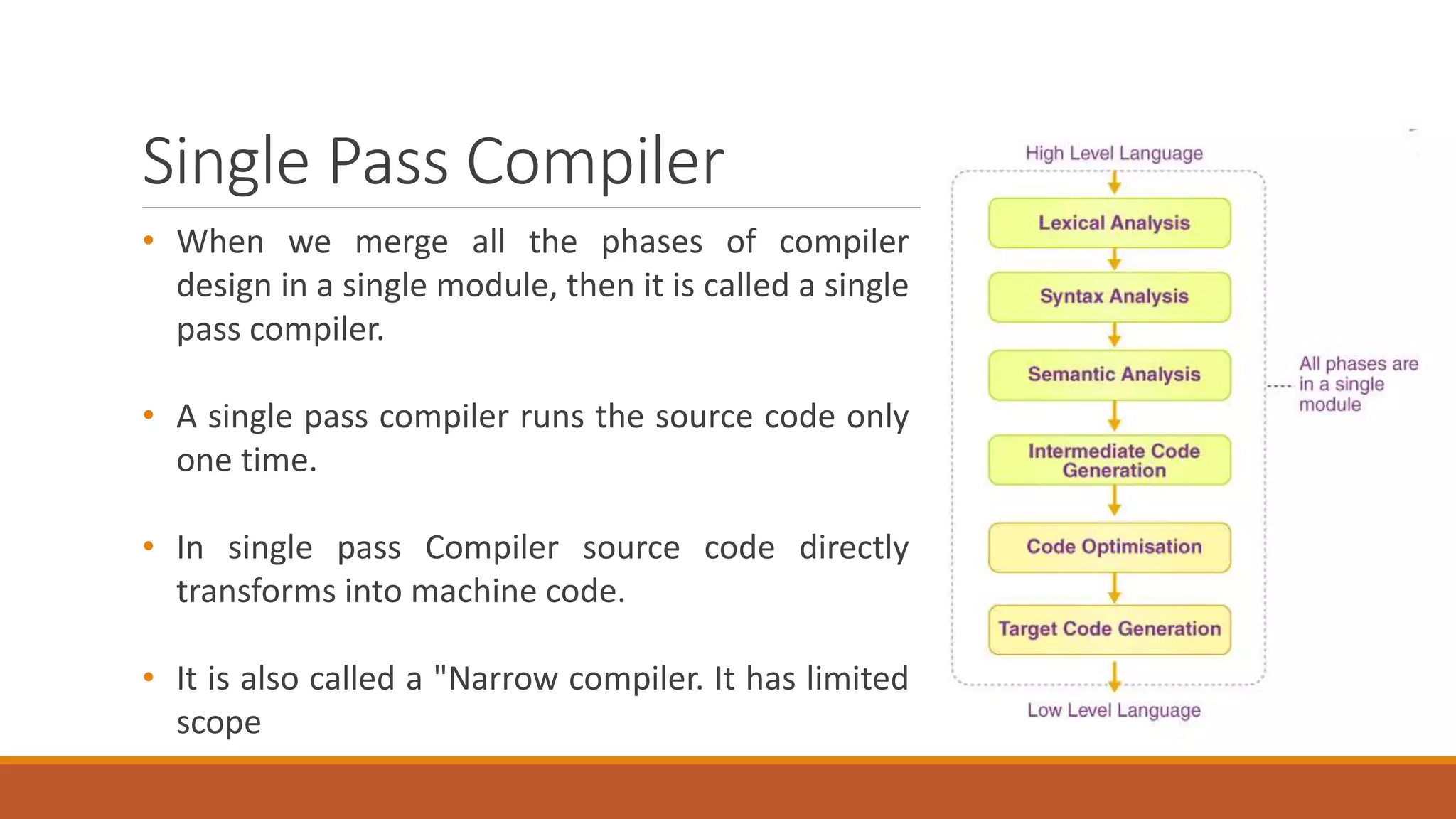
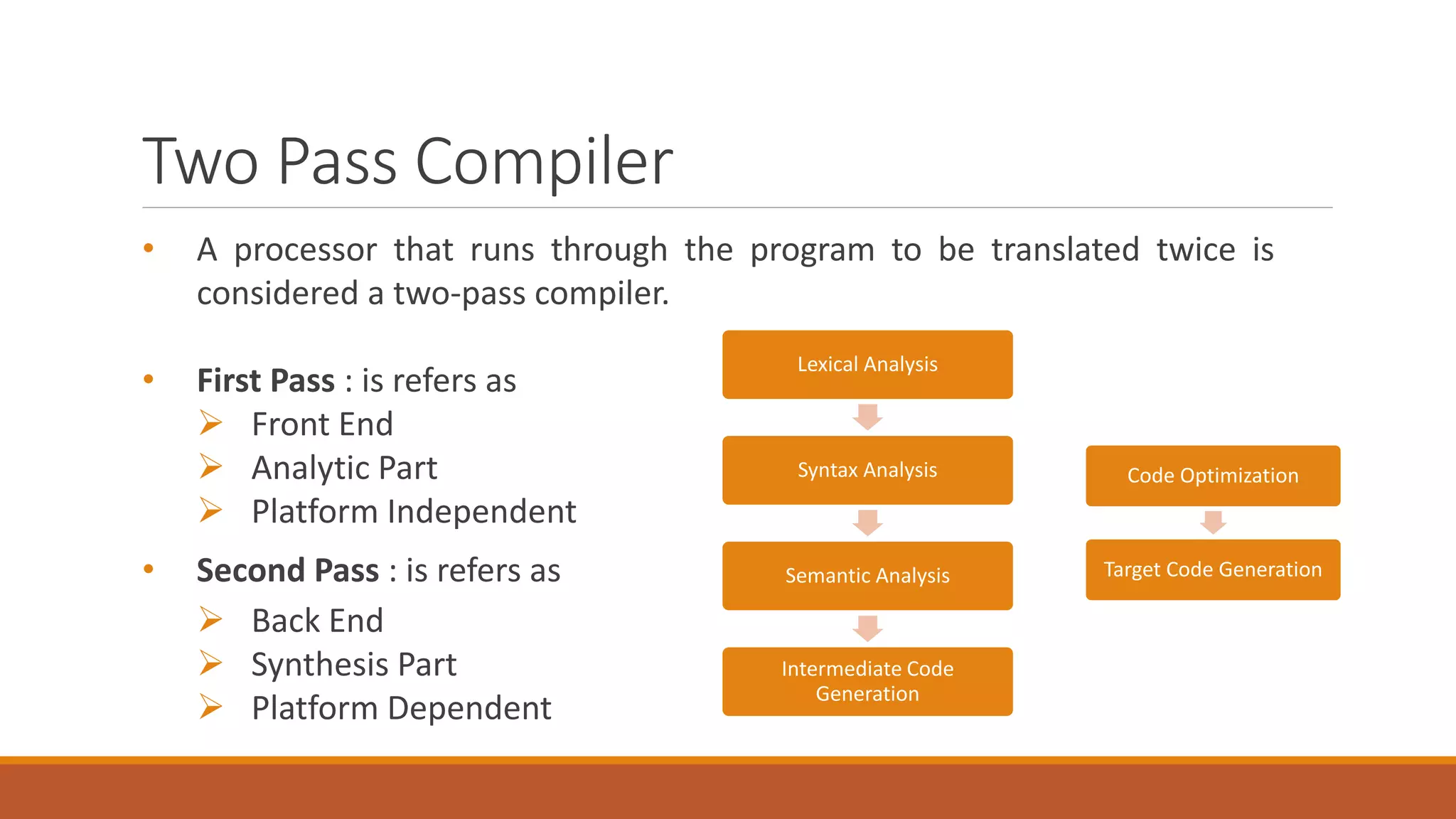
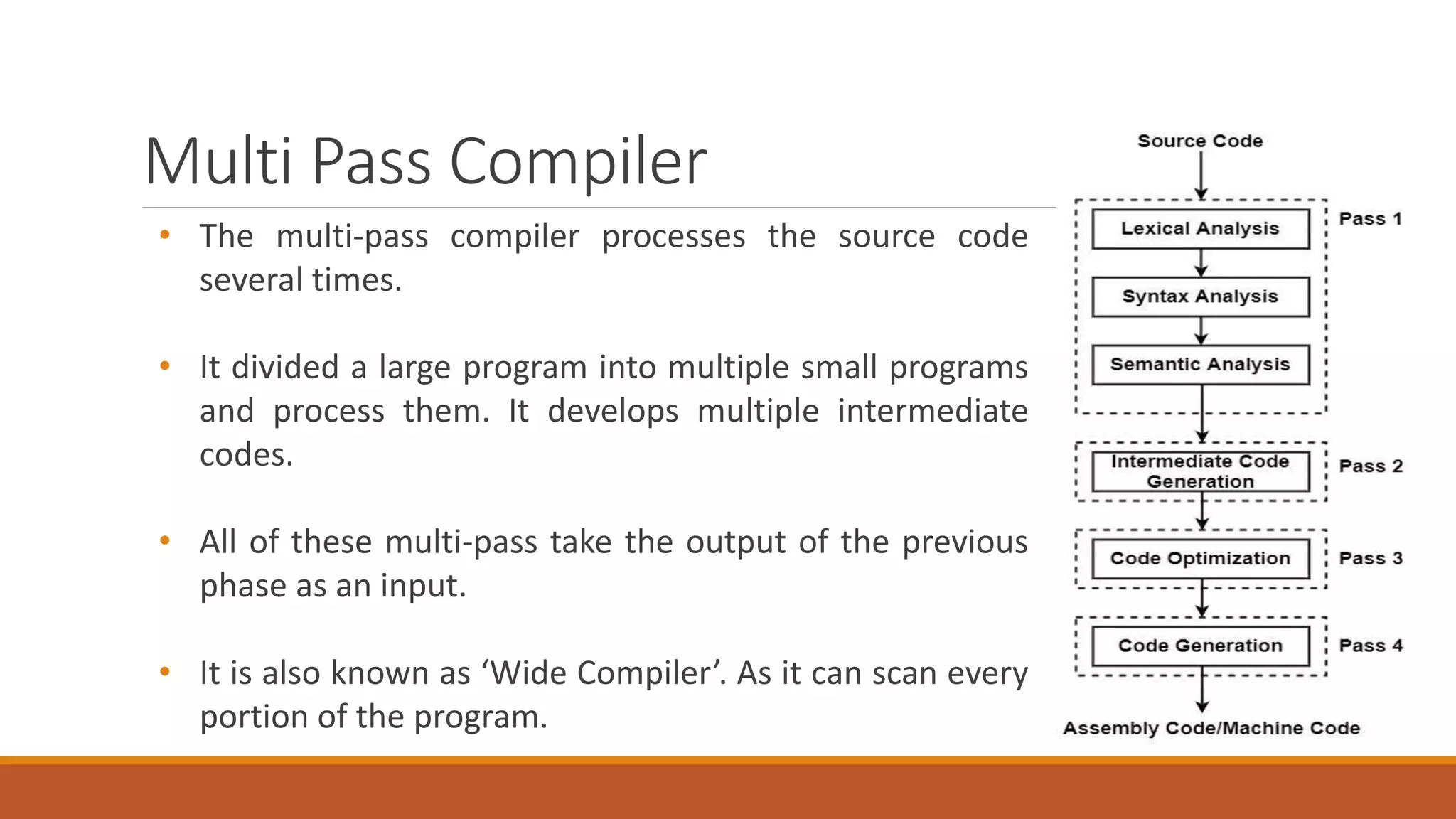
The document discusses compiler passes, detailing three types of compilers: single pass, two pass, and multi pass. It explains that single pass compilers run the source code once, while two pass and multi pass compilers process the code multiple times for better optimization and generation. Comparisons highlight that single pass compilers are faster but less efficient compared to multi pass compilers, which provide better code optimization at the cost of speed.