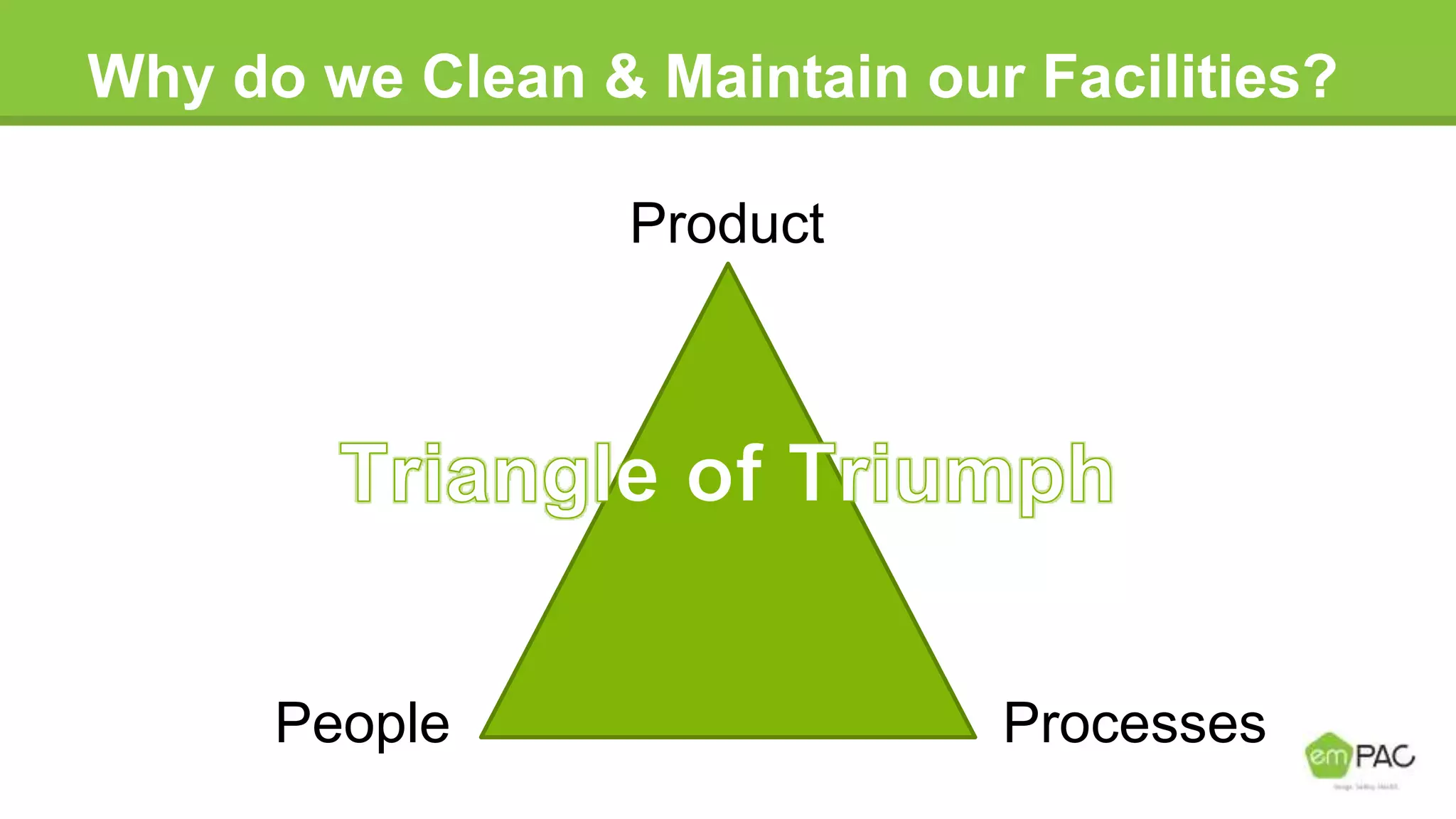
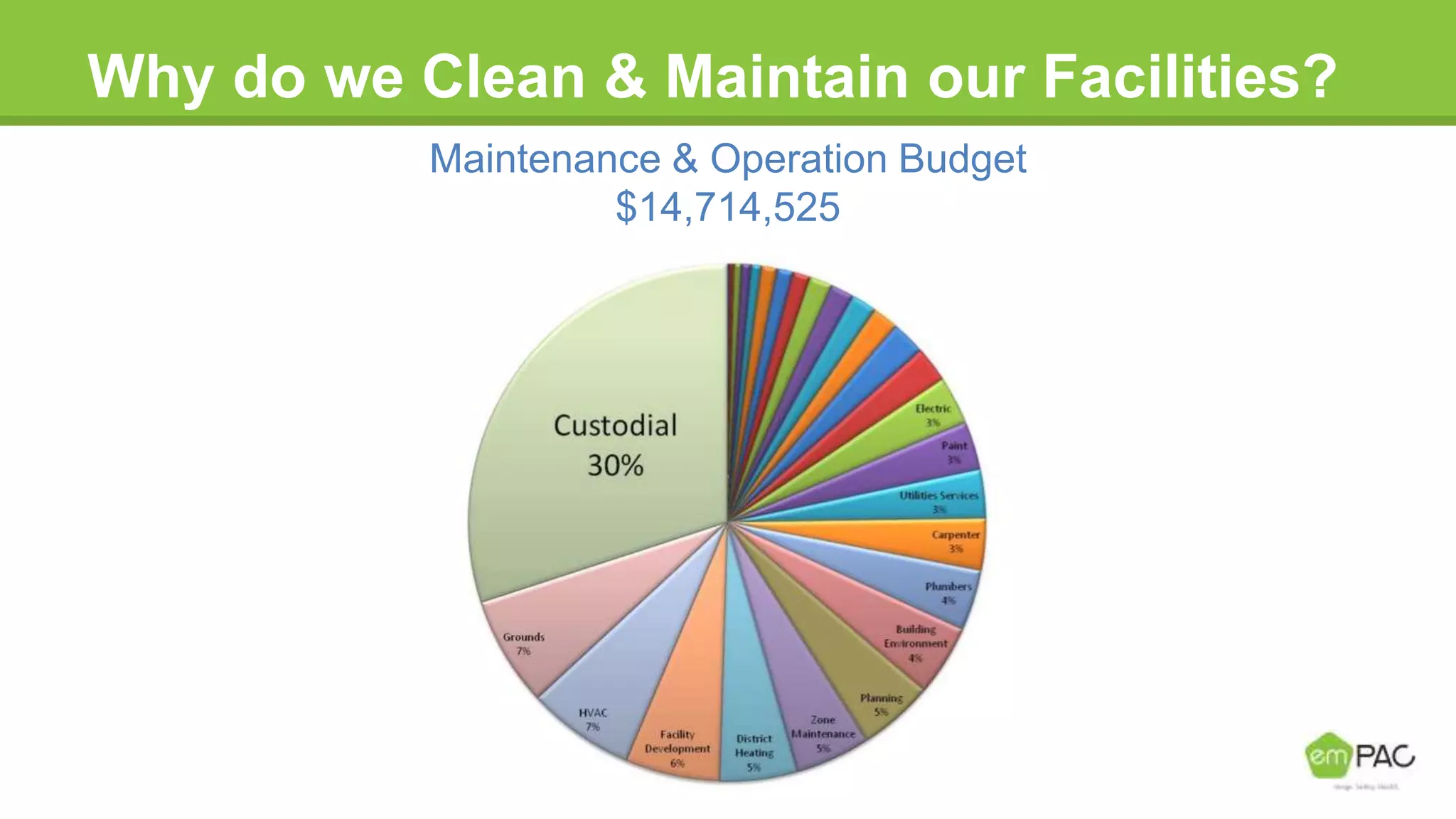
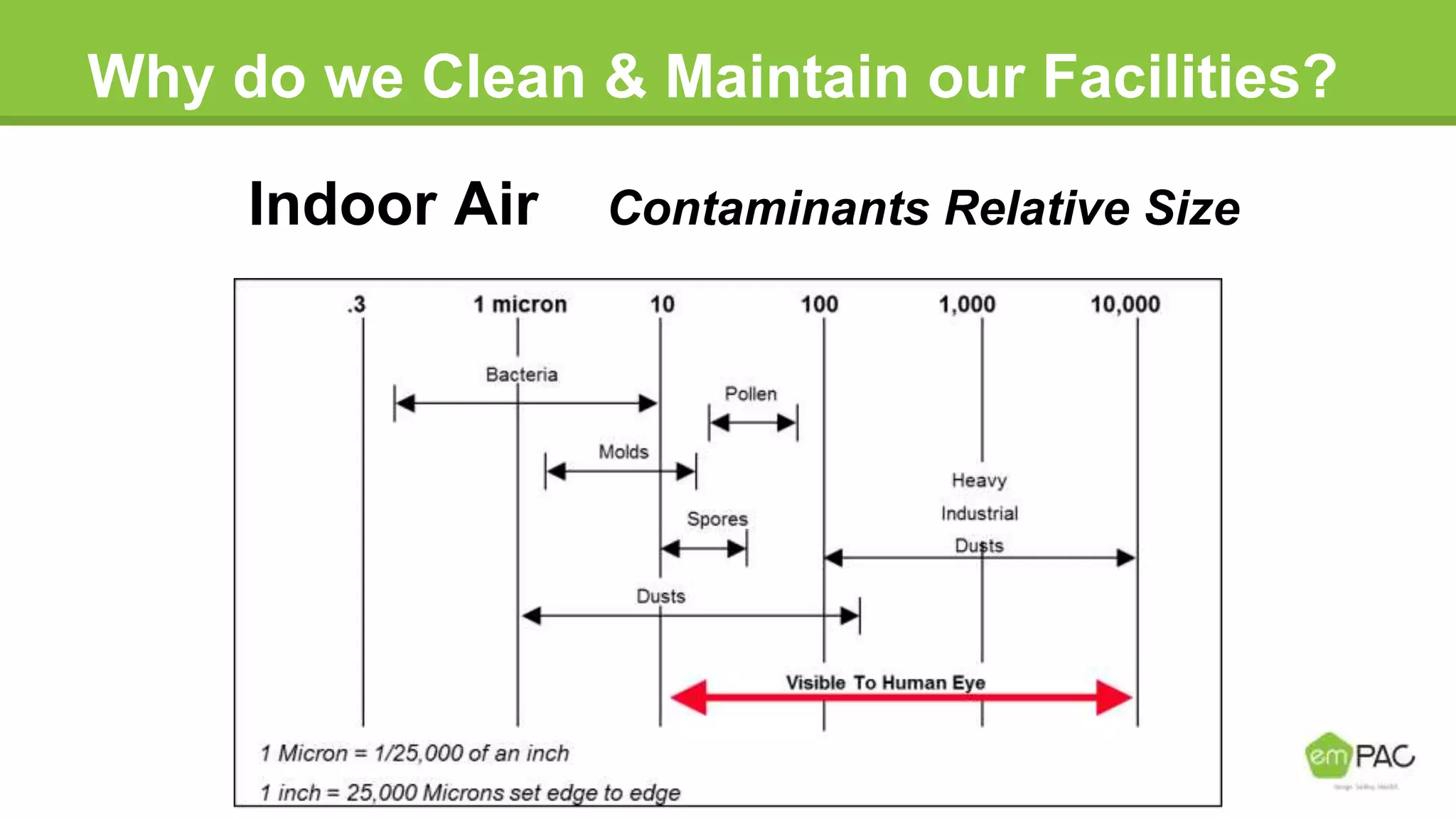
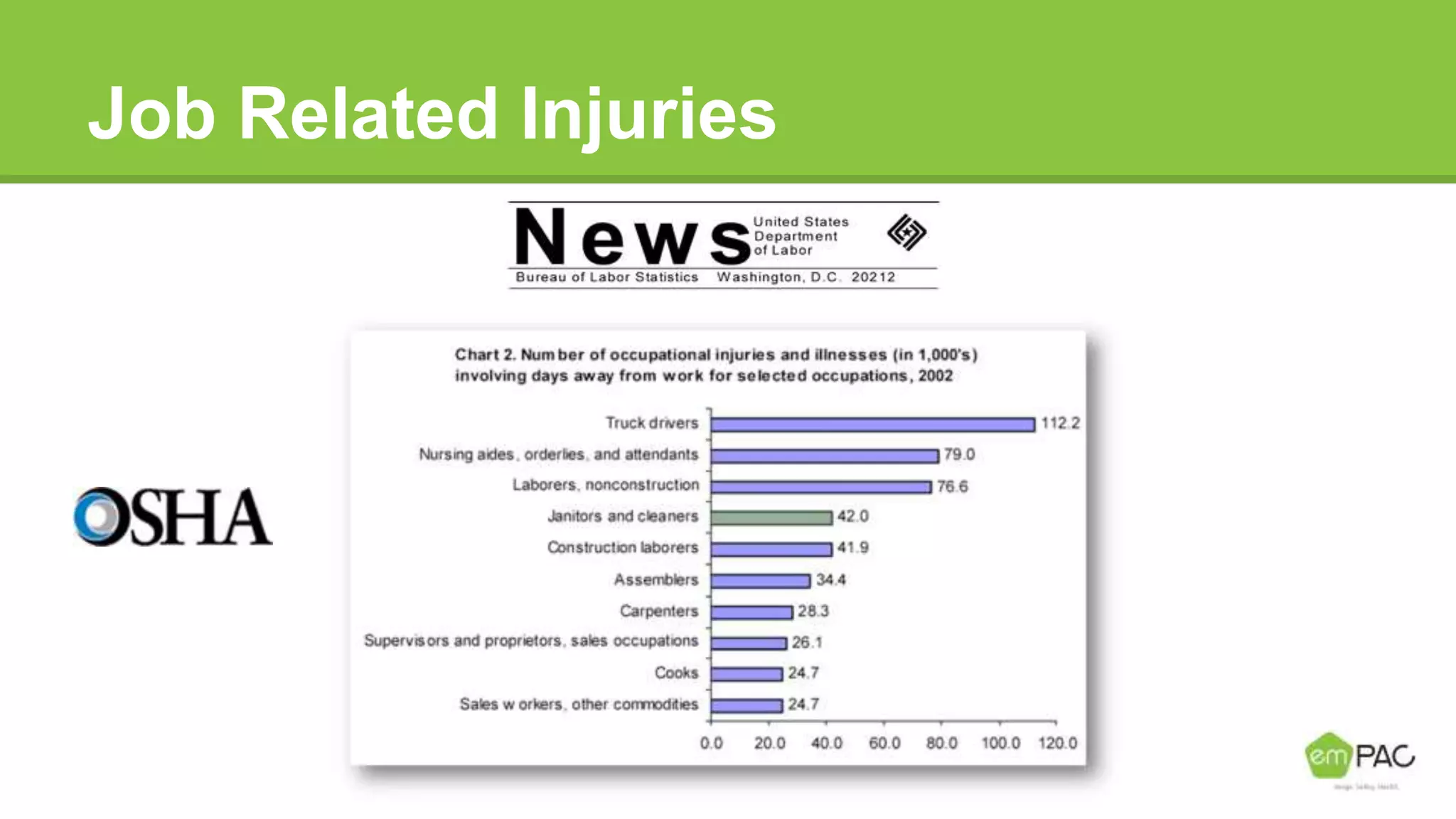
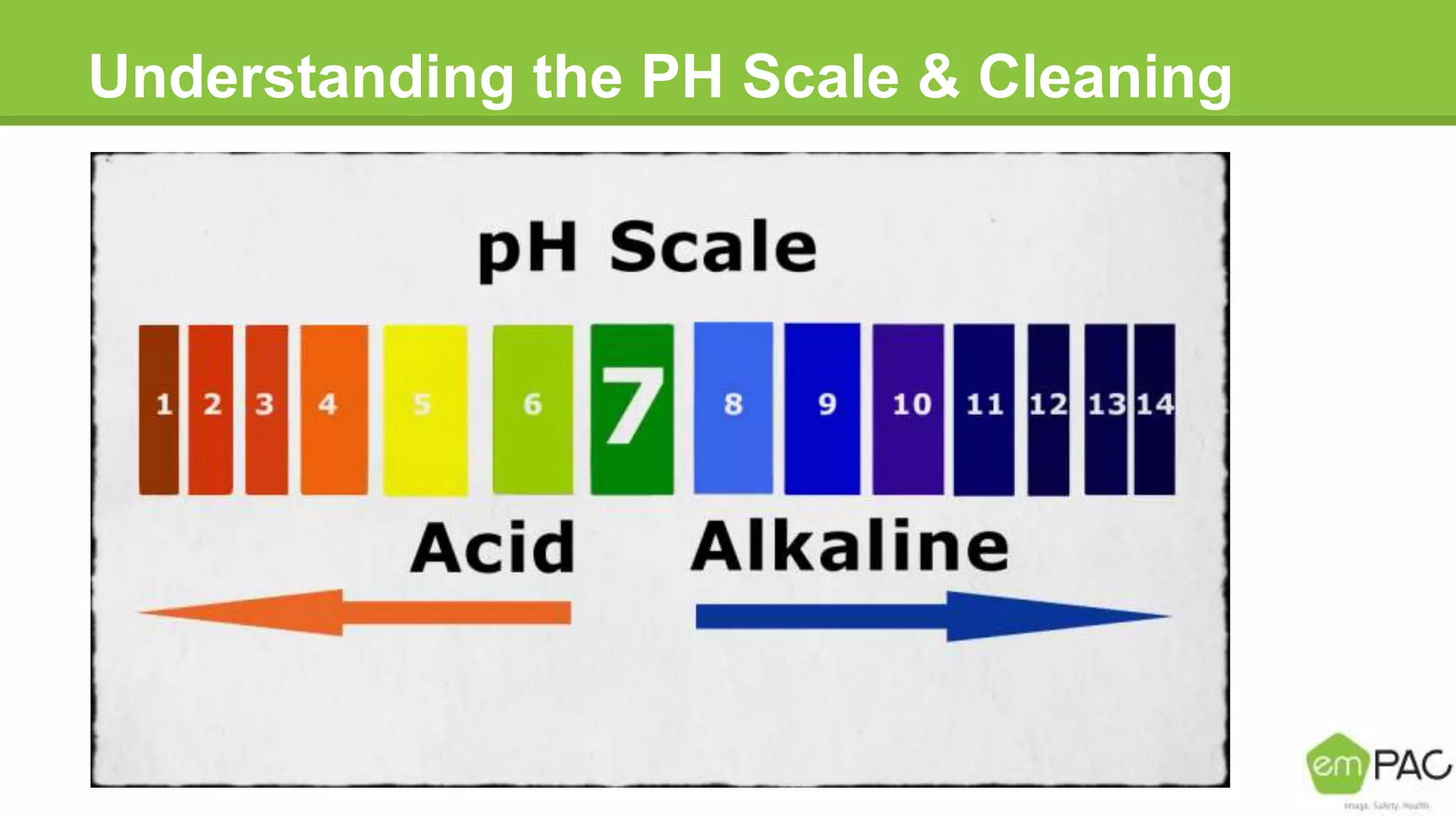
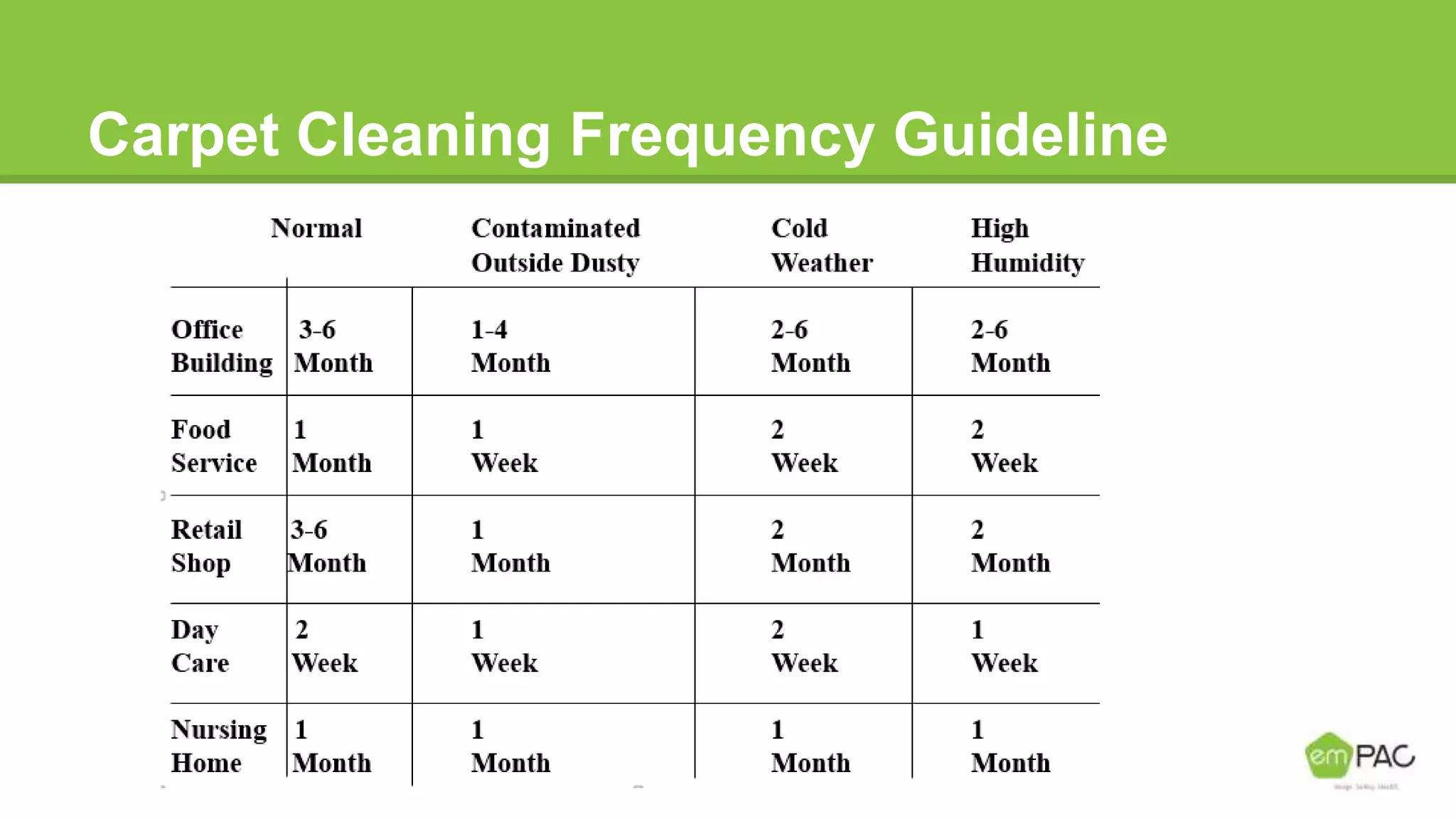
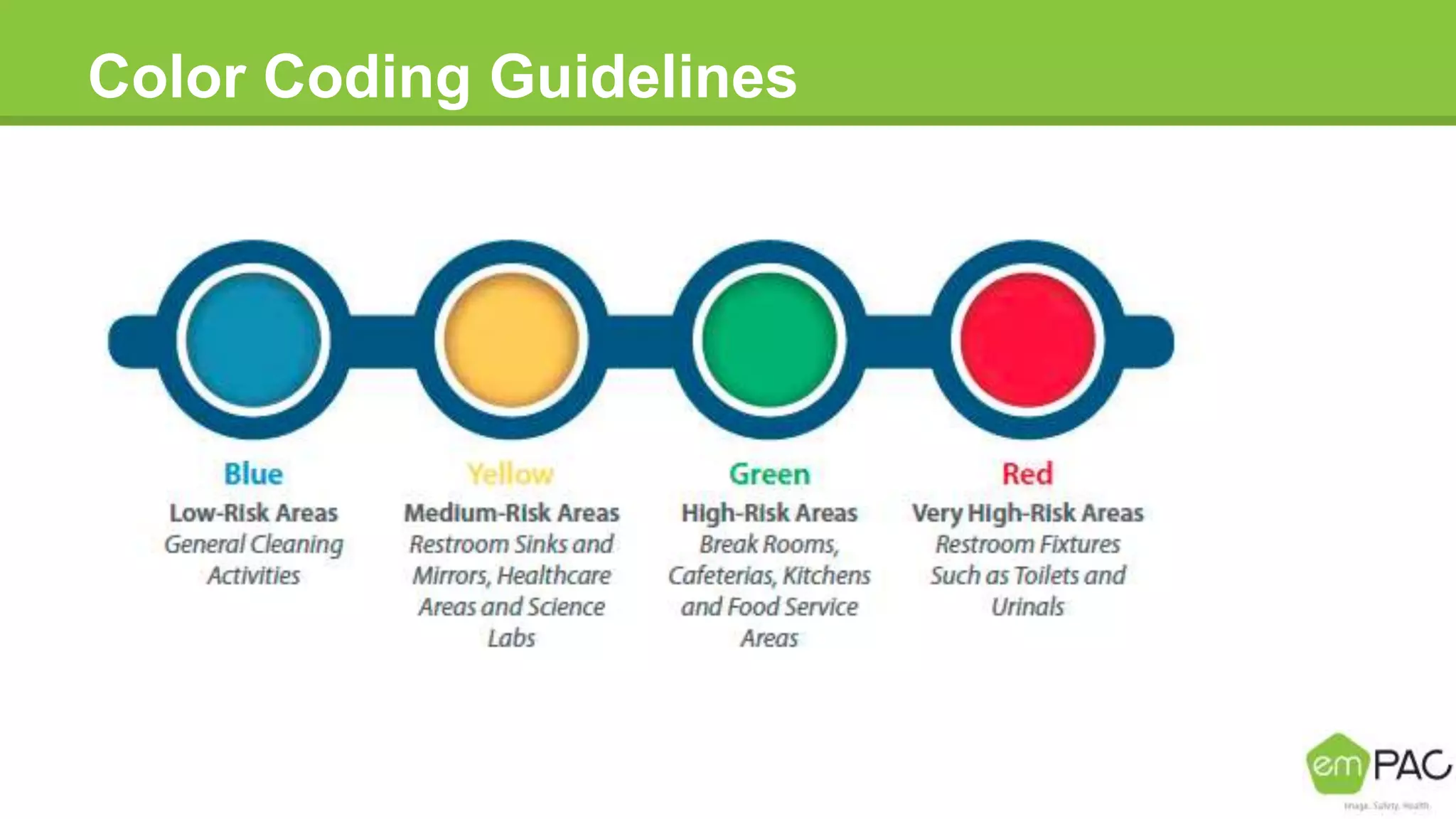
This document provides information on cleaning and maintaining facilities. It discusses why facilities need to be cleaned and maintained, including reducing costs, extending the lifespan of assets, and improving indoor air quality. It also covers how facilities should be cleaned and maintained, with sections on safety practices, using different cleaning tools and methods for hard floor care like dust mopping, damp mopping, scrubbing, stripping, applying coatings, and burnishing. The goal is to provide guidance on cleaning efficiently and effectively to reduce labor costs and properly care for facilities.