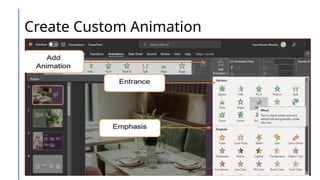
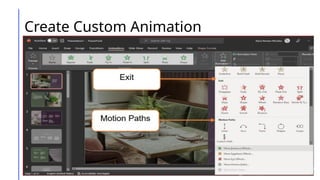
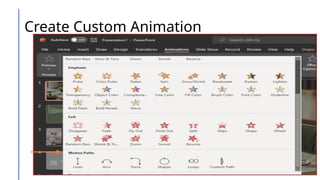
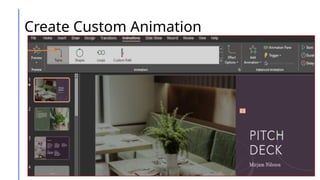
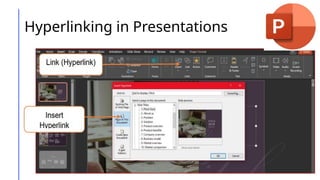
This document outlines a lesson on advanced presentation skills using MS PowerPoint, detailing objectives such as creating powerful slides and utilizing custom animations and hyperlinking. It provides guidance on effective slide creation, emphasizing simplicity, clarity, design principles, and technical preparedness for presentations. Additionally, it includes instructions for creating custom animations and hyperlinks to enhance presentation interactivity.