The document provides an overview of augmented reality (AR) and its applications and effectiveness for marketing. Some key points:
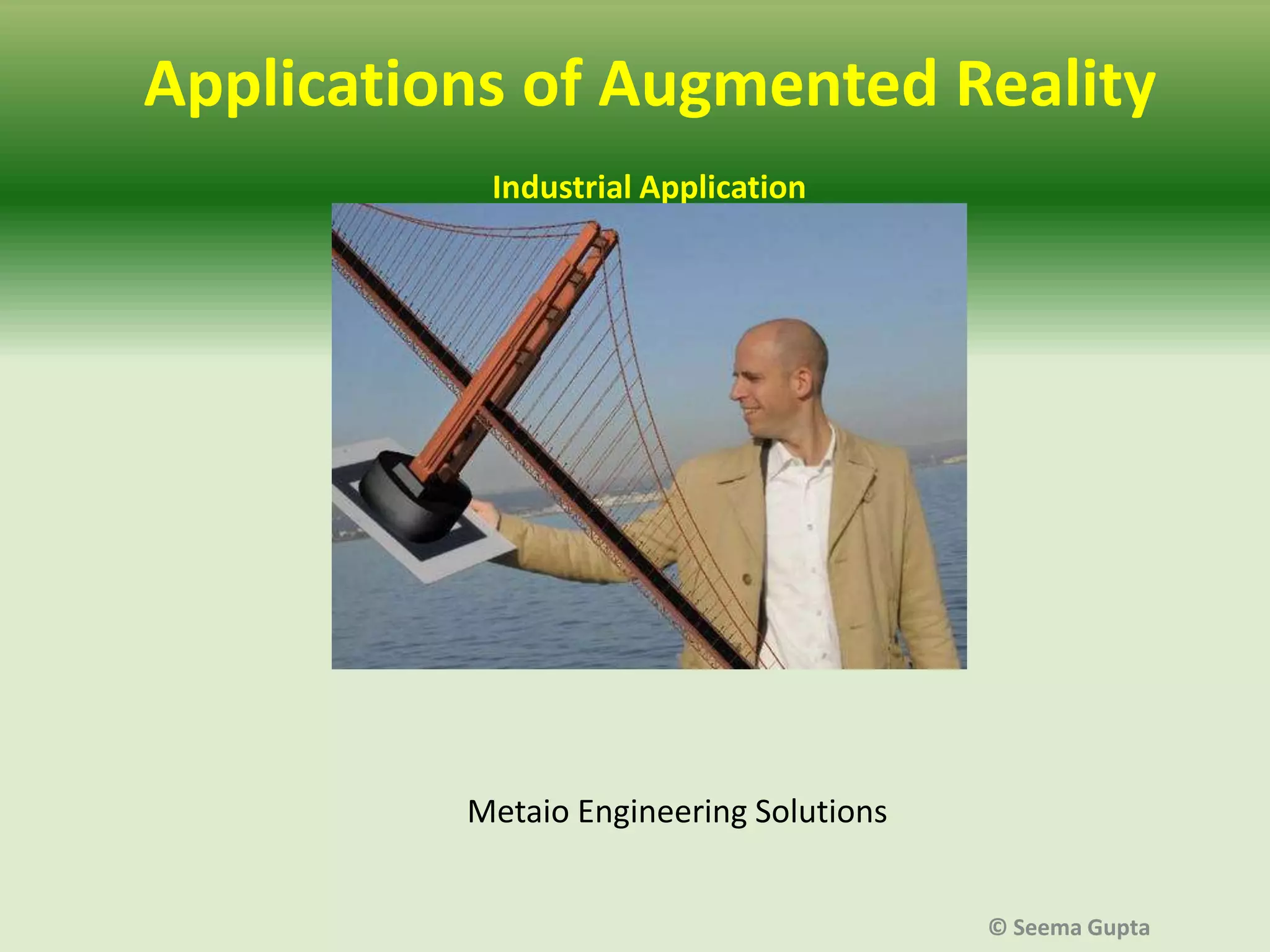
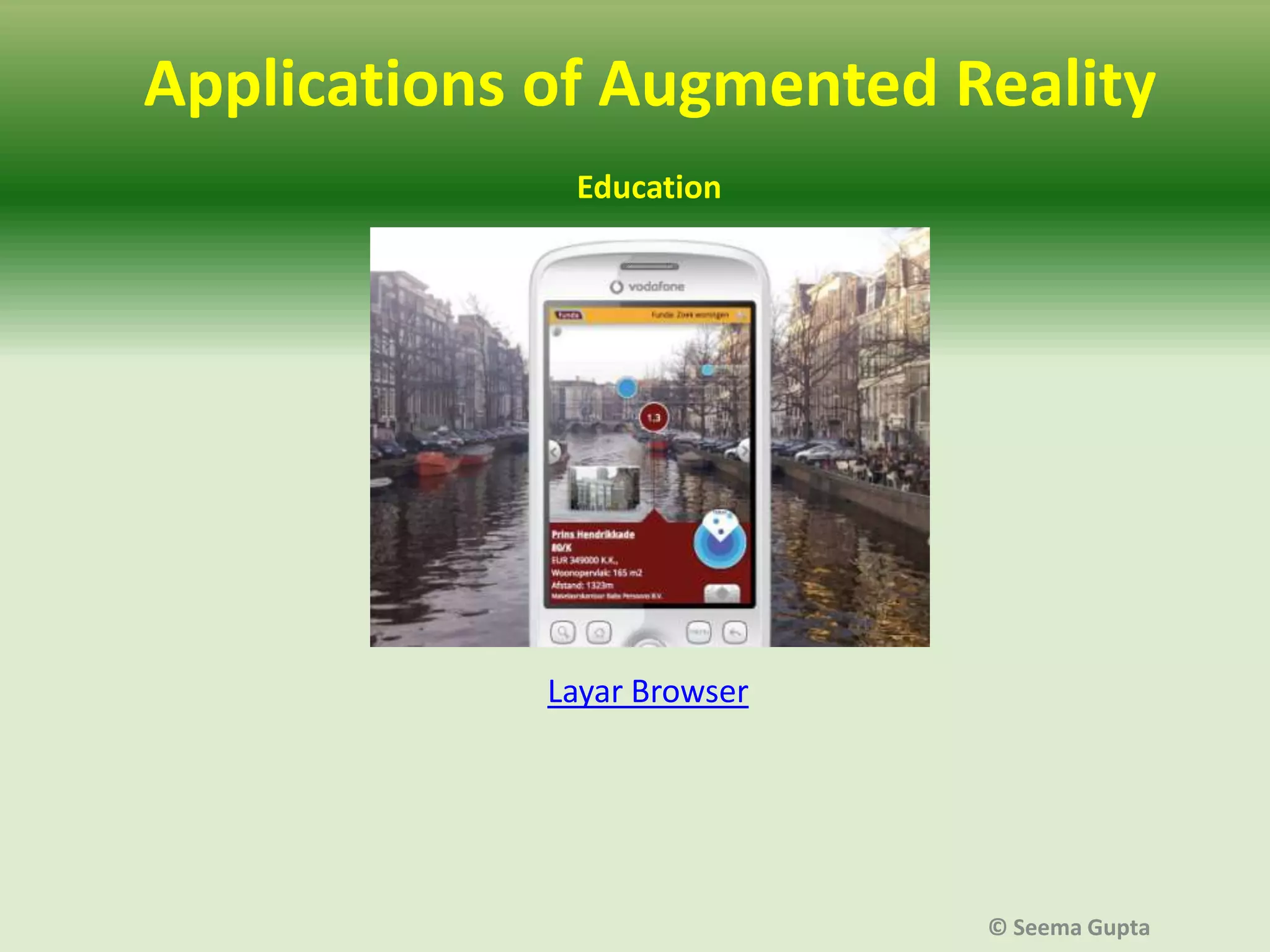
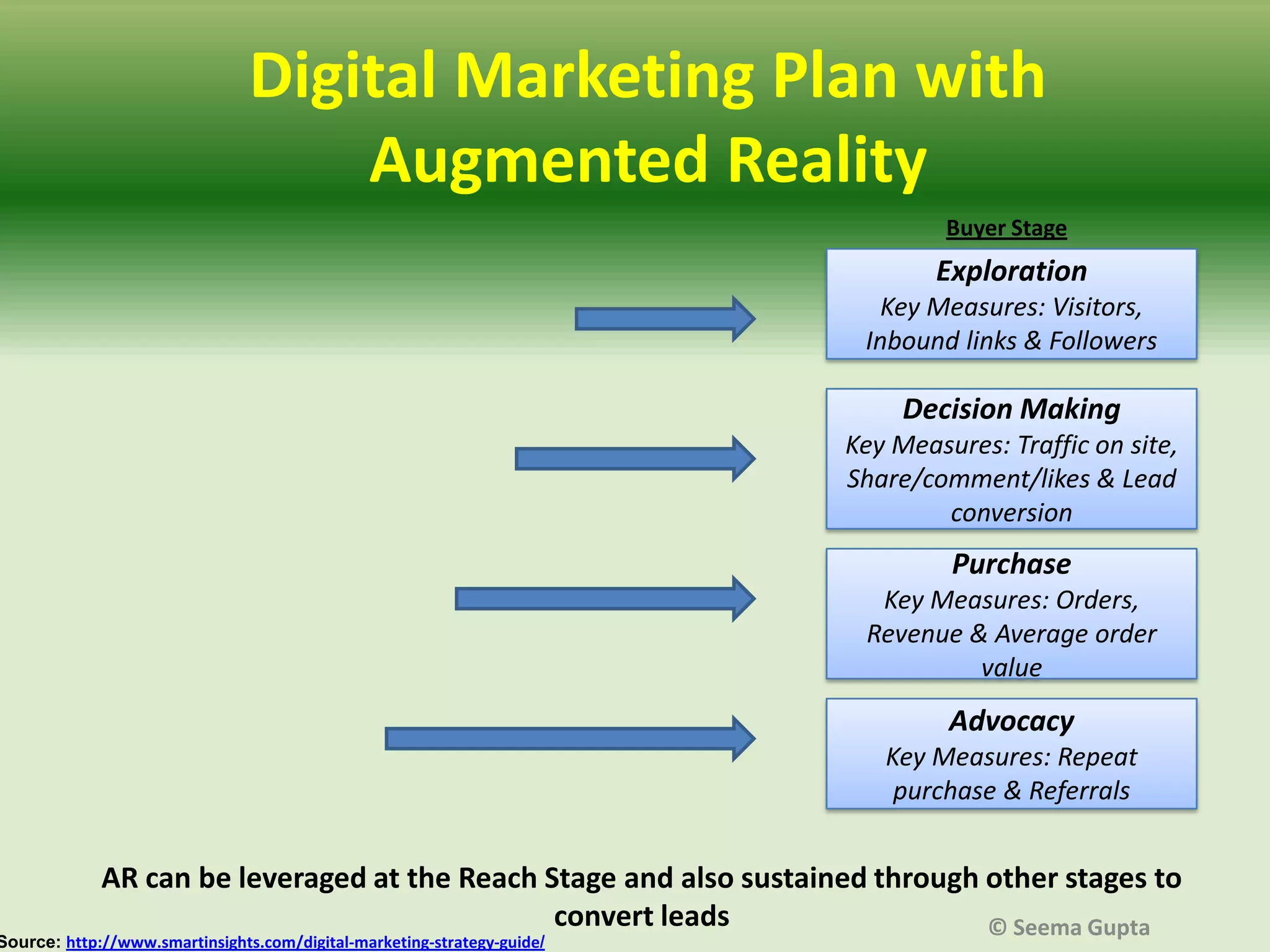
- AR augments the real physical world with virtual objects seen through technology like smartphones or webcams. It can be used for promotions, product launches, brand communication, online sales, gathering customer intelligence, industrial and educational applications, and entertainment.
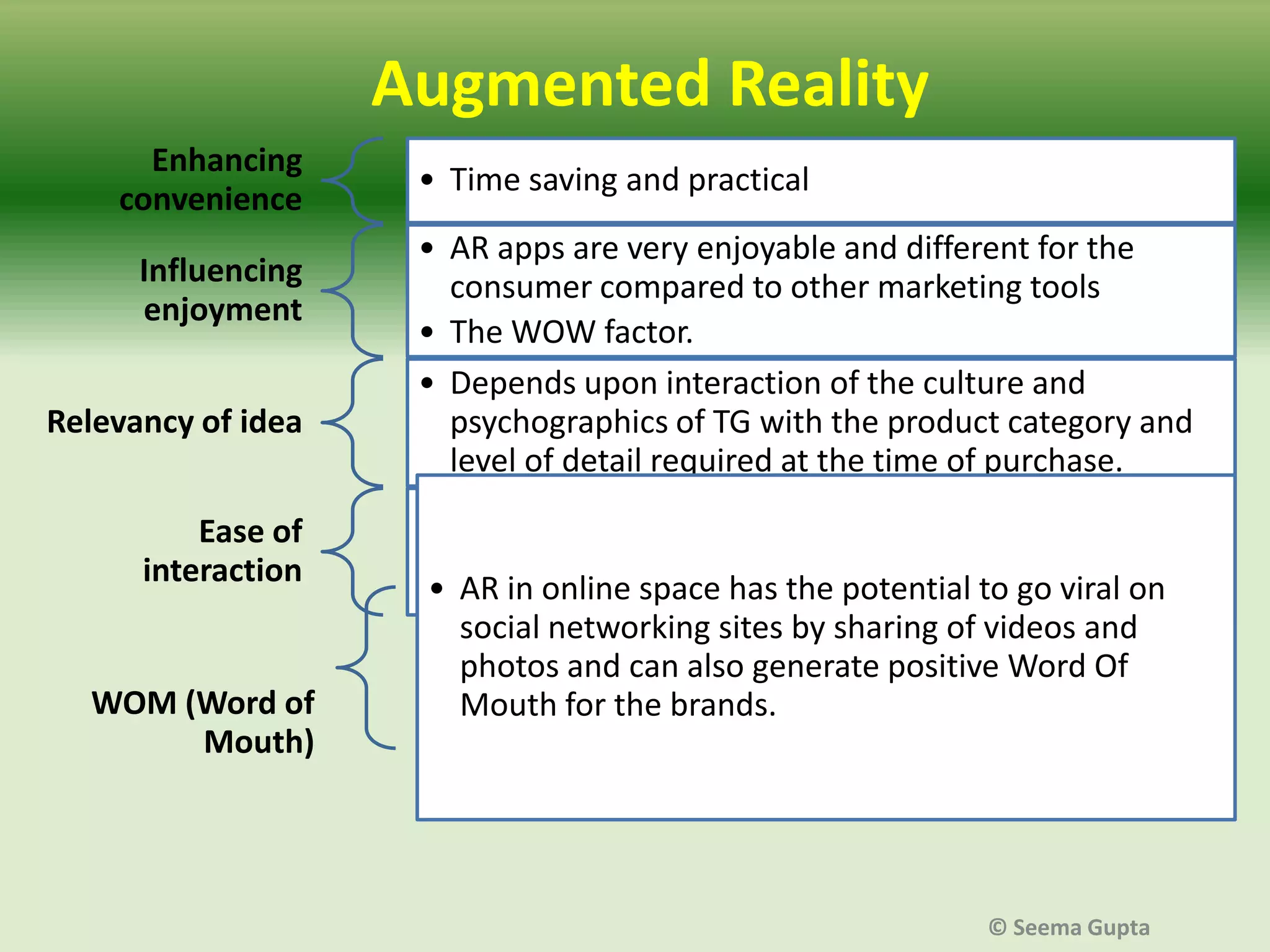
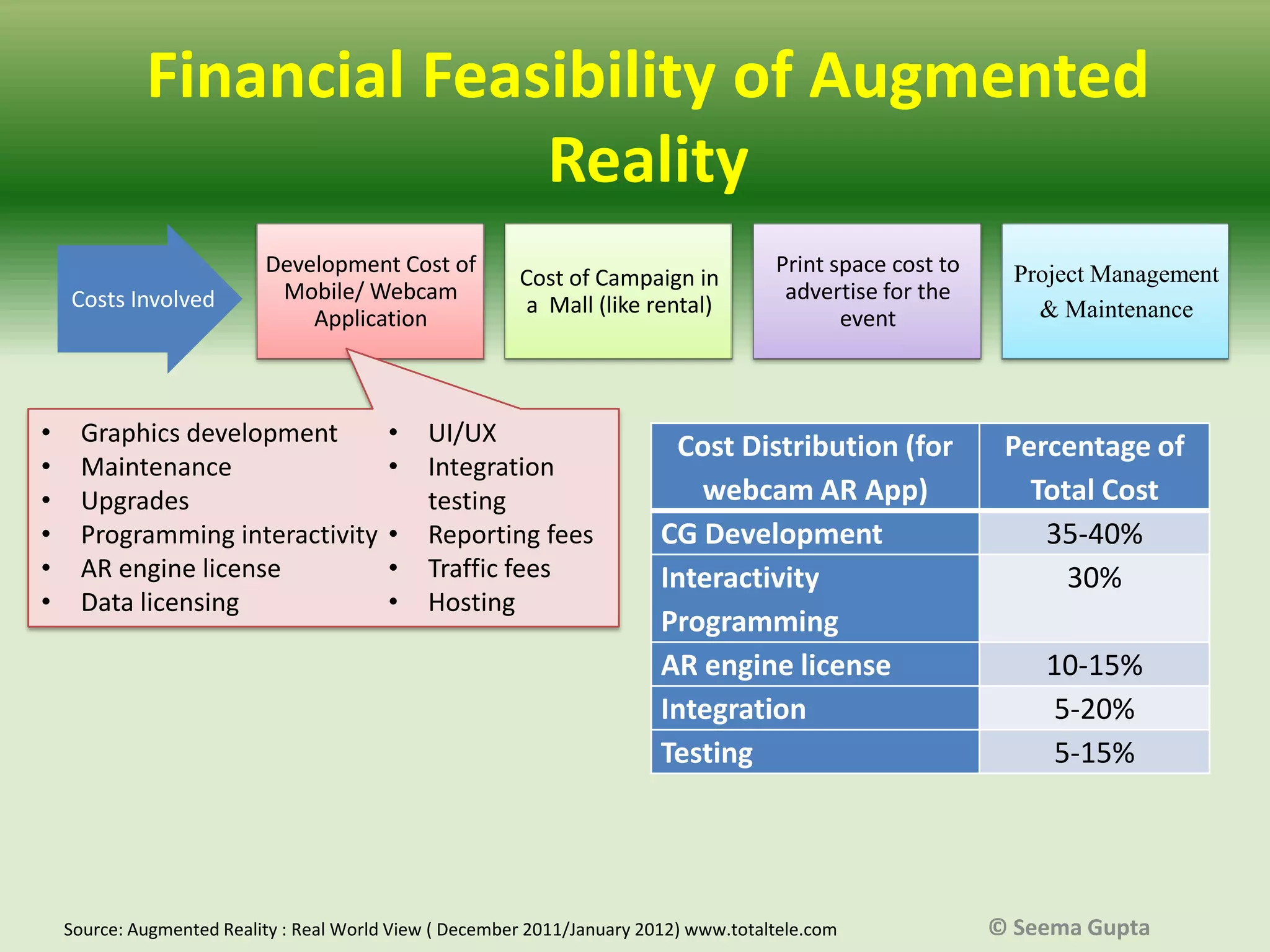
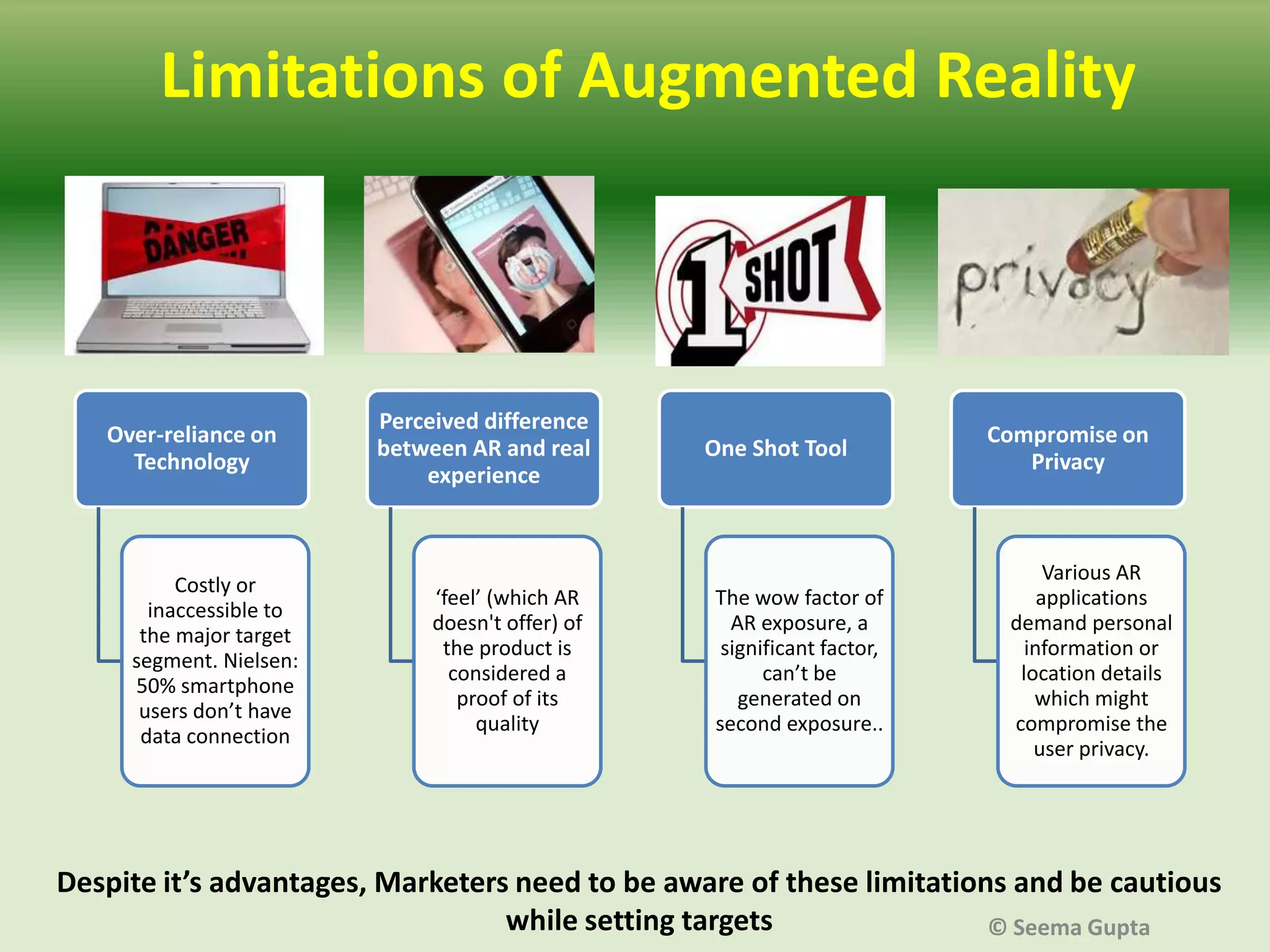
- Marketers are concerned about the financial costs of AR strategies and their integration with existing marketing approaches. AR also needs to provide value to customers through functional, emotional or transformational experiences.
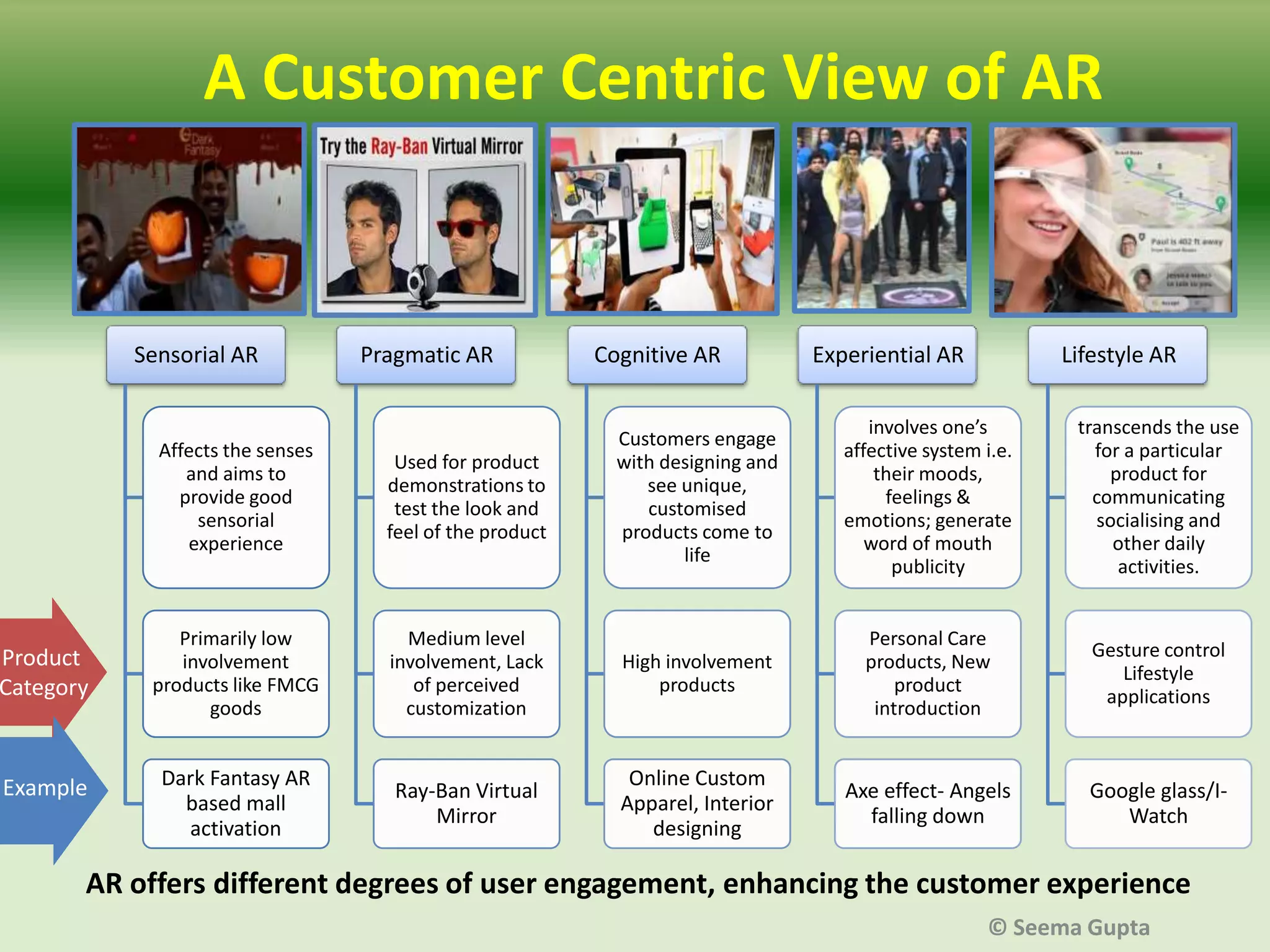
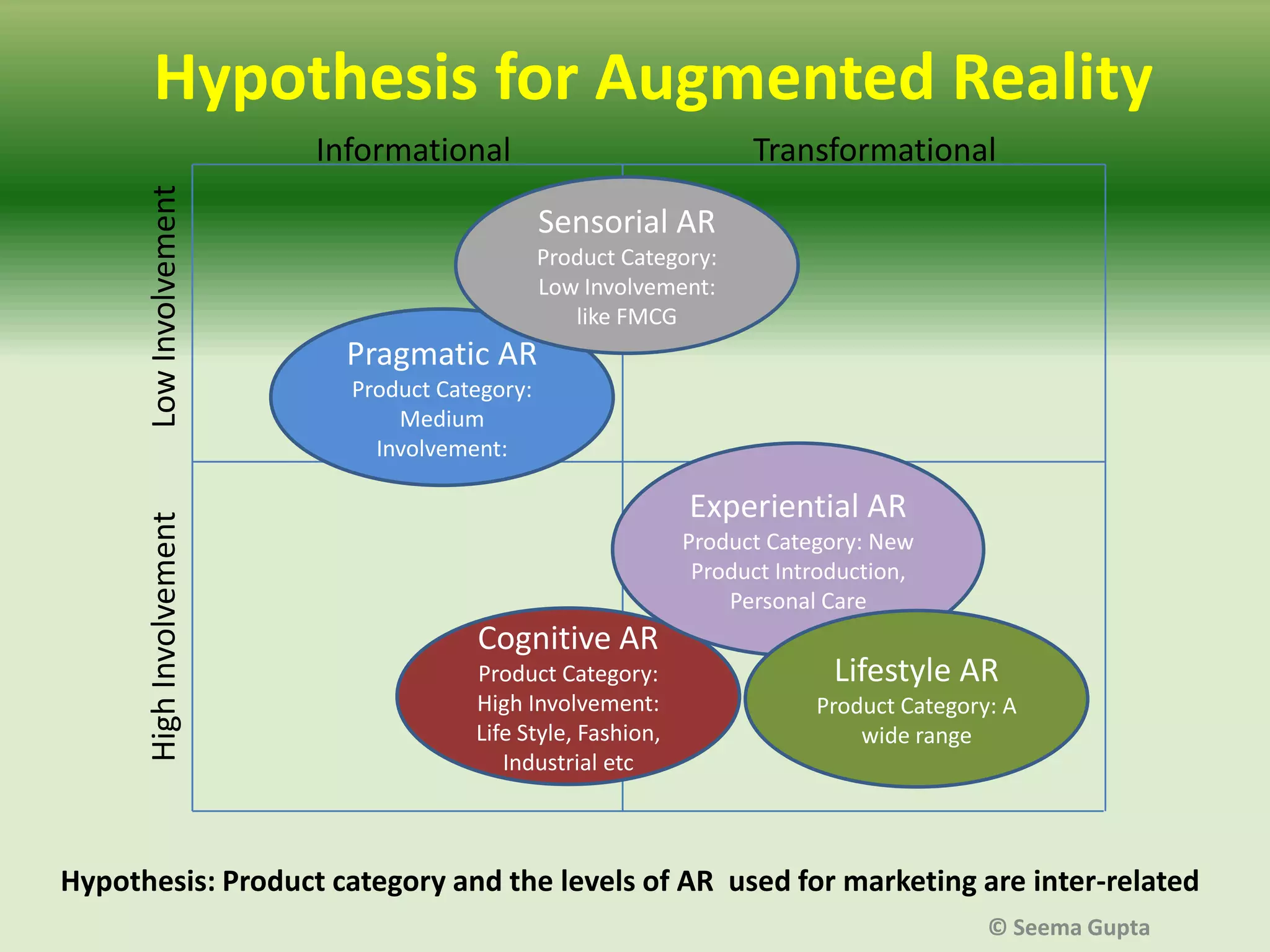
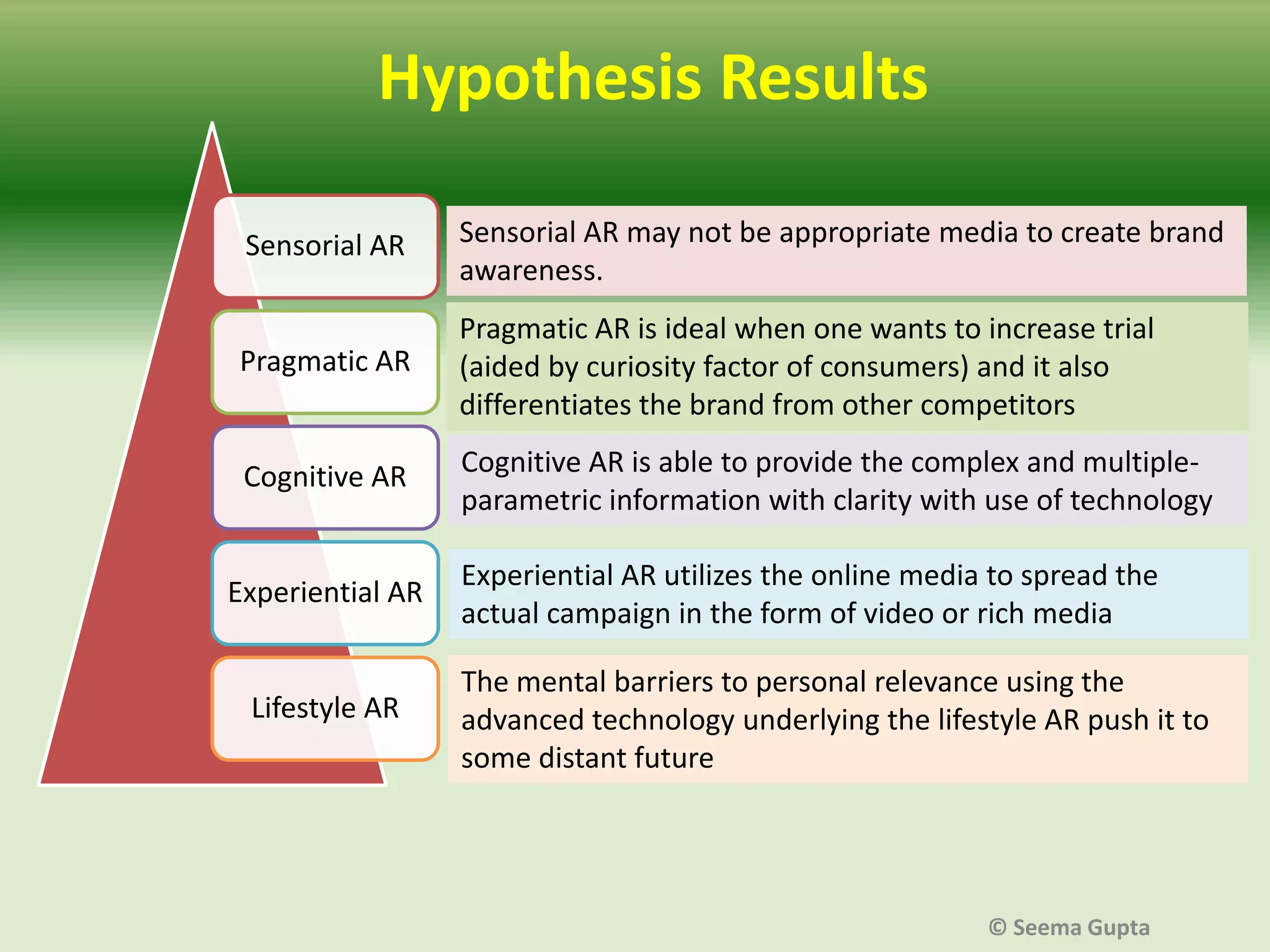
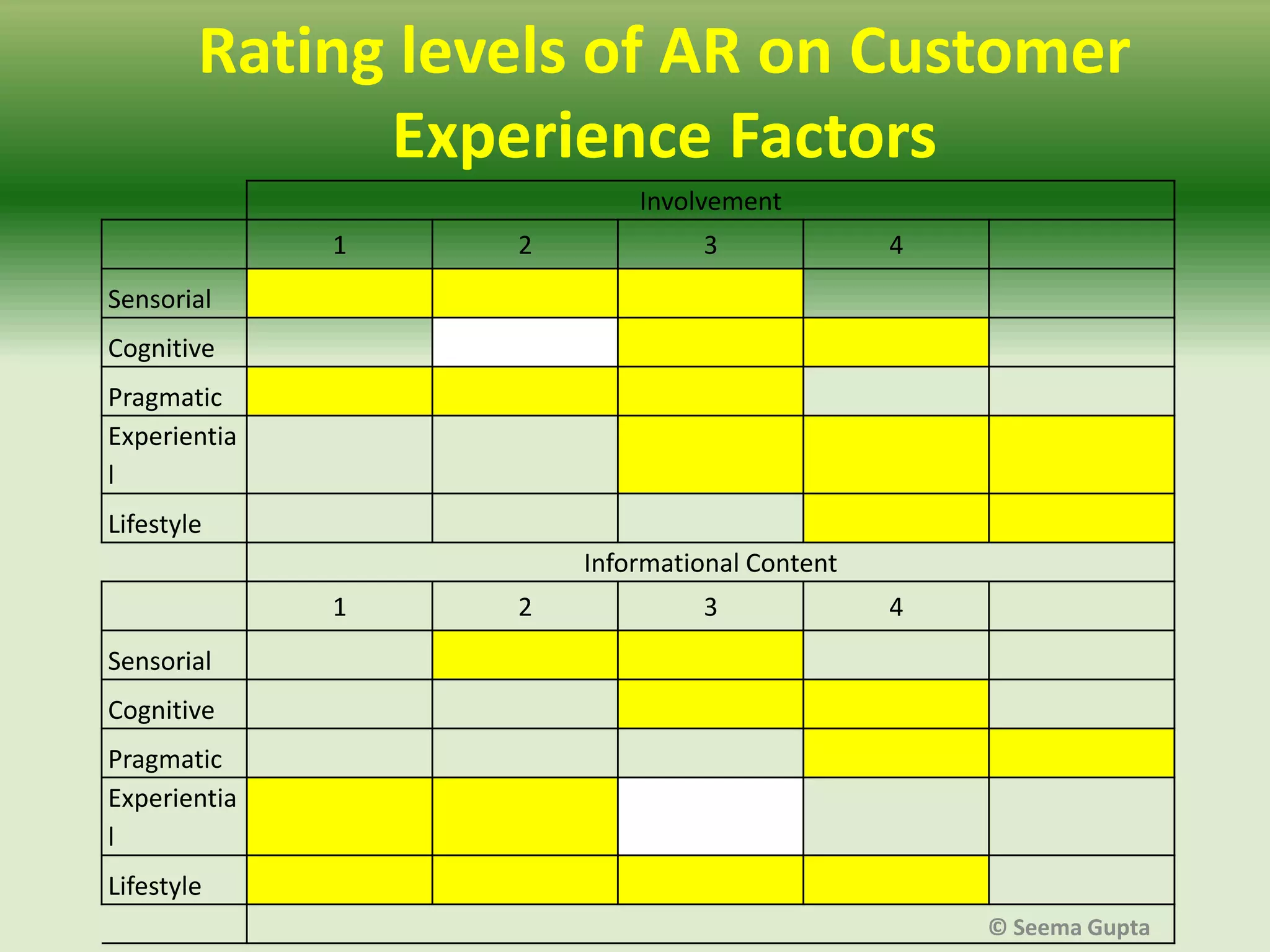
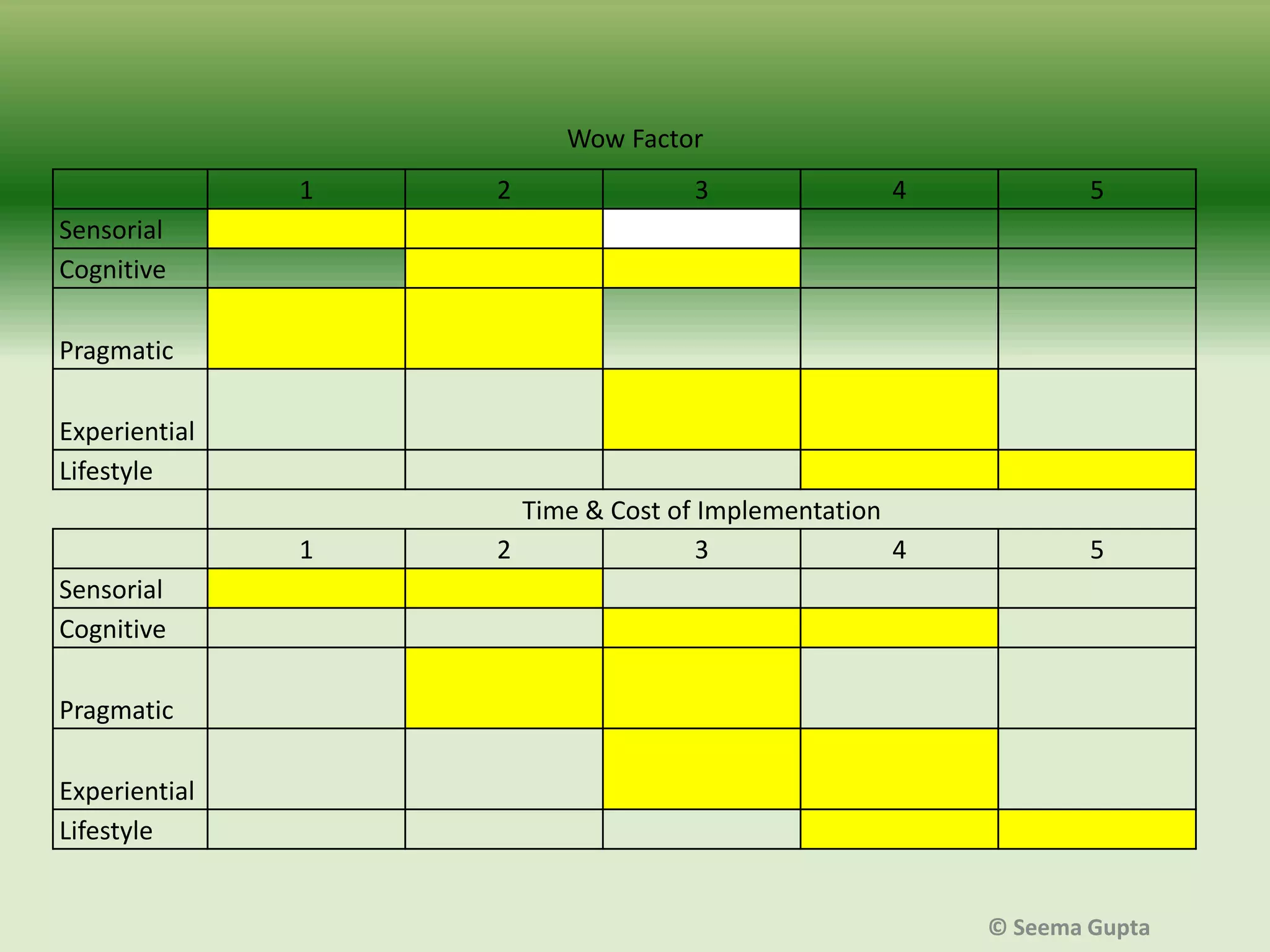
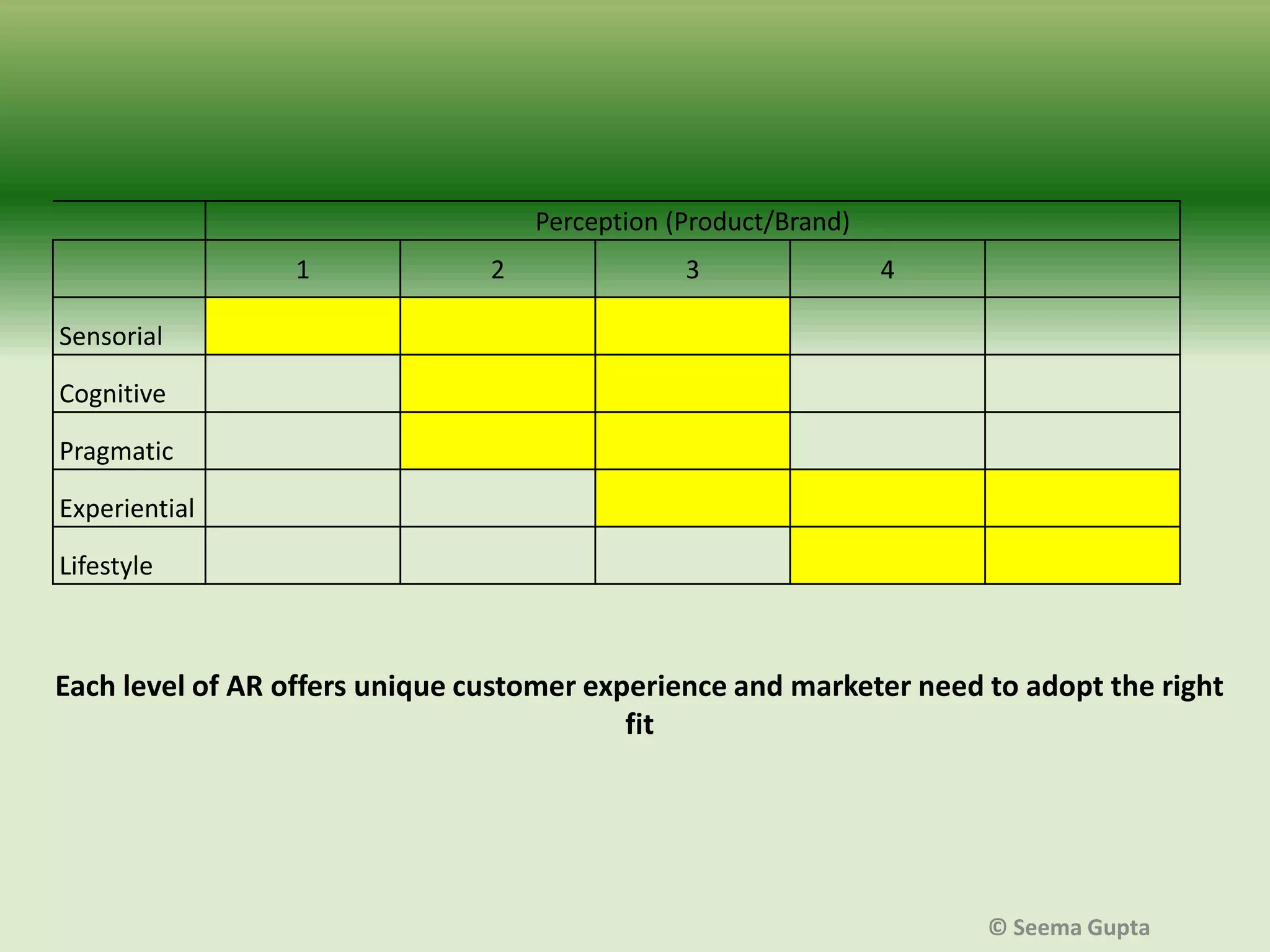
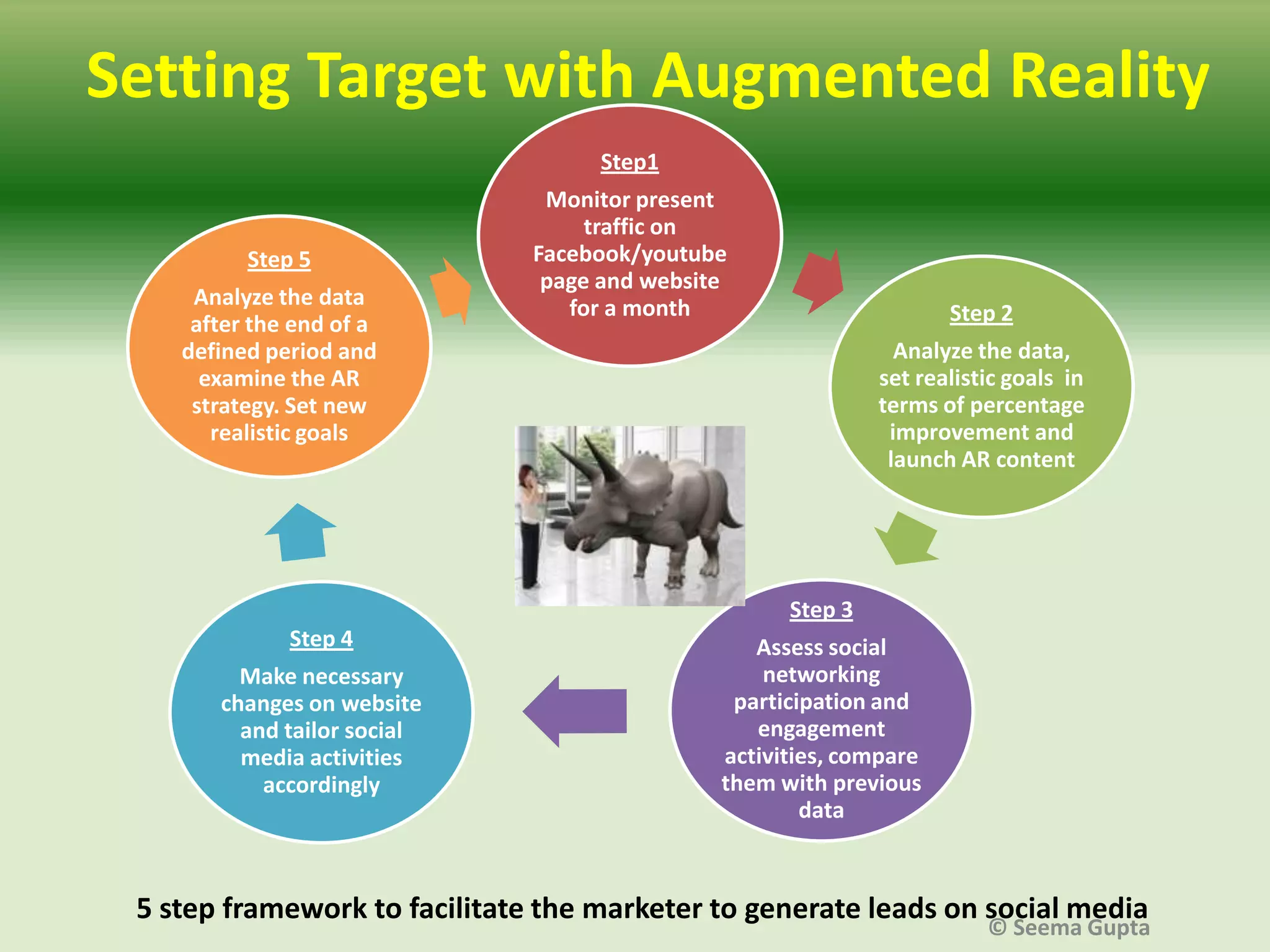
- The effectiveness of AR depends on factors like the level of user interaction and engagement, as well as the type of product. Different "levels" of AR