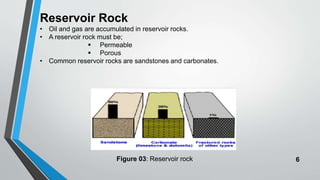
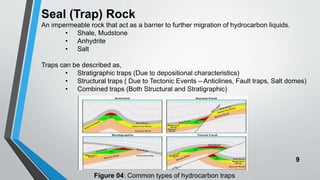
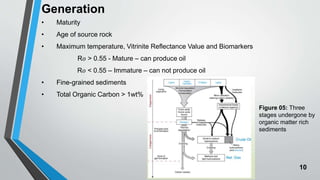
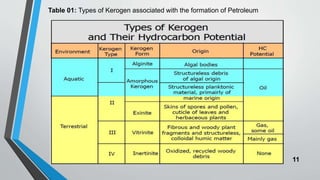
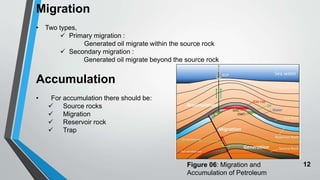
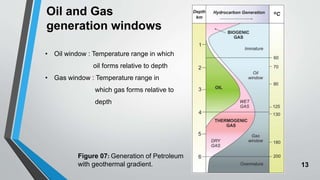
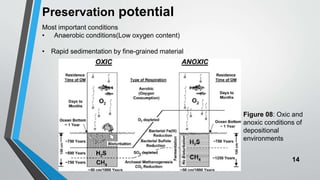
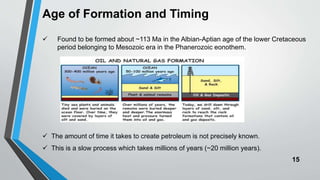
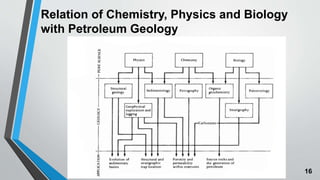
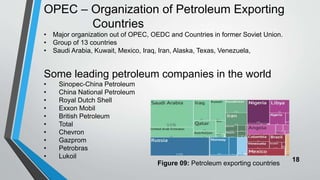
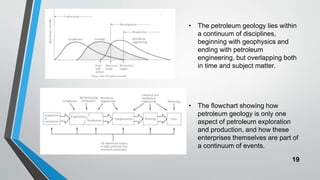
Petroleum is formed from organic materials that are deposited in sedimentary basins over millions of years. The key steps in petroleum formation include: (1) deposition and burial of organic-rich source rocks; (2) generation of hydrocarbons from the buried organic matter through thermal maturation; (3) migration of hydrocarbons from the source rock into reservoir rocks; and (4) accumulation of hydrocarbons in structural or stratigraphic traps in reservoir rocks where they are preserved. Successful petroleum exploration requires identification of source, reservoir, and seal rocks in areas with suitable burial and thermal histories to generate and trap commercial quantities of oil and gas.