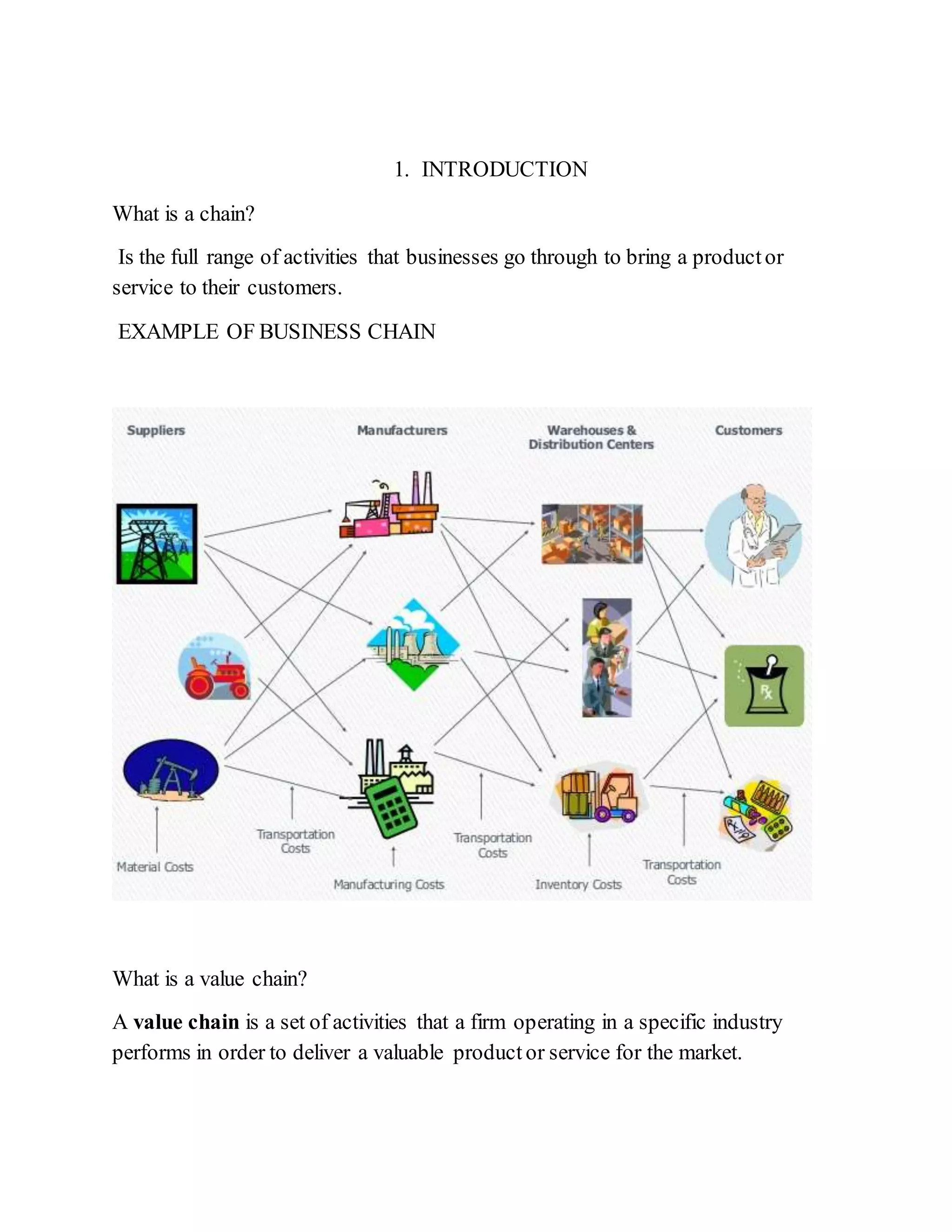
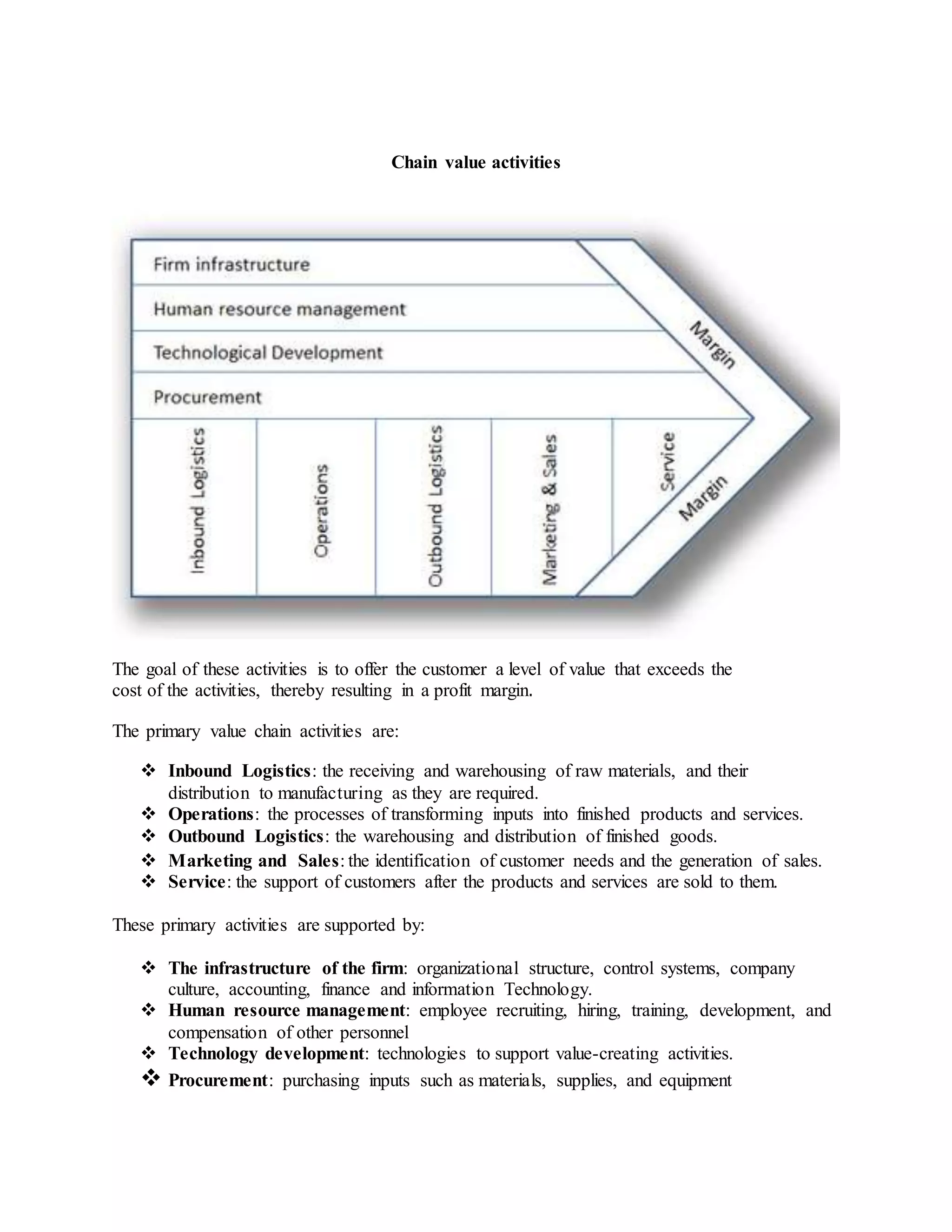
This document discusses the concepts of upstream and downstream processes within value chains in various industries, particularly in agriculture and production. It defines the roles and activities involved in these processes, emphasizing the importance of enhancing linkages between them to improve efficiency and competitive advantage. Additionally, it outlines various value chain activities and their impact on a firm's profitability and customer satisfaction.