Embed presentation
Downloaded 62 times



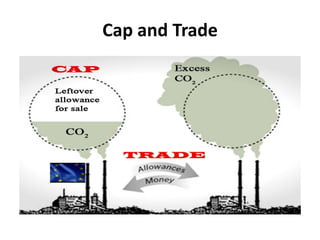


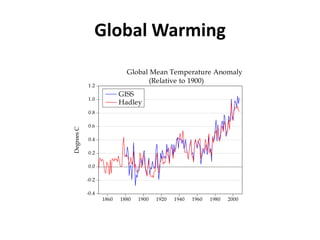

This document compares and contrasts carbon taxes and cap-and-trade policies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. A carbon tax sets a fee per ton of carbon emissions to make polluting more expensive and encourage energy efficiency and cleaner energy. Cap-and-trade sets a limit on total emissions and allows companies to trade permits to emit. It provides an economic incentive to reduce emissions. Both approaches aim to lower emissions over time, but a carbon tax provides more predictability while cap-and-trade may face fewer political obstacles. An ideal solution would involve international cooperation on carbon pricing and flexible allowance prices with a focus on developing alternative energy sources.







