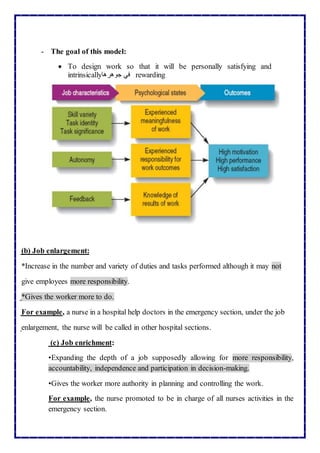
This document outlines a framework for redesigning hospitals. It discusses three main components of hospital redesign: job redesigning, organizational restructuring, and environmental redesign. Job redesigning involves examining tasks and responsibilities to improve efficiency and job satisfaction. Organizational restructuring examines relationships and structures to optimize resources. Environmental redesign aims to create a patient-centered environment through features like easy navigation, comforting patient units, and decentralized nursing stations. The overall goal of hospital redesign is to improve outcomes like productivity, quality of care, and patient and employee satisfaction.